Guidelines on preparing lesson No.4 of grade 10 Chemistry (Structure of the Electron Shell of Atoms) in Vietnam
Guidelines on preparing lesson No.4 of grade 10 Chemistry (Structure of the Electron Shell of Atoms) in Vietnam
|
Guidelines on preparing lesson No.4 of grade 10 Chemistry (Structure of the Electron Shell of Atoms) in Vietnam (1) How do electrons move in an atom and what energy levels do they occupy? What is the sequence of these energy levels? What principles and rules govern the distribution of electrons in an atom? |
Note: The above content on the electron shell structure of atoms is for reference purposes only.
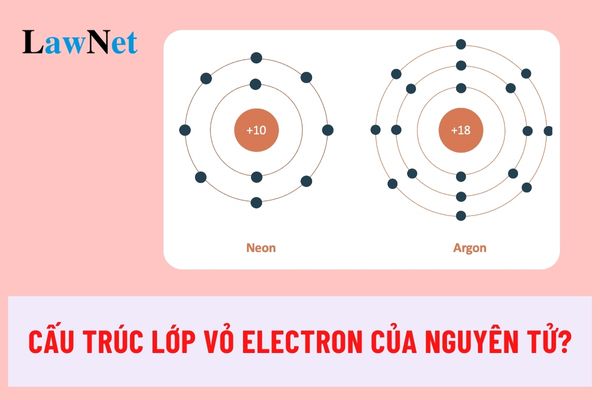
Guidelines on preparing lesson No.4 of grade 10 Chemistry (Structure of the Electron Shell of Atoms) in Vietnam (Image from the Internet)
What are forms, methods, and tools for assessing Chemistry subject in Vietnam?
Based on Subsection 3, Section 7 of the General Education Program for Chemistry issued together with Circular 32/2018/TT-BGDDT, the forms, methods, and tools for assessing the Chemistry subject are as follows:
(1) Assessment Forms:
Combining formative assessment (continuous assessment), summative assessment (periodic assessment), and large-scale assessments at the national, local, and international levels to ensure comprehensive, frequent assessment integrated into the teaching and learning activities of teachers and students.
(2) Assessment methods and tools:
- Combining teacher assessment with self-assessment and peer assessment by students.
Coordinating situational assessment; assessment through testing; assessment through projects and portfolios; assessment through feedback and reflection; assessment through observation.
- Combining assessment of learning products (essay tests, objective tests, oral responses, presentations, laboratory experiments, research projects, ...) with assessment through observation (attitude and behavior in discussions, group work, experiments, field trips, ...).
What are other orientations on teaching methods for Chemistry subject as per the 2018 program in Vietnam?
The General Education Program for Chemistry is issued together with Circular 32/2018/TT-BGDDT on other orientations on teaching methods for Chemistry subject as per the 2018 program as follows:
* Orientations for methods of forming and developing essential qualities and general competencies
(1) Methods of forming and developing essential qualities
Through organizing learning activities, teachers help students form and develop a scientific worldview, cultivate honesty, love of labor, and a sense of responsibility;
Based on experimental, practical activities, especially field trips, laboratory practices, and production facilities to enhance students' awareness of protecting and rationally using natural resources, the responsibility of workers, and safety principles in production, especially in chemical-related industries.
Teachers employ diverse learning forms to nurture students’ interest and confidence in learning, scientific exploration, respect for scientific labor results, and the ability to apply scientific knowledge to life.
(2) Methods of forming and developing general competencies
- In teaching Chemistry, teachers organize activities for students to explore, discover, and practice science, especially searching and handling resources for self-learning (including digital resources), designing, and performing experiments, and learning projects to enhance students' self-reliance and self-learning.
- Chemistry has many advantages in forming and developing communication and cooperation skills as students often engage in group learning projects and laboratory experiments, allowing for the exchange, presentation, sharing of ideas, and study content, creating opportunities for communication and cooperation.
- Solving problems and creativity are intrinsic to understanding and exploring the scientific world.
Through Chemistry learning activities, teachers create opportunities for students to apply chemical knowledge to explore, discover, and identify problems in the natural world and propose solutions, develop plans, and implement plans to solve problems creatively.
Employing project-based learning and teamwork methods help students objectively and truthfully identify and solve problems based on scientific analysis.
* Orientations for methods of forming and developing chemical competencies
(1) To develop chemical cognitive competence, teachers create opportunities for students to mobilize existing knowledge and experiences to participate in forming new knowledge.
Emphasizing activities that connect new knowledge with previously learned knowledge systems such as comparison, classification, systematization of knowledge, application of learned knowledge to explain objects, phenomena, or solve simple problems, ...
(2) To develop competence in exploring the natural world through a chemical perspective, teachers employ some advantageous teaching methods such as visual methods (especially laboratory practices, ...), problem-based teaching methods, project-based teaching methods, ... enabling students to pose questions, identify issues to explore, independently seek evidence to analyze information, test predictions, hypotheses through conducting experiments, or searching and collecting information through books, the Internet, ...,
Simultaneously, focusing on developing students’ chemical thinking through chemistry exercises that require critical, creative thinking (open-ended exercises, having multiple solutions, ...), exercises linked to practical content reflecting the chemical essence, reducing computational exercises, ...
(3) To develop the competence to apply knowledge and skills learned, teachers create opportunities for students to read, access, and present information on practical issues related to chemical knowledge and propose solutions.
Teachers need to focus on practicing the skills of problem identification; research planning; problem-solving (collecting, presenting information, processing information to draw conclusions); evaluating problem-solving results; proposing solutions for remediation, improvement;
Simultaneously, incorporating STEM education into teaching to develop students' ability to integrate knowledge and skills of Mathematics, Technology, and Chemistry in researching and solving some real-life situations.









- Vietnam: What is the sample outline of an essay on the analysis of expressions of national spirit in the Poem "Việt Bắc" for 12th-grade students? What patriotic qualities are required for 12th-grade students?
- Vietnam: What are your thoughts on the Poem "Tiếng ru" by To Huu? How many lessons are there in the 12th-grade Literature curriculum per year?
- What are the sample essays describing your grandfather for 5th-grade students in Vietnam? What are the assessment criteria for 5th-grade students in 2024?
- Vietnam: What are the sample social argumentative essays on social media etiquette for 10th-grade students? What Vietnamese knowledge do 10th-grade students learn?
- Vietnam: Why is the French Bourgeois Revolution considered the most thorough one? What learning outcomes are required for 11th-grade students after studying the bourgeois revolution?
- Vietnam: What is the atmosphere? What is the grade at which students are required to master the knowledge of the atmosphere in the History and Geography curriculum?
- Vietnam: Why does the phenomenon of day and night alternation occur on Earth? What is the grade at which students learn about the phenomenon of day and night alternation on Earth?
- What is the newest report template on distance education at the higher education level in Vietnam?
- Vietnam: What are the shortest sample expositions on Ba Den Mountain for 9th-grade students? What learning outcomes are required for the writing process in the 9th-grade Literature curriculum?
- In Vietnam, what does local time mean? What is the grade at which local time is taught in the History and Geography curriculum?

