When will the TIN of dependant be converted into a personal TIN in Vietnam?
When will the TIN of dependant be converted into a personal TIN in Vietnam?
According to the regulation at point b, clause 3, Article 30 of the Law on Tax Administration 2019, the following is provided:
Subject of taxpayer registration and issuance of TIN
...
3. The issuance of TINs is regulated as follows:
b) An individual is issued a unique TIN for use throughout their lifetime. A dependant of an individual is assigned a TIN to allow deductions for personal family circumstances related to personal income tax. The TIN issued to a dependant concurrently serves as the individual's TIN when the dependant incurs obligations to the state budget;
...
Thus, when a dependant generates taxable personal income, their TIN will be converted by the tax authority into a personal TIN without the need for a conversion procedure.

When will the TIN of dependant be converted into a personal TIN in Vietnam? (Image from the Internet)
How many dependants does a person have for personal exemption in Vietnam?
Currently, personal exemption consists of two parts: deduction for oneself and deduction for dependants. The taxpayer is automatically entitled to a personal exemption for calculating personal income tax, and there is no maximum limit on the number of dependants eligible for deduction.
Based on point c, clause 1, Article 9 of Circular 111/2013/TT-BTC, several principles for calculating personal exemptions are summarized as follows:
- Taxpayers with income from salaries or wages automatically receive personal exemptions;
- Taxpayers can claim personal exemptions for dependants once they have taxpayer registration and have been issued a TIN.
- Each dependant can only be deducted once for one taxpayer within the tax year. When multiple taxpayers share a common dependant, they must mutually agree to register the personal exemption for one taxpayer.
Thus, the law does not limit the number of dependants for one taxpayer; as long as they qualify for deduction and meet corresponding conditions under the regulations, they will be granted personal exemption.
What is the appendix of the personal exemption for dependants in Vietnam?
Sample 05-3/BK-QTT-TNCN, the appendix of detailed dependant personal exemptions, is issued with Circular 80/2021/TT-BTC as follows:
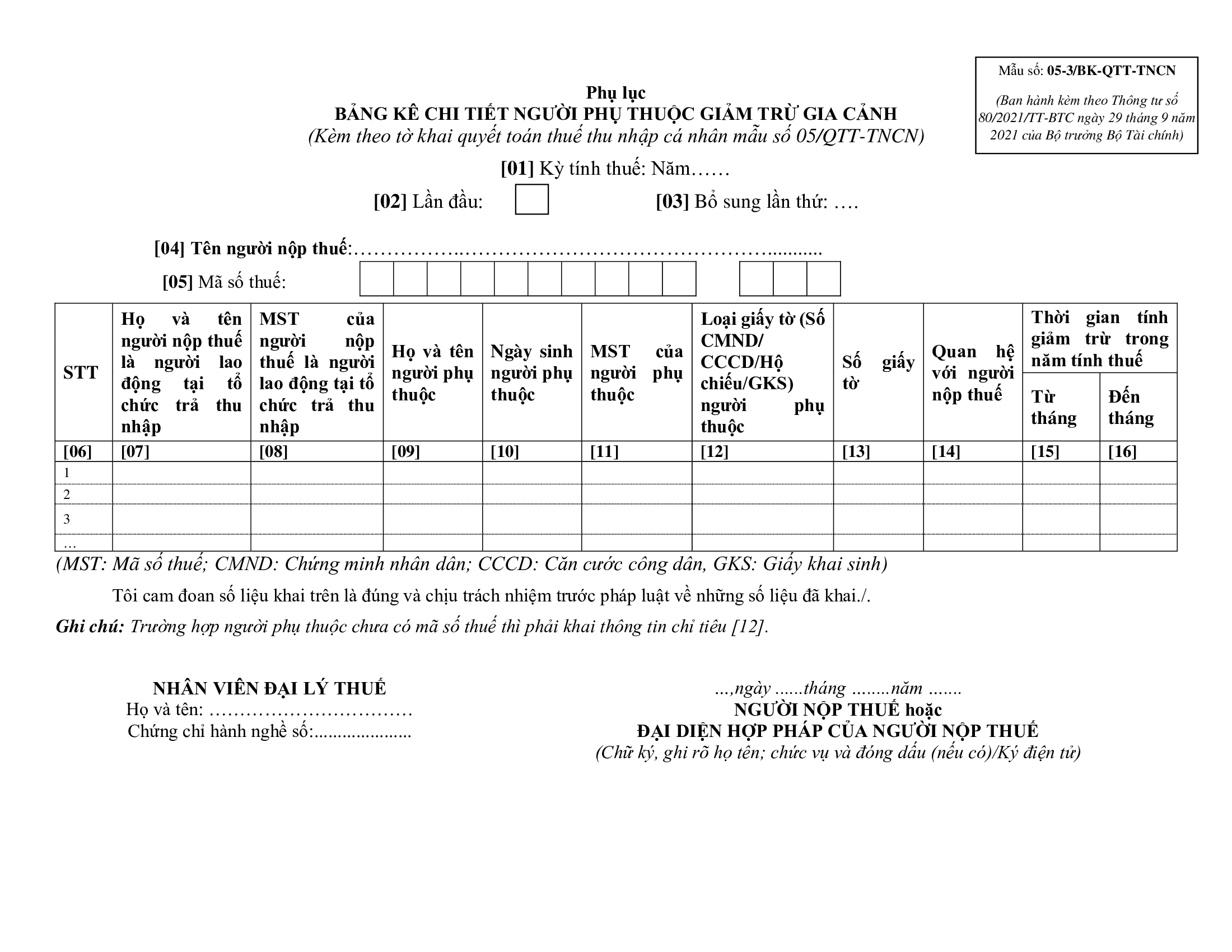
Download Sample 05-3/BK-QTT-TNCN: here
Which income is not subject to personal exemption when calculating personal income tax?
According to the regulation in clause 1, Article 19 of the Personal Income Tax Law 2007 (amended by clause 4, Article 1 of the Amended Personal Income Tax Law 2012) and clause 4, Article 6 of the Amended Laws on Taxation 2014, the personal exemption is the sum deducted from taxable income before calculating taxes on income from business, salaries, or wages of resident taxpayers.
