What is the Law of Cosines in Mathematics? When do students in Vietnam learn the Law of Cosines in Mathematics?
What is the Law of Cosines in Mathematics?
The Law of Cosines is one of the important theorems in trigonometry, which helps us establish the relationship between the lengths of the sides of a triangle and the cosine of the opposite angle. This theorem plays a crucial role in solving problems related to triangles, especially when we do not have sufficient data to apply the Pythagorean Theorem.
|
Statement of the Theorem In any triangle ABC, with sides a, b, c opposite to angles A, B, C, respectively, we have: a² = b² + c² - 2bc * cosA *Example |
*Geometric Significance
The Law of Cosines shows us that the square of a side in a triangle equals the sum of the squares of the other two sides minus twice the product of those two sides multiplied by the cosine of the opposite angle.
*Note: Above information is for reference only./.
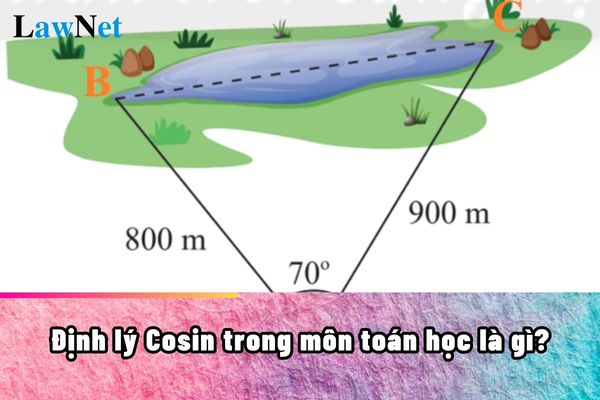
What is the Law of Cosines in Mathematics? When do students in Vietnam learn the Law of Cosines in Mathematics? (Image from the Internet)
When do students in Vietnam learn the Law of Cosines in Mathematics?
Firstly, according to Section III of the Appendix of the General Education Program in Mathematics issued with Circular 32/2018/TT-BGDDT, the main objectives at the upper secondary school level are as follows:
- Contribute to the formation and development of mathematical competence with the requirement to be able to pose and answer questions when reasoning, problem-solving; use reasoning, inductive, and deductive methods to understand different approaches to problem-solving;
- Establish mathematical models to describe situations, thereby finding out how to solve the mathematical problems posed in the established models; implement and present the problem-solving solutions and evaluate the implemented solutions, reflect on the value of the solution, generalize to similar problems; use math learning tools and means in learning, exploring, and solving mathematical problems.
- Have basic and essential mathematical knowledge and skills about:
+ Algebra and Some Elements of Analysis: Calculating and using calculation tools; using algebraic language and symbols; transforming algebraic and transcendental expressions (trigonometric, exponential, logarithmic), equations, systems of equations, inequalities; recognizing basic elementary functions (power, trigonometric, exponential, logarithmic); survey functions and graph functions using derivatives;
- Use the language of functions, function graphs to describe and analyze some processes and phenomena in the real world; use integrals to calculate the area of flat shapes and the volume of objects in space.
Additionally, at Section V of the Appendix of the General Education Program in Mathematics issued with Circular 32/2018/TT-BGDDT, one of the topics covered in the grade 9 mathematics curriculum is as follows:
- Recognize the values of sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent of acute angles.
- Explain the trigonometric ratios of special acute angles (30°, 45°, 60°) and of two complementary angles.
- Calculate the (exact or approximate) values of trigonometric ratios of acute angles using a calculator.
- Explain some trigonometrical identities involving the sides and angles in right triangles (the leg equals the hypotenuse multiplied by the sine of the opposite angle or cosine of the adjacent angle; the leg equals the other leg multiplied by the tangent of the opposite angle or cotangent of the adjacent angle).
- Solve some practical problems related to the trigonometric ratios of acute angles (e.g., Calculating the length of line segments, the degree of angles, and applying them in solving right triangles, etc.).
Thus, the Law of Cosines is taught in grade 9 mathematics.
What are the educational method orientations for grade 9 Mathematics in Vietnam?
