TCVN 8685-25:2018: What are the procedures for testing the Aujeszky's disease vaccine for pigs in Vietnam?
What are the materials and reagents for the Aujeszky's disease vaccine for pigs in Vietnam?
According to Section 5 of the National Standard TCVN 8685-25:2018, the materials and reagents for Aujeszky's disease vaccine for pigs are as follows:
- Healthy, white mice weighing from 15g to 20g.
- Healthy, guinea pigs weighing from 300g to 350g.
- Healthy rabbits weighing from 1.8kg to 2kg.
- Piglets aged from 14 days to 28 days, without antibodies against Pseudorabies virus.
- Pigs weighing from 15kg to 35kg, without antibodies against Pseudorabies virus.
- 96-well plates with a layer of PK-15 cells.
- Plastic 96-well plates.
- MEM cell culture medium, 1x.
- EMEM growth medium.
- Fetal calf serum (FCS) at a concentration of 5%.
- PBS buffer solution, pH 7.2.
- Standard Pseudorabies antigen.
- Sterile physiological saline solution with a concentration of 0.9%.

TCVN 8685-25:2018: What are the procedures for testing the Aujeszky's disease vaccine for pigs in Vietnam?
What are the procedures for testing the Aujeszky's disease vaccine for pigs in Vietnam?
According to Section 7 of the National Standard TCVN 8685-25:2018, the procedure for testing the Aujeszky's disease vaccine for pigs is as follows:
- Sensory testing:
+ Toxin vaccine: Visual observation is conducted to check if the vaccine meets the criteria, such as the closed vial without cracks, consistent foam, homogeneous color, and complete dissolution in physiological saline solution (5.13) after gentle shaking for 2 minutes.
+ Inactivated vaccine: Visual observation is conducted to check if the vaccine meets the criteria, such as a homogeneous solution without clotting or sedimentation.
- Sterility testing:
+ Bacterial contamination testing according to TCVN 8684: 2011.
+ Fungal contamination testing according to TCVN 8684: 2011.
- Safety testing:
One of the following methods is used:
+ Weight method:
The vaccine is injected into 2 pigs (5.4), with each pig receiving 10 doses (for the toxin vaccine) or 1 dose (for the inactivated vaccine) following the manufacturer's recommendations. The experimental pigs are monitored for 14 days (for the inactivated vaccine) or 21 days (for the toxin vaccine). The vaccine meets the safety criteria if all pigs remain healthy, develop normally, and show no signs of Aujeszky's disease, such as respiratory disorders (coughing, difficulty breathing) or neurological disorders (tremors, excessive salivation, eye spasms).
+ Replacement method:
One of the following methods is used:
++ The vaccine is injected into 10 white mice (5.1), with each mouse receiving 0.5 ml of the vaccine intraperitoneally or subcutaneously. The experimental mice are monitored for 7 days (for the toxin vaccine) or 14 days (for the inactivated vaccine). The vaccine meets the safety criteria if all mice remain healthy, develop normally, and show no local or systemic abnormalities.
++ The vaccine is injected into 2 guinea pigs (5.2), with each guinea pig receiving 0.5 ml of the vaccine intraperitoneally or subcutaneously. The experimental guinea pigs are monitored for 7 days. The vaccine meets the safety criteria if all guinea pigs remain healthy, develop normally, and show no local or systemic abnormalities.
- Efficacy testing:
+ Efficacy testing for the toxin vaccine:
A 96-well plate with a layer of PK-15 cells (5.6) is used to determine the virus titer in each vaccine dose (see Appendix A). The vaccine meets the efficacy criteria if each vaccine dose has a virus titer of ≥ 102.3 TCID50.
+ Efficacy testing for the inactivated vaccine:
10 pigs (5.5) are divided into 2 groups:
Group 1: 5 pigs, each pig is injected with the vaccine dose indicated on the label following the manufacturer's recommendations.
Group 2: 5 control pigs, each pig is injected with physiological saline solution (5.13) at a similar dose and route of administration as Group 1.
After 14 days of vaccination, blood samples are collected from pigs in both groups, and serum is separated to test for antibodies using neutralization reaction (see Appendix B).
The vaccine meets the efficacy criteria if at least 80% of the serum from Group 1 has a titer of ≥ 1:8 and at least 80% of the serum from Group 2 has a titer of < 1:2.
What is the method for virus titer determination in vaccines in Vietnam?
In Appendix A of TCVN 8685-25:2018, the method for virus titer determination in vaccines is described as follows:
(1) Preparation:
- Vaccine to be tested
- 96-well plate with a layer of PK-15 cells (5.6)
- MEM 1X cell culture medium (5.8)
- PBS solution (5.11)
(2) Procedure:
- Dilute the vaccine with MEM 1X cell culture medium (5.8) in a 1:10 ratio to obtain concentrations ranging from 10-1 to 10-8.
- Using a micropipette (6.6), add 100 µl of diluted vaccine (A.2.1) into each of the 96 wells with a layer of PK-15 cells, infecting 5 wells per concentration.
- Place the 96-well plate (A.2.2) in a CO2 incubator (6.1) for 1 hour.
- Wash off non-adherent viruses on the cell surface with PBS solution (5.9).
- Using a micropipette (6.6), add 100 µl of 5% MEM medium into all wells of the 96-well plate.
- Place the 96-well plate (A.2.5) back into the CO2 incubator (6.1) and observe cytopathic effects for a period of 4 to 5 days. Calculate the virus titer causing 50% cell destruction (TCID50) using the Spearman-Kaber method as follows:
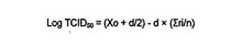
Where:
Xo is the log of the highest dilution of the virus.
d is the log of the dilution.
ri is the number of negative wells at each dilution.
n is the number of wells infected at each dilution.
LawNet