What is the structure of the Earth? What are major tectonic plates of the Earth's crust? How many periods are there in grade 6 History and Geography subject in Vietnam?
What is the structure of the Earth? What are major tectonic plates of the Earth's crust?
Describing the structure of the Earth is one of the topics that students must achieve in the subject of History and Geography in Grade 6. Below is a guide for presentation.
1. Describe the structure of the Earth
The Earth is composed of three main layers: the crust, the mantle, and the core. Specifically, as follows:
Crust
- Thickness: From 5 to 70 km.
- Characteristics: This is the outermost, thinnest, and most important layer of the Earth. The crust is primarily composed of silicate rocks and is in a solid state. The temperature gradually increases from the surface inward, with a maximum of about 1000°C.
Mantle
- Thickness: From 70 to 2900 km.
- Characteristics: The mantle lies beneath the crust and occupies most of the Earth's volume. It is divided into the upper mantle and the lower mantle. The material in the mantle ranges from a plastic to a liquid state, with temperatures from 1500°C to 4700°C.
Core
- Thickness: From 2900 km to the center of the Earth (approximately 6371 km).
- Characteristics: The core is divided into two parts: the outer core and the inner core. The outer core is in a liquid state, while the inner core is solid. The temperature at the core can reach 5000°C or higher. The core is mainly composed of iron and nickel, with a very high density.
2. The major tectonic plates of the Earth's crust
The Earth has 7 major tectonic plates, including the Pacific Plate, the North American Plate, the Eurasian Plate, the African Plate, the South American Plate, the Antarctic Plate, and the Indo-Australian Plate.
In addition, there are many other smaller tectonic plates. These tectonic plates move and interact with each other, causing geological phenomena such as earthquakes, volcanoes, and the formation of mountain ranges.
Below is a map of the major tectonic plates of the Earth.
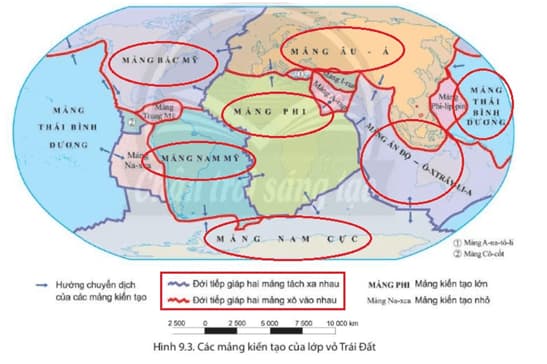
Note: Content is for reference only!

What is the structure of the Earth? What are major tectonic plates of the Earth's crust? How many periods are there in grade 6 History and Geography subject in Vietnam? (Image from the Internet)
How many periods are there in grade 6 History and Geography subject in Vietnam?
According to the General Education Curriculum for the subject of History and Geography issued with Circular 32/2018/TT-BGDDT, the number of periods allocated for the subject is 105 periods/class/year. The percentage of periods allocated for the content strands is in the table below:
| Content Strand | Grade 6 | Grade 7 | Grade 8 | Grade 9 | Total |
| Geography | 45 | 42 | 41 | 40 | 42 |
| General Physical Geography | 45 | 11 | |||
| Geography of Continents | 42 | 11 | |||
| Physical Geography of Vietnam | 41 | 10 | |||
| Economic and Social Geography of Vietnam | 40 | 10 | |||
| History | 45 | 42 | 41 | 40 | 42 |
| World | 22 | 20 | 20 | 19 | 20 |
| Vietnam | 23 | 22 | 21 | 21 | 22 |
| Common Topics | 6 | 8 | 10 | 6 | |
| Periodic Assessment | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
Thus, the History and Geography subject in Grade 6 has a duration of 105 periods, including 45 periods for History, 45 periods for Geography, and the remaining 10 periods are for periodic assessment.
What are regulations on the logiccal development of the History and Geography curriculum in lower secondary schools in Vietnam?
According to the General Education Curriculum for the subject of History and Geography issued with Circular 32/2018/TT-BGDDT, the logiccal development of the History and Geography curriculum in lower secondary schools in Vietnam is as follows:
- The historical education content for all three educational levels differs from the current program in that it is not designed concentrically from low to high levels. At the lower secondary level, students will learn history from ancient times to the present. Therefore, significant events, phenomena, and historical figures from world history and national history are arranged chronologically.
- The differences in the levels within the lower secondary program are not just in the content volume or the details of historical events, but primarily in the fundamental understanding of the nature of historical events, the causes of historical changes, the diversity of social models, the theoretical understanding of society, and the focus on training learning skills and applying knowledge to new situations.
- At the lower secondary level, based on the psychological characteristics of students and the characteristics of the subject, the Geography sub-discipline is developed logically: from general physical geography in Grade 6 to geography of continents in Grade 7, followed by the physical geography of Vietnam (Grade 8), and the economic and social geography of Vietnam (Grade 9). This logic ensures that upon completing the curriculum in lower secondary school, students will have basic and general knowledge of geography, especially about Vietnamese geography, to continue their education in high school or participate in the workforce.
- In geography teaching, the process of forming basic concepts often goes from geographic icons to geographic concepts. Forming geographic icons is particularly important for Grade 6 and 7 students, ensuring they easily remember icons and concepts, and connect concepts with real-life situations.
- Forming basic concepts is a process that, in some cases, must go through many lessons and chapters. Some concepts are formed gradually throughout an entire educational level or program. This is something that teachers should be aware of when teaching to avoid overloading in lower classes and create vertical linked learning between classes.
- Many general physical geography concepts are initially formed in Grade 6 and further developed in Grades 7 and 8. For example, the concept of atmospheric circulation in Grade 6 is only presented through diagrams of pressure belts and winds. The concept of atmospheric circulation is utilized and developed further when students study Geography 7, such as discussing monsoon circulation in the monsoon regions of Asia.
- Concepts related to fronts or tropical convergence may be used when students study the geography of Vietnam in Grades 8 and 9. Some concepts about economic and social geography may be introduced in a simple manner in Grade 7 and used at a higher level when discussing the economic and social geography of Vietnam in Grade 9. Interdisciplinary concepts require an even longer time for formation and development.









- What are the answers to the "Learn about Law on Road Traffic Order and Safety 2024" contest of Vinh Phuc Province? Will the training results of students committing violations against traffic regulations in Vietnam be lowered?
- What is the list of 14 Ministries and 03 Ministerial agencies in Vietnam according to Resolution 176/2025/QH15?
- Vietnam: What are the 03+ sample articles expressing feelings on the 50th anniversary of Southern Liberation and National Reunification Day?
- What is the sample analysis essay on the poem "Spring Day" by poet Anh Tho for 9th-grade students in Vietnam? What are the duties of 9th-grade students in Vietnam?
- What are the 10+ sample 400-word argumentative essays on a life matter of your interest for 7th-grade students in Vietnam?
- What are the 07+ sample analysis essays on a favorite story for 8th-grade students in Vietnam? What are the required outcomes regarding speaking and listening skills in the 8th-grade Literature curriculum in Vietnam?
- What is the full text of Conclusion 126 of the Politburo of Vietnam in 2025 on streamlining the organizational apparatus of the political system? What are the current principles for training in political theory?
- What are the 2nd mid-semester question papers and answers for 8th-grade Mathematics in 2025? What are practical and experiential activities in the 8th-grade Mathematics curriculum in Vietnam?
- What are the methods of enrollment for upper secondary education in Vietnam?
- Is Official Dispatch 674 guiding the implementation of Circular 29 on extra classes by the Department of Education and Training of Ho Chi Minh City available?