Thus, this implies that the types of income specified in Article 2 of Circular 111/2013/TT-BTC below are not subject to personal exemption:
(1) Income from capital investment, including:
- Interest from loans.
- Dividends.
- The increased part of capital value received upon the dissolution of enterprises, change of operation model, division, separation, merger, or consolidation of enterprises, or withdrawal of capital.
- Income from capital investment in other forms, except income from bonds issued by the Government of Vietnam.
(2) Income from capital transfer, including:
- Income from the transfer of capital in economic organizations.
- Income from securities transfer.
- Income from capital transfer in other forms.
(3) Income from real estate transfer, including:
- Income from the transfer of land use rights and assets attached to land.
- Income from the transfer of ownership or use rights of houses (including future housing projects).
- Income from the transfer of land rental rights or water surface lease rights.
- Other income received from real estate transfer in any form.
(4) Income from winnings, including:
- Lottery winnings.
- Prizes from promotional events.
- Winnings from betting activities.
- Prizes from games, contests, and other forms of winnings.
(5) Income from royalties, including:
- Income from the transfer or licensing of intellectual property rights.
- Income from technology transfer.
(6) Income from franchising.
(7) Income from inheritance is securities, capital shares in economic organizations, business establishments, real estate, and other assets requiring ownership or usage registration.
(8) Income from gifts is securities, capital shares in economic organizations, business establishments, real estate, and other assets requiring ownership or usage registration.










- How long is the duration of exemption from licensing fees for a new enterprise in Vietnam? What are cases of licensing fee exemption in Vietnam?
- What are cases where the input VAT must not be deducted in Vietnam? What are the conditions for VAT input deduction?
- What are cases where personal income late payment interest is charged in Vietnam?
- How long can a taxpayer delay submitting tax declaration dossiers before their information is published in Vietnam?
- What is the Form 01/CT-KTT for amendments to the information of tax accounting books in Vietnam?
- When is the deadline for submitting annual financial statements in Vietnam? How much is the penalty for late submission?
- Shall import-export duties be paid in foreign currency in Vietnam?
- What is the excise tax rate for beer in Vietnam in 2024?
- What is coefficient K for monitoring invoicing beyond a safety threshold in Vietnam? What is the formula for calculating coefficient K in Vietnam?
- What are cases where the input VAT must not be deducted in Vietnam?

