Sample Test for Grade 10 Mathematics in 2025 in Hanoi with Answers
Sample Test for Grade 10 Mathematics in 2025 in Hanoi with Answers
On January 29, 2024, the Hanoi Department of Education and Training announced the format and sample entrance exam for grade 10 public schools for the year 2025, constructed according to the General Education Program 2018 in Announcement 2988/TB-SGDDT 2024.
>> Download Announcement 2988/TB-SGDDT 2024.
The sample entrance exam for grade 10 in Mathematics 2025 in Hanoi is as follows:
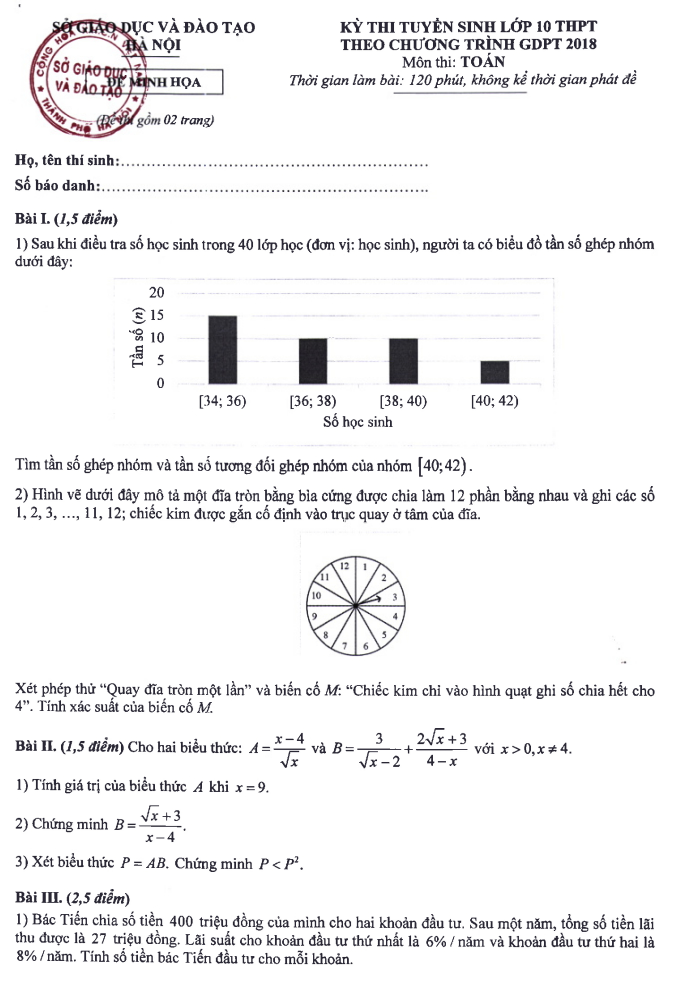
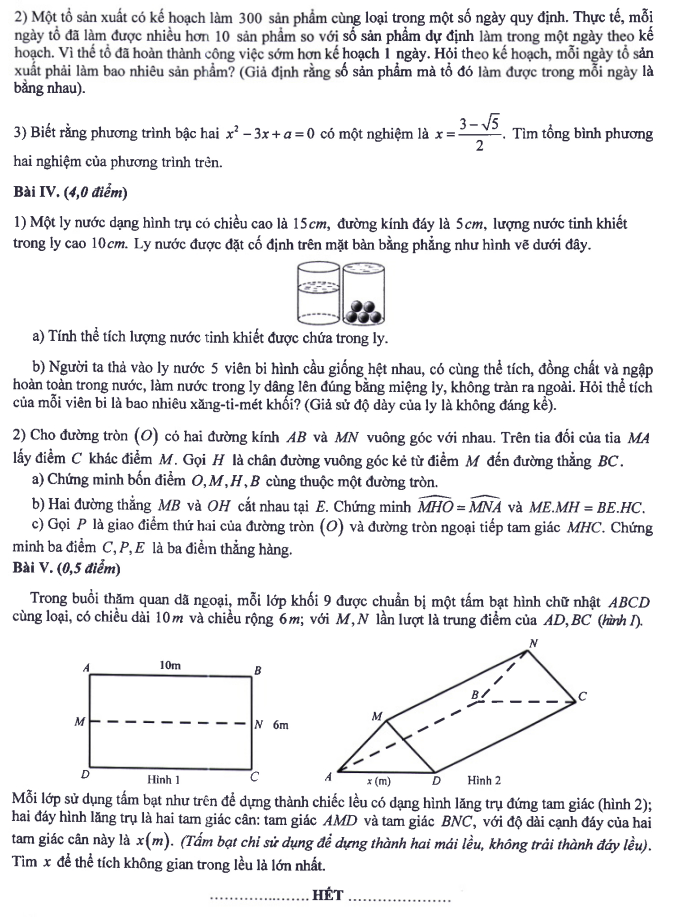
Answer key for the sample entrance exam for grade 10 in Mathematics 2025 in Hanoi:








Note: The above answers are for reference purposes only.