Based on Section VI of the General Education Program in Mathematics issued with Circular 32/2018/TT-BGDDT, regarding the mathematics curriculum in general and the grade 9 mathematics curriculum in particular, the following methods will be used:
- Teaching methods in the Mathematics curriculum must meet the following basic requirements:
+ Suitable to the cognitive process of students (from concrete to abstract, from easy to difficult); not only valuing the logic of mathematical science but also paying attention to approaches based on students' experiences and experiences;
+ Thoroughly implement the spirit of “learner-centered approach”, promoting activeness, self-discipline, attention to individual student's needs, cognitive abilities, and different learning styles; organize the teaching process in a constructive direction, where students are involved in exploring, discovering, reasoning, and solving problems;
+ Flexibly apply various active teaching methods and techniques; creatively blend traditional teaching methods and techniques; combine classroom learning activities with practicing experiential activities, applying mathematical knowledge to reality. Ensure the balanced, harmonious ratio between core knowledge, applied knowledge, and other components in lesson structure.
+ Adequately and effectively use the minimum teaching aids and tools for Mathematics; can use self-made teaching aids suitable for the content and student audience; strengthen the use of information technology and modern teaching aids appropriately and effectively;
- Direction for forming and developing essential qualities and general competences
+ Methods to form and develop essential qualities
Through organizing learning activities, Mathematics contributes with other subjects and educational activities, helping students cultivate honesty, love of labor, responsibility, consciousness in completing learning tasks; nurturing self-confidence, interest in learning, the habit of reading, and the consciousness of exploring and understanding science.
+ Methods to form and develop general competences
++ Mathematics contributes to the formation and development of self-study and autonomous learning capabilities through training students to know how to choose learning objectives, create learning plans, form self-study methods, draw experiences, and adjust to apply in other situations during the learning of mathematical concepts, knowledge, and skills, as well as when practicing or independently solving mathematical problems with meaningful content.
++ Mathematics contributes to the formation and development of communication and cooperation skills through listening comprehension, reading comprehension, taking notes, and interpreting necessary mathematical information in mathematical texts; through effective use of mathematical language combined with ordinary language to discuss and present mathematical content, ideas, or solutions in interaction with others, while demonstrating confidence and respect for interlocutors when describing and explaining mathematical content and ideas.
++ Mathematics contributes to the formation and development of problem-solving and creative abilities by helping students recognize problematic situations; share their understanding of the problem with others; know how to propose, choose methods, procedures to solve the problem and know how to present solutions; know how to evaluate the solutions implemented and generalize for similar problems.
- Mathematics teaching methods contribute to the formation and development of computational skills, language competences, and other specific abilities. Specifically:
+ Mathematics, with outstanding advantages, has many opportunities to develop computational competence manifested in providing mathematical knowledge, training computational skills, estimating, and helping form and develop elements of mathematical competence (thinking and reasoning competence, modeling competence, problem-solving competence; communication competence and competence in using mathematical tools and means).
+ Mathematics contributes to the development of language competence through practicing reading comprehension, interpreting, analyzing, evaluating situations with meaningful mathematical contexts, using mathematical language effectively along with ordinary language to present and explain mathematical content, ideas, and solutions.
+ Mathematics contributes to developing informatics competence through using information and communication technology tools and means as supporting tools in learning and self-learning; creating an experiential learning environment.
+ Mathematics contributes to developing aesthetic competence by helping students become familiar with the history of mathematics, the biographies of mathematicians, and recognizing the beauty of mathematics in the natural world.
Download detailed insight into the General Education Mathematics Program issued with Circular 32/2018/TT-BGDDT.


- What are sample exam papers for High School Graduation Examination in 2025 in Vietnam?
- Which was the first communist organization established in Vietnam? What is the study duration for the specialized topic in Grade 12 History in Vietnam?
- What is the sample exam papers of History subject for High School Graduation Examination in 2025 in Vietnam? What is the date for the High School Graduation Examination in 2025 in Vietnam?
- What are guidelines on preparing the lesson "Nam quốc sơn hà" for grade 8 students in Vietnam? What are grounds for assessments of the training outcomes of grade 8 students in Vietnam?
- What is the sample exam paper of Geography for 2025 High School Graduation Examination in Vietnam? What are procedures for transporting and handling exam papers for the High School Graduation Exam in Vietnam?
- What are sample essays describing a memorable experience for grade 6 students in Vietnam? What is the age of grade 6 students in Vietnam?
- What are sample essays describing the poinciana tree for grade 4 students in Vietnam? What are types of organizational structures of primary schools in Vietnam?
- What is integral? What is formula for integral? When do students in Vietnam learn about integral according to Mathematics curriculum in Vietnam?
- What is a chemical element? When do students in Vietnam learn about chemical element?
- What is the Department of Higher Education in Vietnam? Is it under the Ministry of Education and Training of Vietnam?

