What is the cash flow statement form in the annual financial statements in Vietnam according to Circular 200?
- What is the regulation on preparing cash flow statement in the annual financial statements in Vietnam prepared by the indirect method?
- What is the regulation on preparing cash flow statement in the annual financial statements in Vietnam prepared by the direct method?
- What are the guidelines for preparation and presentation of cash flow statement in Vietnam?
What is the regulation on preparing cash flow statement in the annual financial statements in Vietnam prepared by the indirect method?
Currently, the form of cash flow statement in financial statements prepared by the indirect method is specified in Form No. B03 - DNN issued together with Circular 200/2014/TT-BTC
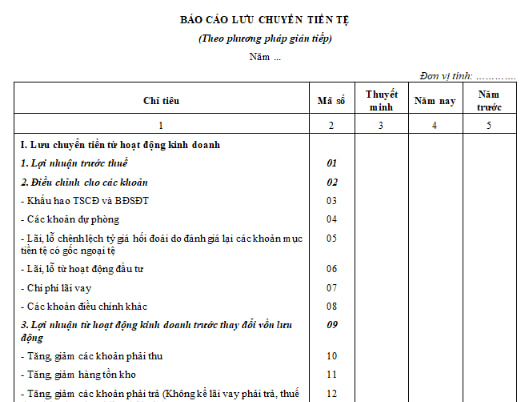
Download the Cash Flow Statement Template in the annual financial statements prepared under the indirect method here
What is the regulation on preparing cash flow statement in the annual financial statements in Vietnam prepared by the direct method?
Currently, the cash flow statement form in the financial statements prepared by the direct method is specified in Form No. B03 - DNN issued together with Circular 200/2014/TT-BTC
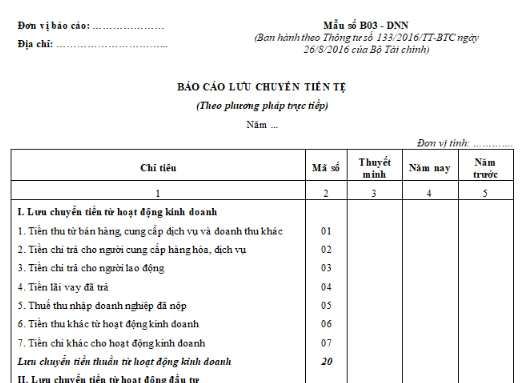
Download the Cash Flow Statement Template in the annual financial statements directly here

What is the cash flow statement form in the annual financial statements in Vietnam according to Circular 200? (Image from the Internet)
What are the guidelines for preparation and presentation of cash flow statement in Vietnam?
Pursuant to Clause 1, Article 114 of Circular 200/2014/TT-BTC, the principles for preparing and presenting the statement of cash flows according to Form No. B03 - DN include:
1. Principles of preparing and presenting cash flow statement
The preparation and presentation of cash flow statement yearly and in interim accounting periods must comply with the provisions of Accounting Standard "Cash flow statement" and Accounting Standards "interim financial statement ". Method for preparation of cash flow statements is guided for the most common transactions, enterprises base on the nature of each transaction to present cash flows accordingly if there is no specific guidance in this Circular. Items without figures are not presented, enterprises may renumber but must not change codes of items.
Short-term investments considered cash equivalents presented in cash flow statements only including short-term investments with recovery term or maturity of within three months may be converted easily into a certain amount and there is no risk of conversion into money from the date of buying such investments at the time of reporting. For example, bank exchange bills, treasury bills, deposit certificates ... with recovery term or maturity of less than 3 months from date of purchase.
Enterprises must present the cash flows in the cash flow Statement in three types of activities: trading, investment and financing activities as prescribed by the standards of "Cash flow statement":
- Cash flows from trading are cash flows arising from activities generating main revenues of enterprises and activities other than investing or financing activities;
- Cash flows from investment are cash flows arising from purchase, construction, liquidation or sale of long-term assets and other investments which are not classified as cash equivalents;
- Cash flows from financial activities are cash flows arising from operations generating changes in the size and structure of owner’s equity and borrowing capital of enterprises.
Enterprises may present cash flows from trading, investing and financial activities in a manner that best suits to the characteristics of the enterprises.
The following cash flows arising from trading, investing and financial activities are reported on a net basis:
- Collecting money and paying of customers such as rental collected, paid and repaid to the owner of the property;
- Collecting money and paying for items with fast turnarounds, short maturities such as: Buying, selling foreign currencies; buying and selling investments; loans or other short-term loans with payment term of within 3 months.
Cash flows arising from transactions in foreign currency must be converted into the official currency used in accounting books and financial statements under the exchange rate at the arising time of transactions.
Transactions in investments and finance which do not directly use cash or cash equivalents are not presented in the Cash flow statement, for example:
- The purchase of assets by receipt of debts related directly or through finance lease operations;
- The purchase of an enterprise through the issuance of shares;
- The transfer of debt into owner’s equity.
The cash and cash equivalents at the beginning and end of the period, the effect of changing exchange rates in currency conversion and current cash equivalents in foreign currencies at the end of period must be presented in separate items in Cash flow statements for comparison of figures with the corresponding items in the Balance Sheet.
Enterprises must present values and reasons of cash and cash equivalents which have the great balance at end of period held by enterprises but unused due to the limitation of legislation or other constraints imposed on enterprises.
If enterprises borrow to make payments directly to contractors, suppliers of goods and services (loans are transferred directly from the lender to the contractors and suppliers without being transferred through the accounts of enterprises), enterprises must still present on the cash flow statement, namely:
- The amount borrowed is presented as cash inflows from financing activities;
- The amount paid to suppliers of goods, services or to contractors is presented as cash outflows from trading or investments, depending on each transaction.
In case enterprises incur the offsetting payment for the same object, the presentation in cash flow statement shall comply with the following principles:
- If the offsetting relates to transactions classified in the same cash flows, enterprises shall present on a net basis (in dissimilar barter transactions...);
- If the offsetting relates to transactions classified in different cash flows, enterprises shall not present on a net basis but must present separately the value of each transaction (for example offsetting the selling money receivable with borrowings ...).
12. For the cash flow from repurchases and resale of government bonds and securities REPO transactions: The seller presents it as the cash flow from financial activities; The buyer presents it as the cash flow from investing activities.
LawNet