Vietnam: What are the guidelines for dental examination during the pre-enlistment check-up from January 1, 2024? What are the pre-enlistment check-up contents?
What are the guidelines for dental examination during the pre-enlistment check-up in Vietnam from January 1, 2024?
Under subsection 3 of Section IV of Appendix I promulgated together with Circular 105/2023/TT-BQP, the guidelines for dental examination during the pre-enlistment check-up in Vietnam from January 1, 2024 are specified as follows:
* No. 17: Tooth cavities
Tooth cavities are denoted with the letter "S".
- S1: Level 1 cavities (Enamel Decay);
- S2: Level 2 cavities (Dentin decay);
- S3: Level 3 cavities (Pulp damage).
For example: Tooth 46 with grade 3 worm is listed as R46S3
* No. 18: Tooth loss
(1) Regulations on tooth symbols: Each tooth has a two-digit symbol:
- The first digit is the symbol of the function quadrant of the object:
Direction | Right side | Left |
Above | 1 | 2 |
Under | 4 | 3 |
+ The right upper molars have the symbol No. 1.
+ The upper left molars have the symbol No. 2.
+ The lower left molars have the symbol No. 3.
+ The right lower teeth have the symbol number 4.
- The second digit denotes each tooth:
+ Middle incisors: No. 1
+ Innermost wisdom teeth: No. 8
Example:
+ Canines of the left maxillary notation 23
+ The lower 5th molars must be marked 45
- Molars have:
+ Small molars (small mortars): including teeth No. 4 and 5;
+ Large molars (large mortars): including teeth No. 6, 7 and 8 (wisdom teeth),
(2) How to calculate chewing power:
- Teeth with pulpitis or necrotic pulp are only considered as temporary loss of chewing power.
- The tooth is shaken to an untreatable level that requires extraction, or losing all crowns and legs is considered to be tooth loss.
- If 1 tooth is lost, it is considered to be loss of both teeth and the number opposite the chewing side.
For example: Losing tooth 16 is considered to lose the ability to chew all teeth 46 and calculates a loss of 10% chewing power.
- If 4 wisdom teeth of the upper and lower jaw are lost, it is not counted as loss of chewing power (because many people do not have wisdom teeth).
How to calculate chewing power:
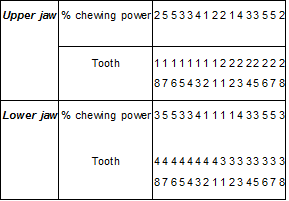
Dentures: Losing teeth that have made good dentures count as 50% of the chewing power of the teeth.
*Nos. 19, 20: Distinguish between, gingivitis and peridontitis:
Gingivitis | Peridontitis |
- Red gums, can inflame 2-3 teeth to the entire 2 jaws | - The gums may be inflamed, red, bleeding, gum recession, cleft neck of the tooth |
- No pockets of pus in the worm | - There are pockets of pus in the depths of many teeth to the entire 2 jaws, pus flows frequently |
- Teeth wobbling little or no wobble | - Teeth wobbling from grade 1 to degree 4 |
- Foul Breath | - Very foul breath |
- Have tartar | - Multiple tartar on the gums and under the gums |
- Longitudinal or transverse socket bone |
* No. 21: Pulpitis, necrotizing pulp, peripeditis tooth:
Peripediculitis other than peridental inflammation is inflammation of the peridental ligaments around the tooth, socket osteolysis, and gingivitis.
- Pediculitis: An inflammation of the terminal area of the tooth where the nerve breast blood vessels enter to nourish the tooth (usually due to necrotic pulp) pain and moisture, the tooth feels protruding, vertical knocking pain, the jaws touch pain, the gums of the peduncle area are slightly heavy. Acute pediculitis: pain localized gums or cheeks, corresponding inflamed teeth, swelling.
- Pulpitis: Natural tooth pain, severe nocturnal pain, diffuse pain, severe pain in episodes depending on spontaneous pulpitis or acute pulpitis, horizontal knocking is more painful than vertical.
Prescribing the symbol for pulpitis with the letter "T", the inscription is similar to the footnote of the entry of carious teeth
- Necrotizing pulpitis: Painless teeth, often gray or opaque yellow teeth.
* No. 24: Inflammation of the salivary glands: Swelling in the parotid gland area. If it is not stable, on examination, squeezing into the parotid gland area will show purulent discharge in the Sténon tube.
