What does Lewis structure mean? What are the 03 academic topics in the 10th-grade Chemistry curriculum in Vietnam?
What does Lewis structure mean?
10th-grade students can refer to the following information on Lewis structure:
|
What does Lewis structure mean? The Lewis structure is a graphic representation of a molecule where the valence electrons of atoms are depicted as dots or lines. This formula is used to describe the chemical bonds between atoms in a molecule and helps us visualize the electron structure of that molecule. |
*Note: The information is for reference only./.
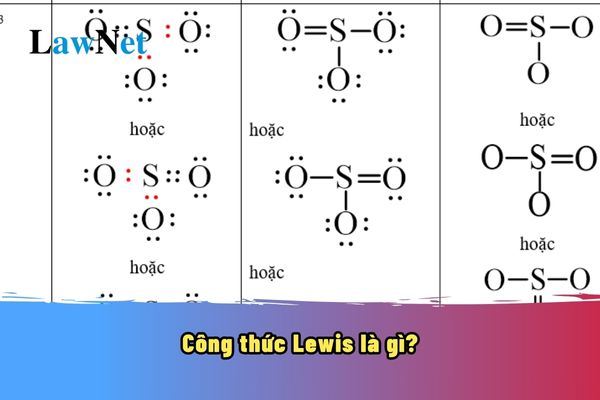
What does Lewis structure mean? What are the 03 academic topics in the 10th-grade Chemistry curriculum in Vietnam? (Image from the Internet)
Is being able to draw the Lewis structure one of the required outcomes in the 10th-grade Chemistry curriculum?
Under Section 5 of the general education program for Chemistry issued alongside Circular 32/2018/TT-BGDDT:
Covalent bond
- Present the concept and provide examples of covalent bonds (single, double, triple bonds) when applying the octet rule.
- Be able to draw the Lewis structure of some simple substances.
- Explain the concept of donor-acceptor bonds.
- Distinguish between types of bonds (nonpolar, polar covalent, ionic) based on electronegativity.
- Explain the formation of bonds and bonding through orbital overlap (AO).
- Present the concept of bond energy (covalent).
- Assemble molecular models, NaCl crystals (according to a preset model).
Thus, under the above regulations, being able to draw the Lewis structure is one of the required outcomes in the 10th-grade Chemistry curriculum.
What are the 03 academic topics in the 10th-grade Chemistry curriculum in Vietnam?
Under Section 5 of the general education program for Chemistry issued alongside Circular 32/2018/TT-BGDDT:
Topic 10.1: CHEMICAL FOUNDATIONS
Chemical Bonds
- Be able to write Lewis structures and use the VSEPR model to predict molecular geometry for some simple molecules.
- Present the concept of AO hybridization (sp, sp2, sp3) and apply it to explain bonds in some molecules (CO2; BF3; CH4;...).
Nuclear Reactions
- Provide an overview of natural radioactivity; give examples of natural radioactivity.
- Apply conservation laws of mass number and charge to nuclear reactions.
- Provide an overview of artificial radioactivity, nuclear reactions.
- State the applications of nuclear reactions for scientific research, life, and production.
- List typical applications of nuclear reactions: determining the age of artifacts, applications in the fields of medicine, energy,...
Activation Energy of Chemical Reactions
- Present the concept of activation energy (regarding its impact on reaction rate).
- State the influence of activation energy and temperature on reaction rate through the Arrhenius equation k = A. .
- Explain the role of catalysts.
Entropy and Gibbs Free Energy Change
- Present the concept of Entropy S (a measure of system disorder).
- Explain the significance of the sign and value of Gibbs free energy change (without explaining what ΔrG is, just state: To determine the direction of a reaction, people rely on Gibbs free energy change ΔrG) of a reaction (ΔG) to predict or explain the direction of a chemical reaction.
- Calculate ΔrGo using the formula ΔrGo = ΔrHo - T.ΔrSo from a provided table of ΔfHo and So values of substances.
Topic 10.2: CHEMISTRY IN FIRE AND EXPLOSION PREVENTION
Overview of Combustion and Explosion Reactions
- Explain the concept, characteristics of combustion reactions (a type of redox reaction that releases heat and light).
- Provide examples of the combustion of inorganic and organic substances (gasoline, oil combustion in air; Mg burning in CO2,...).
- State the necessary and sufficient conditions for combustion reactions to occur.
- Explain the concept, basic characteristics of explosion reactions (occur quickly with a sudden increase in volume and release of huge amounts of heat).
- Explain the concepts of physical and chemical explosion reactions.
- Present the concept of “dust explosion” (a dust explosion is caused by small solid dust particles (most organic solid materials such as plastic powder, sugar powder, cereal powder as well as metal powder that can react with oxygen and release strong heat) in the air).
- Present the harmful products often produced in combustion reactions: CO2, CO, HCl, SO2,... and their effects on humans.
(CO is very toxic to humans. At 1.28% CO concentration, people lose consciousness after 2-3 breaths, die after 2-3 minutes)
Flashpoint, Autoignition Temperature, and Combustion Temperature
- Define flashpoint (the lowest temperature at atmospheric pressure that a volatile organic compound or material can vaporize to ignite in air upon contact with a spark source).
- Define autoignition temperature (the lowest temperature at which a substance can spontaneously ignite without an external heat source under atmospheric pressure conditions).
- Explain the use of flashpoints to distinguish between flammable and combustible liquids. (Liquids with flashpoints below 37.8°C are considered flammable liquids. While liquids with flashpoints above that temperature are considered combustible liquids).
- Present the concept of combustion temperature.
- Analyze signs of and ways to reduce fire and explosion risks; ways to handle fires, and explosions. (Note to study, gather information about flashpoints, combustion temperatures of substances commonly encountered in life such as gasoline, oil, building materials)
Chemistry of Combustion and Explosion Reactions
- Calculate ΔrHo for some combustion and explosion reactions (according to ΔfHo or bond energy) to predict the intensity of combustion and explosion reactions.
- Calculate changes in combustion reaction speed, “respiration reaction rate” based on assumptions about dependency on O2 concentration.
- Explain the principles of firefighting (reduce combustion reaction speed) based on factors affecting chemical reaction rates.
- Explain why CO2 is commonly used for firefighting (isolate and reduce O2 concentration; CO2 is heavier than air).
- Explain why water is commonly used for firefighting (reduce temperature below the combustion temperature,...).
- Explain reasons why in some cases water should not be used for firefighting (gasoline, oil fires; fire containing chemicals reacting with water,...) but sand, CO2 should be used...
- Explain why fires with highly reactive metals such as alkali, alkaline earth metals, and aluminum... should not use water, CO2, sand (mainly SiO2), fire foam (a mixture of air, water, and surfactants) to extinguish the fire.
Topic 10.3: CHEMISTRY PRACTICE AND INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
(Select 2 of the 3 contents below)
- Draw molecular structures
- Practice virtual chemistry experiments
- Calculate structural parameters and energies
- Draw structural formulas, Lewis structures of some inorganic and organic substances.
- Save files, insert images into Word, and PowerPoint files.
- Conduct virtual experiments according to teacher-given content. Analyze and explain the results of virtual experiments.
- Explain the calculation process using semi-empirical methods (input file, choose calculation method, perform calculations, save results).
- Use calculated results to visualize molecular geometry, trends in bond lengths, angles, and molecular energies across a series of substances (same group, period, homologous series,...).







- Summary of the Article "Termites and Ants?" How Many Literature Classes Do 7th Grade Students Have in a Year?
- What are the guidelines for preparing the shortest lesson "Dục Thúy Sơn"? What are the required outcomes regarding literary texts for 10th-grade students in Vietnam under the Literature curriculum?
- What is the link to view the preliminary round results of the Contest "Youth Learning and Following the Ideology, Morality, and Style of Ho Chi Minh"?
- Vietnam: What are the 6+ sample paragraphs showing opinions about the topic "Students should respect and be grateful to workers"?
- What is the weather of Hanoi during the Lunar New Year 2025? Will outdoor activities not be organized for students in Hanoi during severe cold days?
- What are the answers for the 3rd examination of the "Learn about the 95th Anniversary of the Founding of the Communist Party of Vietnam and the History of the CPV Committee of Quang Ninh Province" contest?
- What is the sample analysis essay on the soldier's image in the poem "Tây Tiến"? What are the 04 assessment levels for the training results in each semester of continuing education students at the upper secondary level in Vietnam?
- What are the sample six-eight poems about mothers? What literary knowledge does the 6th-grade Literature curriculum in Vietnam include?
- What is the sample argumentative essay on the analysis of a literary work for 10th-grade students in Vietnam? What are the regulations on regular assessment for 10th-grade students in Vietnam?
- What are the guidelines for preparing the lesson "Đây mùa thu tới"? What are the two assessment methods for 11th-grade Literature in Vietnam?

