From May 15, 2024, what are the regulations on list of dangerous goods in Vietnam according to Decree 34/2024/ND-CP?
From May 15, 2024, what are the regulations on list of dangerous goods in Vietnam according to Decree 34/2024/ND-CP?
Based on Clause 1, Article 5 of Decree 34/2024/ND-CP, the List of Dangerous Goods in Vietnam is regulated as follows:
List of Dangerous Goods
1. The List of Dangerous Goods is categorized by Class, Division along with the United Nations code and hazard number specified in Appendix I of this Decree.
Thus, the list of dangerous goods is specified in Appendix I of Decree 34/2024/ND-CP.
According to Appendix I attached to Decree 34/2024/ND-CP, the List of Dangerous Goods includes:
Below is the List of Dangerous Goods:
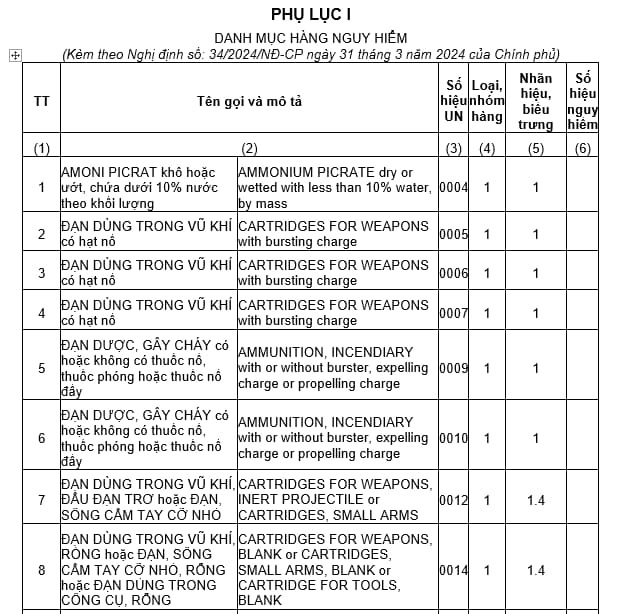
>> View the detailed List of Dangerous Goods: Download

From May 15, 2024, what are the regulations on list of dangerous goods in Vietnam according to Decree 34/2024/ND-CP? (Internet image)
What are the requirements for road motor vehicles carrying dangerous goods in Vietnam?
Based on Article 10 of Decree 34/2024/ND-CP, the requirements for road motor vehicles carrying dangerous goods in Vietnam are:
(1) The transport means must meet the conditions to participate in traffic as prescribed by law. The specialized equipment of the transport means for dangerous goods must ensure national standards or national technical regulations or comply with the regulations of the specialized management ministry.
(2) The transport means of dangerous goods must bear the symbol of dangerous goods. If there are multiple classes of dangerous goods on one vehicle, the vehicle must bear the symbols of all those classes. The placement of the symbols must be on both sides, front, and back of the vehicle, ensuring easy observation and identification.
(3) The transport means of dangerous goods, after unloading all dangerous goods and if not continuing to transport such goods, must be cleaned and remove dangerous symbols on the transport means. The transport unit and the vehicle operator are responsible for cleaning and removing dangerous symbols on the vehicle when not continuing to transport that Class of dangerous goods.
The transport means of dangerous goods must meet the 03 conditions above.
How are dangerous goods in Vietnam classified into classes and divisions?
According to Article 4 of Decree 34/2024/ND-CP, the classification of dangerous goods in Vietnam is as follows:
Depending on the chemical, physical properties, dangerous goods are classified into 9 classes and divisions as follows:
- Class 1: Explosive substances and articles;
+ Division 1.1: Substances and articles with a mass explosion hazard.
+ Division 1.2: Substances and articles with a projection hazard but not a mass explosion hazard.
+ Division 1.3: Substances and articles with a fire hazard and either a minor blast hazard or a minor projection hazard or both, but not a mass explosion hazard.
+ Division 1.4: Substances and articles that present no significant hazard.
+ Division 1.5: Very insensitive substances with a mass explosion hazard.
+ Division 1.6: Extremely insensitive articles with no mass explosion hazard.
- Class 2: Gases;
+ Division 2.1: Flammable gases.
+ Division 2.2: Non-flammable, non-toxic gases.
+ Division 2.3: Toxic gases.
- Class 3: Flammable liquids and desensitized explosives;
- Class 4;
+ Division 4.1: Flammable solids, self-reactive substances and solid desensitized explosives.
+ Division 4.2: Substances liable to spontaneous combustion.
+ Division 4.3: Substances which, in contact with water, emit flammable gases.
- Class 5;
+ Division 5.1: Oxidizing substances.
+ Division 5.2: Organic peroxides.
- Class 6;
+ Division 6.1: Toxic substances.
+ Division 6.2: Infectious substances.
- Class 7: Radioactive materials;
- Class 8: Corrosive substances;
- Class 9: Miscellaneous dangerous substances and articles.
Thus, dangerous goods are classified into 9 classes with Class 1 having 6 divisions, Class 2 having 3 divisions, Class 4 having 3 divisions, Class 5 having 2 divisions, and Class 6 having 2 divisions.
Who has the authority to issue dangerous goods transport licences in Vietnam?
Based on Article 17 of Decree 34/2024/ND-CP, the authority to issue licences in Vietnam is as follows:
Authority to grant dangerous goods transport licences and cases of exemption from grant thereof
1. The Ministry of Public Security organizes the issuance of dangerous goods transport licences for classes 1, 2, 3, 4, and 9 as prescribed in Clause 1, Article 4 of this Decree (except for plant protection chemicals and the provisions in Clause 2 of this Article).
2. The Ministry of Defense organizes the issuance of dangerous goods transport licences for organizations and enterprises under the management of the Ministry of Defense.
3. The Ministry of Science and Technology organizes the issuance of dangerous goods transport licences for classes 5, 8 as prescribed in Clause 1, Article 4 of this Decree.
4. The People's Committees of provinces and centrally affiliated cities organize the issuance of dangerous goods transport licences for plant protection chemicals.
5. The agency issuing dangerous goods transport licences shall determine the transport routes and time based on the Class and Division of dangerous goods as prescribed in Clause 1, Article 4 of this Decree.
6. The issuance of dangerous goods transport licences for Class 7 is carried out according to the regulations in the Decree on radiation activities and support services for the application of atomic energy.
7. The agency issuing dangerous goods transport licences shall refuse to issue licences for the transport of highly flammable or explosive substances whose routes pass through bridges, tunnels, and ferries as specified in Article 12 of this Decree.
Thus, dangerous goods transport licences are issued by the competent ministries. Additionally, the People's Committees of provinces and centrally affiliated cities organize the issuance of licences for the transport of plant protection chemicals.
LawNet