What are guidelines on comparison of the February Revolution and the October Revolution in Russia? How many periods does grade 8 History and Geography subject in Vietnam have?
What are guidelines on comparison of the February Revolution and the October Revolution in Russia?
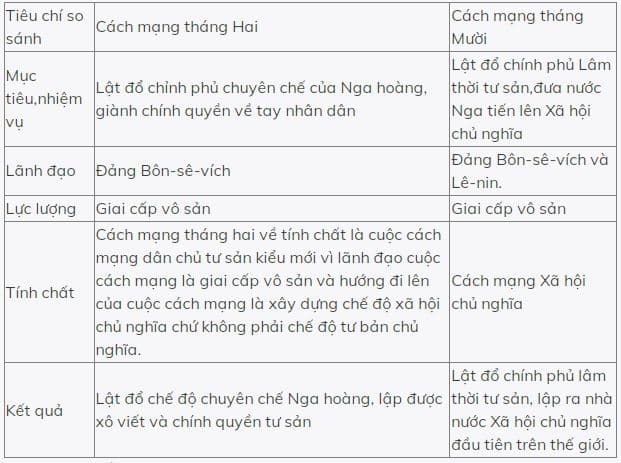
The February Revolution and the October Revolution in Russia in 1917 are two significant historical events that mark major turning points in Russian history. Below are some points of comparison between the February Revolution and the October Revolution in Russia:
1. Historical Context
- February Revolution: Occurred in February 1917 (according to the old Russian calendar), in a context where Russia was under immense pressure from World War I. The economy was collapsing, famine was widespread, and popular discontent with the policies of Tsar Nicholas II was increasing.
- October Revolution: Occurred in October 1917, after the February Revolution had overthrown the Tsarist policies but led to a dual power situation: the Provisional Government led by the bourgeoisie and the Soviet government representing the working class and peasants.
2. Leadership and Participating Forces
- February Revolution: Initially initiated by the proletariat, but the power eventually fell into the hands of the bourgeoisie. This revolution mainly involved workers, peasants, and intellectuals.
- October Revolution: Led by the Bolshevik Communist Party under the direction of Vladimir Ilyich Lenin. The participating forces primarily included workers, soldiers, and peasants.
3. Objectives and Outcomes
- February Revolution: The objective was to overthrow the autocratic monarchy of the Tsar, establish a democratic bourgeois government. The result was the overthrow of the Tsarist policies, the establishment of the provisional government, but it failed to address the fundamental issues of Russian society.
- October Revolution: The goal was to overthrow the bourgeois provisional government, establish the Soviet government, and advance towards building socialism. The outcome was the establishment of the Soviet government, marking the birth of the world’s first socialist state.
4. Nature
- February Revolution: It was a new type of democratic bourgeois revolution, initiated by the proletariat but with final power falling into the bourgeoisie’s hands.
- October Revolution: It was a socialist revolution, led by the proletariat through the Bolshevik Communist Party.
5. Historical Significance
- February Revolution: Marked the end of over 300 years of autocratic monarchy under the Romanov dynasty, opening a new phase in Russian history.
- October Revolution: Marked the birth of the world’s first socialist state, having a profound influence on revolutionary movements and national liberation across the world.
A concise comparative table of the February Revolution and the October Revolution in Russia is as follows:
Note: Content is for reference only!

What are guidelines on comparison of the February Revolution and the October Revolution in Russia? How many periods does grade 8 History and Geography subject in Vietnam have? (Image from the Internet)
How many periods does grade 8 History and Geography subject in Vietnam have?
According to the curriculum for the History and Geography subject at secondary school, issued with Circular 32/2018/TT-BGDDT, the allocated time for the subject is 105 lessons/class/year. The percentage allocation for content streams is in the following table:
| Content Stream | Grade 6 | Grade 7 | Grade 8 | Grade 9 | Whole Stage |
| Geography | 45 | 42 | 41 | 40 | 42 |
| General Physical Geography | 45 | 11 | |||
| Geography of Continents | 42 | 11 | |||
| Physical Geography of Vietnam | 41 | 10 | |||
| Economic - Social Geography of Vietnam | 40 | 10 | |||
| History | 45 | 42 | 41 | 40 | 42 |
| World | 22 | 20 | 20 | 19 | 20 |
| Vietnam | 23 | 22 | 21 | 21 | 22 |
| Common Theme | 6 | 8 | 10 | 6 | |
| Periodic Assessment | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
Thus, the History and Geography subject for grade 8 consists of 105 lessons/year, with 41 lessons for History, 41 lessons for Geography, 8 lessons for common themes, and 10 lessons for periodic assessments.
What are the minimum teaching equipment requirements for grade 8 History and Geography in Vietnam?
According to the lower secondary school History and Geography curriculum issued with Circular 32/2018/TT-BGDDT, the minimum teaching equipment for the History and Geography subject includes the following types:
- Educational wall maps (of the world, regions, Vietnam) appropriate for the content of each grade level's themes and student cognitive characteristics;
- General Physical Geography atlases, continent geography atlases, Vietnam geography atlases, history map sets;
- Models of artifacts, historical paintings, photographs, audio recordings of historical figures, etc.;
- Samples of natural phenomena;
- Printed images (on paper, digital static and dynamic images), diagrams, sketch maps, video clips edited for educational purposes, appropriate for each topic’s content;
- Study sheets with source materials; Worksheets (maps, diagrams, charts, schematics);
- Standard tools and devices for natural observation (compasses, thermometers, hygrometers, barometers);
- Some practical and field equipment;
- Digital libraries containing teaching resources for History and Geography;
- Educational software.
Where possible, subject-specific rooms should be organized.
The primary purpose of using teaching equipment is to provide a technical and material foundation for organizing learning activities, enabling students’ self-exploration of history and geography knowledge actively and creatively.

