Liver Fluke Disease: Causative Agent?
Liver Fluke Disease and Its Causative Agents
According to Section 1 of the Guidelines for Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention of Liver Fluke Disease issued under Decision 1203/QD-BYT in 2022, the content is specified as follows:
- Liver Fluke Disease is a parasitic disease caused by several species of liver flukes belonging to the family Fasciolidae, causing lesions and abscesses in the liver or other organs when ectopic parasitism occurs.
- People contract the disease by eating raw aquatic vegetables such as rice-paddy herb, water spinach, water dropwort, watercress, and lotus stems, or by drinking water contaminated with liver fluke larvae.
Causative Agents:
- Liver fluke disease in humans is primarily caused by two species: Fasciola hepatica and Fasciola gigantica.
- The species Fasciola hepatica is mainly distributed in Europe, South America, Africa, and Asia. The species Fasciola gigantica is mainly distributed in Asia such as China, Taiwan, Japan, Korea, the Philippines, and Vietnam where F. gigantica hybridizes with F. hepatica.
The Cycle of Liver Fluke Disease According to Current Regulations
Based on Section 1.3 of the Guidelines for Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention of Liver Fluke Disease issued under the above-mentioned decision, the cycle is specified:
- Adult flukes lay eggs via the bile ducts into the intestine and then out through the feces. Liver fluke eggs measure 140 x 80µm.
- Eggs released into the water hatch into miracidia. Miracidia invade certain species of snails, which are the first intermediate host. Within the snails, miracidia develop into cercariae, which then leave the snails and attach to aquatic plants or swim freely in the water.
- Humans or animals such as buffaloes, cows, sheep, goats, etc., who consume aquatic plants or drink untreated water containing larvae can be infected with liver fluke disease.
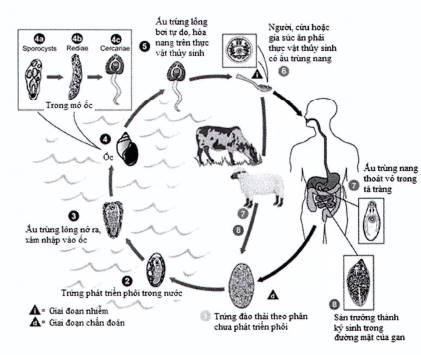
Figure 1. Development cycle of liver fluke (Source USA-CDC, 2018)
- Eggs excreted from the bile ducts pass out in the environment through feces
- Eggs develop in the water environment
- Eggs hatch into miracidia
- Miracidia develop through various stages within the first intermediate host, freshwater snails
- Cercariae leave the snails and live freely in the water
- Cercariae attach to aquatic plants and develop into metacercariae7-8) Herbivores or humans ingest aquatic plants or drink water containing live metacercariae larvae; the larvae enter the stomach, penetrate the intestinal wall into the abdominal cavity, eventually reaching the liver and other organs to parasitize
Respectfully!