Vietnam: What is the overview of industrial revolutions over periods in the 10th-grade History curriculum? What knowledge about industrial revolutions do 10th-grade students learn?
What is the overview of industrial revolutions over periods in the 10th-grade History curriculum in Vietnam?
Students may refer to the overview of industrial revolutions over periods in the 10th-grade History curriculum in Vietnam below:
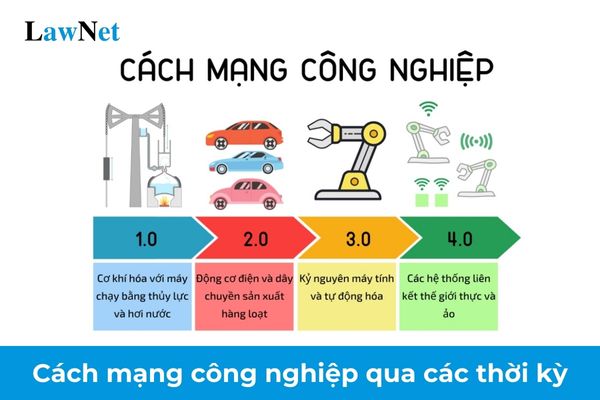
The First Industrial Revolution was a revolution in the production sector; it marked a fundamental change in economic, social, cultural, and technical conditions starting in England and then spreading worldwide. During this period, simple, small-scale economies based on manual labor were replaced by large-scale industry and machinery manufacturing.
The first industrial revolution began with the development of the textile industry's goods production. Subsequently, the need to supply machinery and energy for the textile industry led to improvements in iron and steel fabrication techniques and large-scale use of coal. The expansion of trade facilitated the emergence of transportation canals and railroads. Additionally, traffic roads were significantly upgraded to accommodate bustling trade activities. Steam engines using coal as fuel and machinery driven by mechanical power led to a remarkable increase in labor productivity. The development of machine tools in the first two decades of the 19th century paved the way for machinery manufacturing, serving other production sectors.
The Second Industrial Revolution began around the 1860s, with economic and technical advancements achieved through the development of the telegraph, telephone, railroads, and the application of mass production assembly lines. By the end of the 19th century, the main drivers of the Second Industrial Revolution were the internal combustion engine and electricity-powered machinery. In 1914, the year World War I began, this second phase ended.
The Third Industrial Revolution commenced around 1960, marked by advancements in electronic infrastructure, computers, and digital technologies based on the development of semiconductors, supercomputers (1960s), personal computers (1970s and 1980s), and the Internet (1990s). By the end of the 20th century, this process was largely completed thanks to high-tech scientific achievements. In 1997, the outbreak of the Asian financial crisis marked the end of the third phase.
The Fourth Industrial Revolution began at the start of the 21st century, building on the significant achievements of the third revolution, established on the foundation of digital revolution improvements, with new technologies like 3D printing, robotics, artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things, S.M.A.C., nanotechnology, biology, new materials, etc. Currently, the world is in the early stages of this revolution, which serves as a pivotal strategy for developing countries to keep pace with global trends and opens a new chapter for human development.
The impacts of industrial revolutions are profoundly extensive. Not only do they change human life, but these revolutions also lead to comprehensive changes in economic and social structures. After the first industrial revolution, the bourgeois class accumulated enough assets and power, leading to the triumph of capitalism over feudal policies. After the Second Industrial Revolution, large factories based on assembly lines replaced small workshops, leading to monopolistic capitalism replacing free-market capitalism, while the working class and certain political movements towards socialism emerged. The third industrial revolution gave rise to modern capitalism. The fourth industrial revolution will once again change the economic and social structures of humanity.
Note: The content is for reference purposes only.
What is the overview of industrial revolutions over periods in the 10th-grade History curriculum in Vietnam? What knowledge about industrial revolutions do 10th-grade students in Vietnam learn? (Image from the Internet)
What knowledge about industrial revolutions do 10th-grade students in Vietnam learn?
Under Section 5 of the General Education Program for History issued with Circular 32/2018/TT-BGDDT,10th-grade students learn the following knowledge about industrial revolutions:
Industrial Revolution of the Modern Period
- The First Industrial Revolution
+ Historical context
+ Basic achievements
- The Second Industrial Revolution
+ Historical context
+ Basic achievements
- Significance of the First and Second Industrial Revolutions
+ Economic
+ Social and cultural
Industrial Revolution of the Modern Era
- The Third Industrial Revolution
+ Historical context
+ Basic achievements
- The Fourth Industrial Revolution (Revolution 4.0)
+ Historical context
+ Basic achievements
- Significance of the Third and Fourth Industrial Revolutions
+ Economic
+ Social and cultural
What are the academic topics in the 10th-grade History curriculum in Vietnam?
Under Section 5 of the General Education Program for History issued with Circular 32/2018/TT-BGDDT, the academic topics in the 10th-grade History curriculum in Vietnam include:
- Occupational orientation: Fields of History
- Practical experiential activities: Conservation and promotion of cultural heritage value in Vietnam
- Knowledge enhancement: State and law of Vietnam throughout history