* No. 26: Broken jawbone: A normal bite is defined when the person being examined closes their mouth in a static position, swallows saliva, has two teeth tightened, is not open, and does not move to the right or left. A displaced bite is when the jaws are exposed or deflected to the side in an upper position.
.png)
What are the newest pre-enlistment check-up contents in Vietnam?
Under the provisions of Article 7, Article 8 of Circular 105/2023/TT-BQP, the pre-enlistment check-up in Vietnam includes 02 rounds: the prequalification round and the detailed check-up round with the following contents:
Round 1: Prequalification round:
- Commune-level health stations shall conduct the prequalification round of pre-enlistment check-ups under the professional direction and guidance of district-level health centers or district-level general hospitals; and supervision of the Military Commands of districts.
- Based on the plan for selecting and conscripting citizens of the district-level military service council, the commune-level military command board shall make a list and call for pre-enlistment check-up for citizens subject to medical examination for military service in the area under their management.
- The contents of the prequalification round include:
+ Exploit personal and family medical history;
+ Detect cases of physical inadequacy, deformities, and deformities specified in Section I, Section II of Annex I promulgated together with Circular 105/2023/TT-BQP; diseases exempt from military service registration specified in Section III of Annex I promulgated together with Circular 105/2023/TT-BQP.
Round 2: Detailed check-up round:
- Pre-enlistment check-up shall be conducted by the district-level pre-enlistment check-up board according to the provisions of Clause 1, Article 40 of the Law on Military Service 2015, including:
- The Chairperson of the district-level pre-enlistment check-up board shall be the Director of the District Health Center or the Director of the District General Hospital;
- The Vice Chairperson of the district-level pre-enlistment check-up board shall be the Deputy Director in charge of professional affairs of the district health center or the deputy director of the district general hospital;
- The Permanent members simultaneously being Secretary of the district-level pre-enlistment check-up board shall be officers who advise the implementation of the state management of health at the district level;
- Members are officers and employees of agencies and units including district-level health centers, district-level general hospitals (if any), district-level health agencies, district-level military medical boards and representatives of relevant units; in case of necessity, provincial-level medical personnel or military medical personnel of provincial-level military commands may be used under decision by the Chairperson of the provincial-level military service council on human resources;
- Members of the district-level pre-enlistment check-up board must ensure sufficient departments and specialties as prescribed in Clause 5 of this Article and must have practice certificates or practice licenses suitable to their duties as prescribed by the law on medical examination and treatment.
- Make a list of citizens subject to the pre-enlistment check-up;
- Notify the time and place of the pre-enlistment check-up (Issue a pre-enlistment check-up order);
- Organize the pre-enlistment check-up according to the contents specified in Clause 5 Article 8 of Circular 105/2023/TT-BQP and follow 2 rounds:
- Physical check-up; clinical by specialties: Ophthalmology, ENT, Maxillofacial Dentistry, Internal Medicine, Neurology, Psychiatry, Surgery, Dermatology, Obstetrics and Gynecology (for women);
- Subclinical check-up: CBC; blood type (ABO); liver function (AST, ALT); kidney function (Urea, Creatinine); blood sugar; hepatitis B virus (HBsAg); hepatitis C virus (Anti-HCV); HTV; whole urine. (10 parameters); general abdominal ultrasound; electrocardiography; Straight cardiopulmonary X-ray; urine tests detect drugs. The Chairperson of the Board shall appoint additional tests according to professional requirements to conclude health accurately.
During physical and clinical check-up, if the citizen does not meet one of the health requirements specified in Clause 1 Article 4 of Circular 105/2023/TT-BQP, the member shall directly report to the Chairperson of the pre-enlistment check-up board for the decision to stop the check-up. Blood and urine tests; HIV and drug tests shall be only applied to citizens meeting health requirements after physical check-up, clinical check-up, ultrasound, electrocardiography, and straight cardiopulmonary X-ray.
Organize HIV counseling and testing per the law on HIV/AIDS prevention and control in case of meeting health requirements;
Thus, the pre-enlistment check-up from January 1, 2024 shall be conducted in 02 rounds anf include the above contents:
- Round 1: The prequalification round of pre-enlistment check-up at the commune health station.
- Round 2: Detailed pre-enlistment check-up round at the district health center
What is the pre-enlistment check-up schedule in Vietnam?
Under the provisions of Clause 7, Article 8 of Circular 105/2023/TT-BQP, the pre-enlistment check-up in Vietnam is conducted from November 1 to December 31 every year. The Ministry of National Defense shall adjust the schedule when necessary.
LawNet