What is the formula for calculating the area of an isosceles triangle in Vietnam?
What is the formula for calculating the area of an isosceles triangle in Vietnam?
The concept of an isosceles triangle is introduced for the first time in primary school (around grade 5).
A deeper understanding of the properties, theorems, and related problems of isosceles triangles is usually carried out in lower secondary school (grades 6, 7, 8).
|
Formula for calculating the area of an isosceles triangle The general formula to calculate the area of any triangle (including isosceles triangles) is: Area = (base x height) / 2 *In which: |
*Note: The information is for reference only./.
|
Some simple exercises on calculating the area of an isosceles triangle Given an isosceles triangle ABC with BC = 10cm, height AH = 6cm. Calculate the area of triangle ABC. Type 2: Given the side and the base angle Given an isosceles triangle ABC with AB = 5cm, angle B = 60°. Calculate the area of triangle ABC. Type 3: Given the sides of the triangle Given an isosceles triangle ABC with AB = AC = 13cm, BC = 10cm. Calculate the area of triangle ABC. Type 4: Calculate the overlapping area Given two equilateral triangles ABC and ABD with sides of 5cm, overlapping such that A, B, D are collinear. Calculate the overlapping area of the two triangles. Type 5: Integrated problems Given an isosceles triangle ABC with the height AH dividing the base BC into two segments BH = 4cm, HC = 6cm. Calculate the length of side AC and the area of triangle ABC. |
*Note: The information is for reference only./.
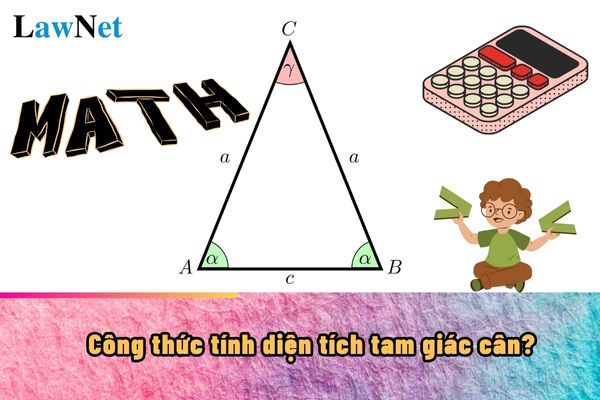
What is the formula for calculating the area of an isosceles triangle in Vietnam? (Image from the Internet)
From which grade in Vietnam is the formula for calculating the area of an isosceles triangle taught?
Based on Section III of the Appendix to the General Education Program in Mathematics issued under Circular 32/2018/TT-BGDDT for grade 5, the requirements are as follows:
For grade 5 Mathematics, in the Geometry and Measurement, plane figures and solid shapes section, the requirements are as follows:
Observe, recognize, and describe the shape and characteristics of some simple plane and solid shapes:
- Recognize trapezoids, circles, some types of triangles like acute triangles, right triangles, obtuse triangles, equilateral triangles.
For the General Education Program in Mathematics issued under Circular 32/2018/TT-BGDDT for grade 7, the more specific requirements are as follows:
Triangles. Congruent triangles. Isosceles triangles. The relationship between perpendicular lines and oblique lines. The concurrent lines of a triangle should ensure that students:
- Explain the theorem about the sum of the interior angles of a triangle being 180 degrees.
- Recognize the relationship between the lengths of the three sides in a triangle.
- Recognize the concept of congruent triangles.
- Explain the cases of congruence of two triangles, or two right triangles.
- Describe and explain the properties of isosceles triangles (for example: two equal sides; two equal base angles).
- Recognize the concepts: perpendicular line and oblique line; the distance from a point to a line. Explain the relationship between the perpendicular line and the oblique line based on the relationship between the sides and opposite angles in a triangle (opposite the larger angle is the longer side and vice versa).
- Recognize the perpendicular bisector of a segment and the basic properties of the perpendicular bisector.
Thus, the formula for calculating the area of an isosceles triangle may have been introduced by teachers from grade 5 and taught in the grade 7 mathematics program.
What are the overall objectives to ensure when teaching Mathematics to students in Vietnam?
Based on Section III of the Appendix to the General Education Program in Mathematics issued under Circular 32/2018/TT-BGDDT, when teaching Mathematics, the overall objectives should be as follows:
- Form and develop mathematical competencies including the following core components: mathematical reasoning and argumentation; mathematical modeling; mathematical problem-solving; mathematical communication; and ability to use mathematical tools and means.
- Contribute to forming and developing students' essential qualities and general competencies at levels appropriate to each subject or grade level as prescribed in the General Education Program.
- Have basic, essential general knowledge and skills in mathematics; develop the ability to solve integrated interdisciplinary problems between mathematics and other subjects such as Physics, Chemistry, Biology, Geography, Information Technology, Technology, History, Arts,...; create opportunities for students to experience and apply mathematics in practice.
- Have a relatively comprehensive understanding of the usefulness of mathematics for each related profession to serve as a basis for career orientation, and have sufficient minimum competencies to self-enquire about mathematics-related issues throughout life.
Download the General Education Program in Mathematics issued under Circular 32/2018/TT-BGDDT.



- Sample explanation essay on flooding for grade 8 students in Vietnam
- Are lower secondary school teachers in Vietnam required to have a master's degree?
- Guidelines on preparing the lesson "Chiều xuân" for grade 11 students in Vietnam
- Ho Chi Minh City propagates, mobilizes, and raises donations to support northern provinces affected by Typhoon No. 3
- Guidelines on preparing the lesson "Ngôi sao sân cỏ" for grade 5 students in Vietnam
- Planning of the Network of Higher Education and Teacher Training Institutions for the Period of 2021-2030
- Poem about Sine, Cosine, Tangent (trigonometric ratios in right triangles) for grade 9 students in Vietnam
- Guidelines on writing a disciplinary report for lower secondary school students in Vietnam
- What is the Application form for extra classes at school in 2024 in Vietnam?
- When is the Mid-Autumn Festival in 2024? How many days until the Mid-Autumn Festival in 2024?