Sample Test for Grade 10 Mathematics in 2025 in Hanoi with Answers (Image from the Internet)
What is the age of grade 10 students in Vietnam?
The age of middle and high school students is stipulated in Article 33 of the Regulations on secondary schools, high schools, and multi-level schools issued together with Circular 32/2020/TT-BGDDT:
Age of secondary and high school students
1. The age for students entering grade 6 is 11. The age for students entering grade 10 is 15. For students who skipped grades in the previous level or students entering school at an age older than the regulated age, the age for entering grade 6 and grade 10 can be adjusted based on the graduation age of the previous level.
2. Students who are ethnic minorities, students with disabilities, students with special difficult circumstances, or students who return from abroad may enter school up to 3 years older than the regulated age.
3. Students may not repeat a grade more than 3 times in one schooling level.
...
Thus, the age for students entering grade 10 is 15. For those who skipped grades in the previous level or enter school at an older age than the regulated age, or repeated a grade, the age for entering grade 10 can be adjusted based on the graduation age of the previous level.
What are regulations on the evaluation of educational outcomes in Mathematics according to the General Education Program 2018 in Vietnam?
Based on Section 7 of the General Education Program in Mathematics issued together with Circular 32/2018/TT-BGDDT, the method of evaluating educational outcomes in Mathematics according to the General Education Program 2018 is as follows:
Combining multiple forms of assessment (process evaluation, periodic evaluation), multiple evaluation methods (observation, recording implementation processes, interviews, objective tests, essays, written tests, practical exercises, learning projects/products, performing practical tasks,...) at appropriate times.
Process evaluation (or continuous evaluation) is organized by the subject teacher, in combination with evaluation from teachers of other subjects, self-evaluation by the student, and feedback from other students in the group or class, or from the student's parents. Process evaluation occurs concurrently with the learning activities of the students, avoiding detachment between the teaching and evaluation processes, ensuring the goal of evaluation for the progress in student learning.
Periodic evaluation (or summative evaluation) mainly aims to assess the achievement of learning objectives. The results of periodic and summative evaluations are used to certify learning levels, recognize students' achievements. Periodic evaluation is organized by educational institutions or through national testing and assessment terms.
Periodic evaluation is also used for managing teaching activities, ensuring educational quality at the institution, and for developing the Mathematics curriculum.
Student competencies are assessed through evidence of the results achieved during the implementation of students' activities.
The evaluation process comprises essential steps such as determining evaluation objectives; identifying necessary evidence; selecting appropriate evaluation methods and tools; collecting evidence; interpreting evidence and providing feedback.
Attention is paid to selecting methods and tools to assess components of mathematical competence. Specifically:
- Assessing mathematical thinking and reasoning competence: various methods and tools such as questions (oral, written), exercises,... are used that require students to present, compare, analyze, aggregate, and systematize knowledge; applying mathematical knowledge to explain and reason.
- Assessing mathematical modeling competence: choosing real-life situations to generate mathematical problems.
Consequently, students need to identify mathematical models (including formulas, equations, tables, graphs,...) for real-life situations; solve mathematical problems in the established model; present and evaluate solutions in a real-life context and improve the model if the solution is not appropriate.
- Assessing problem-solving competence in mathematics: methods such as requiring students to identify situations, discover and state the problems to be solved; describing, explaining initial information, goals, aspirations of the considered problem situation; gathering, selecting, arranging information and connecting with existing knowledge; using questions (which may require oral or written answers) that demand students apply knowledge to solve problems, especially real-life problems;
Simultaneously, using observation methods (such as checklists based on predefined criteria), observing students during the problem-solving process; assessing through students' practical products (e.g., products of learning projects); reasonably considering integrative evaluation tasks.
- Assessing mathematical communication competence: methods may include asking students to listen, understand, read, understand, take notes (summarize), analyze, select, and extract key mathematical information in spoken or written texts; using mathematical language combined with ordinary language to present, express, raise questions, discuss, and debate mathematical content, ideas, solutions in interaction with others.
- Assessing the ability to use mathematical tools and means: methods may include asking students to recognize names, uses, rules of use, maintenance methods, strengths, and limitations of mathematical tools; demonstrating the proper use of mathematical tools and means to perform learning tasks or to express mathematical reasoning and proofs.
When planning lessons, teachers need to establish evaluation criteria and methods to ensure that at the end of each lesson, students achieve basic requirements based on the stated criteria before undertaking subsequent learning activities.
>> See the General Education Program in Mathematics issued together with Circular 32/2018/TT-BGDDT:

