What are alkali metals? What is the position of alkali metals in the periodic table of chemical elements? What is the content structure of grade 12 Chemistry subject in Vietnam?
What are alkali metals? What is the position of alkali metals in the periodic table of chemical elements?
1. What are Alkali Metals?
Alkali metals are elements belonging to Group 1 of the periodic table, including Lithium (Li), Sodium (Na), Potassium (K), Rubidium (Rb), Cesium (Cs), and Francium (Fr). These metals are characterized by their high reactivity and are often found in compounds rather than in their free forms due to their high chemical activity.
2. The Position of Alkali Metals in the Periodic Table of Chemical Elements
- Alkali metals belong to Group 1 (IA) of the periodic table, located in the main subgroup on the left-hand side of the periodic table.
- Alkali metals have one electron in their outermost shell, making it easy for them to lose this electron and form positive ions (cations) with a charge of +1. Consequently, they are very reactive and often have strong reactions with water, producing hydrogen and alkali solutions.
Description of the position of alkali metals in the periodic table of chemical elements as follows:
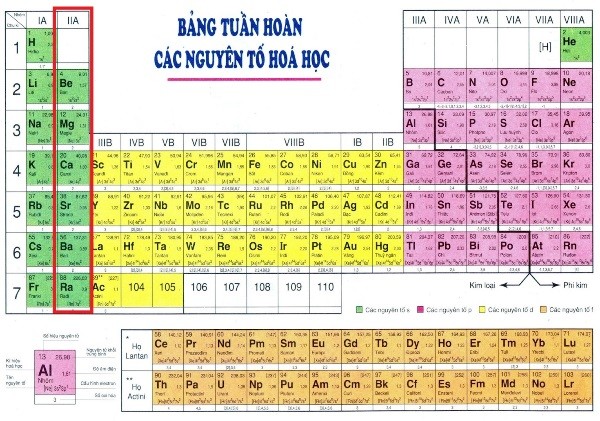
3. Physical Properties of Alkali Metals:
- Softness: Alkali metals are very soft and can be easily cut with a knife.
- Color: They have a shiny silver-white color when freshly cut.
- Low Melting and Boiling Points: The melting and boiling points of alkali metals are much lower than other metals.
- Low Density: The density of alkali metals is low, lighter than water (except for Li).
- Good Conductivity: Alkali metals have good electrical and thermal conductivity.
4. Chemical Properties of Alkali Metals:
- Reaction with Water: Alkali metals react strongly with water, creating alkaline solutions (metal hydroxides) and hydrogen gas.
Example: 2Na + 2H₂O → 2NaOH + H₂↑
- Reaction with Oxygen: Alkali metals react with oxygen to form oxides or peroxides.
Example: 4Li + O₂ → 2Li₂O (Oxide)
2Na + O₂ → Na₂O₂ (Peroxide)
- Reaction with Halogens: Alkali metals react strongly with halogens to form halide salts.
Example: 2Na + Cl₂ → 2NaCl
- Reaction with Acids: Alkali metals react strongly with acids, producing salts and releasing hydrogen gas.
Example: 2Na + 2HCl → 2NaCl + H₂↑
Alkali metals are chemically very active and must be stored in oil or inert gases to prevent reactions with air or water.
Note: This content is for reference purposes only!

What are alkali metals? What is the position of alkali metals in the periodic table of chemical elements? What is the content structure of grade 12 Chemistry subject in Vietnam? (Image from the Internet)
What is the content structure of grade 12 Chemistry subject in Vietnam?
According to the Upper Secondary School Chemistry Curriculum issued along with Circular 32/2018/TT-BGDDT, the content structure for Grade 12 Chemistry is outlined as follows:
| Content Structure | Grade 12 |
| General Chemistry Knowledge | |
| Batteries and electrolysis | x |
| Inorganic Chemistry | |
| Overview of metals | x |
| Group IA and IIA elements | x |
| Brief overview of the first transition metal series and complexes | x |
| Organic Chemistry | |
| Esters - Lipids | x |
| Carbohydrates | x |
| Compounds containing nitrogen | x |
| Polymers | x |
| Study Topics | x |
What is teaching equipment for Chemistry at upper secondary level in Vietnam?
Based on the Upper Secondary School Chemistry Curriculum issued along with Circular 32/2018/TT-BGDDT, the chemistry teaching equipment comprises:
1. Equipment for Demonstration and Proof
- The periodic table of chemical elements; solubility tables; electron configuration charts for metals/transition metal ions in the first series; color tables for certain compounds of transition metals.
- Pictures and diagrams showing the geometry of some complexes, Cu2+ salts in water; structures of some biologically important complexes like heme B, chlorophyll, vitamin B12, and medical uses like cisplatin, carboplatin, etc.; 3R symbol; aluminum recycling; silicate industry; cement, industrial, and craft ceramics production. Drawings of distillation diagrams, processing, and applications of petroleum. Images illustrating the applications of alkanes, alkenes, alkadienes, arenes in reality; applications of halogen derivatives; alcohols and phenols in reality; the role of amino acids, glucose, and starch in life.
- Molecular models/set for assembling hollow and solid forms of some alkanes; benzene, halogen derivatives, ethylic alcohol (ethyl alcohol), and phenol; amines, amino acids, peptides, and proteins.
- Electronic learning materials:
+ Software: software for calculations; virtual experiment software.
+ Videos of certain hazardous, explosive, and complex experiments, for example, experiments with chlorine, bromine, and interactions of alkali, alkaline earth metals with water.
2. Equipment for Practice
- Analytical and measurement tools: a set for electrolysis of copper(II) sulfate and sodium chloride solutions; electric conductivity testing equipment; handheld pH meters; etc.
- Adequate equipment, tools, and chemicals as per the minimum teaching equipment list specified by the Ministry of Education and Training.



- Discussion on Students' Late Arrival to School: What Criteria Must the Grade 9 Literature Curriculum Meet?
- Vietnam: When was the directive on national resistance given? What education level does 9th Grade fall under?
- Vietnam: What is the overview of industrial revolutions over periods in the 10th-grade History curriculum? What knowledge about industrial revolutions do 10th-grade students learn?
- What is the Plan for organizing professional training for English teachers in Ho Chi Minh City about?
- Vietnam: What are the sample outlines of a social argumentative essay on kindness for 9th-grade students? What are the kindness qualities required for 9th-grade students?
- Vietnam: What are the sample argumentative essays on respecting people's differences for 11th-grade students? What are the conditions for 11th-grade students to be eligible for grade advancement?
- Are students pursuing dance in Vietnam eligible for tuition reduction?
- What are the standards for facilities of a Center for Continuing Education and Vocational Education in Vietnam?
- What are the conditions for a foreign educational institution to establish a representative office in Vietnam?
- What is the term of office of the principal of an intermediate school in Vietnam?

