The latest form of contract for purchase and sale of goods in 2023? Is the contract for purchase and sale of goods in Vietnam necessary to be made in writing?
- The latest form of contract for purchase and sale of goods in 2023?
- Is the contract for purchase and sale of goods in Vietnam necessary to be made in writing?
- What goods shall be considered not appropriate to the contract?
- In the contract for purchase and sale of goods before delivery, who is responsible for the defects of the goods?
The latest form of contract for purchase and sale of goods in 2023?
Currently, the law does not stipulate the form of a contract for purchase and sale of goods. Below is the latest form of contract for purchase and sale of goods (for reference only):
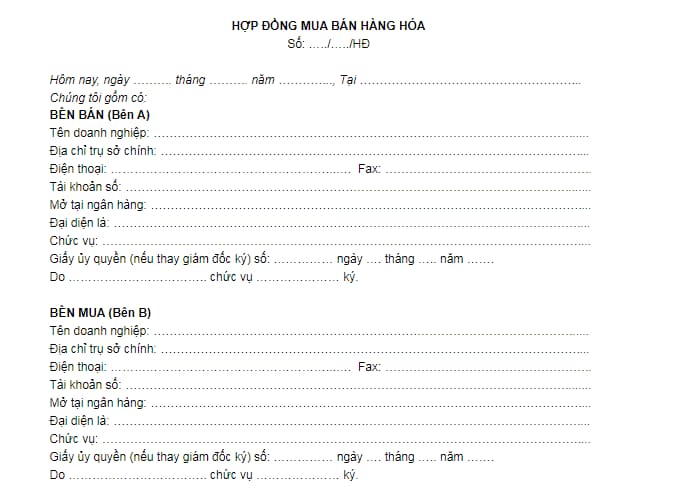
Download the latest form of contract for purchase and sale of goods in 2023: Download.

The latest form of contract for purchase and sale of goods in 2023? Is the contract for purchase and sale of goods in Vietnam necessary to be made in writing? (Image from the Internet)
Is the contract for purchase and sale of goods in Vietnam necessary to be made in writing?
Pursuant to Clause 1, Article 24 of the 2005 Commercial Law of Vietnam:
Form of contracts for purchase and sale of goods
1. Contracts for sale and purchase of goods may be expressed in verbal or written form or established by specific acts.
2. For types of contracts for purchase and sale of goods, which, as provided for by law, must be made in writing, such provisions must be complied with.
Thus, according to the provisions of the contracts for purchase and sale of goods, it is not necessary to be made in writing, but contracts for purchase and sale of goods can be concluded in many other forms such as in verbal or written form or established by specific acts.
What goods shall be considered not appropriate to the contract?
Pursuant to Clause 1, Article 39 of the 2005 Commercial Law of Vietnam:
Goods which are not appropriate to contracts
1. Where it is not specified in the contract, goods shall be considered not appropriate to the contract when they fall into one of the following cases:
a/ They are not suitable to common use purposes of goods of the same type;
b/ They are not suitable to any specific purpose that has been notified by the purchaser to the seller or the seller should have known at the time the contract is entered into;
c/ Their quality is not the same as the quality of the samples previously handed over by the seller to the purchaser;
d/ They are not preserved or packaged by a method common to such goods, or not preserved by proper preserving methods in cases where no common preserving method is available.
2. The purchaser may reject the goods if such goods are not appropriate to the contract according to the provisions of Clause 1 of this Article.
Thus, goods shall be considered not appropriate to the contract when they fall into one of the following 4 cases:
- They are not suitable to common use purposes of goods of the same type;
- They are not suitable to any specific purpose that has been notified by the purchaser to the seller or the seller should have known at the time the contract is entered into;
- Their quality is not the same as the quality of the samples previously handed over by the seller to the purchaser;
- They are not preserved or packaged by a method common to such goods, or not preserved by proper preserving methods in cases where no common preserving method is available.
In the contract for purchase and sale of goods before delivery, who is responsible for the defects of the goods?
Pursuant to Clauses 4 and 5, Article 44 of the 2005 Commercial Law of Vietnam as follows:
Pre-delivery examination of goods
1. Where it is agreed by the parties that the purchaser or the purchaser’s representative shall examine the goods before the delivery, the seller must ensure that the purchaser or the purchaser’s representative shall be given conditions for conducting such examination.
2. Except where it is otherwise agreed, the purchaser or the purchaser’s representative in the cases mentioned in Clause 1 of this Article must examine the goods within the shortest period of time allowed by practical circumstances. Where the contract provides for the transportation of goods, the examination of goods may be postponed until the goods are transported to the destination.
3. Where the purchaser or the purchaser’s representative does not conduct the examination of goods before the delivery of goods as agreed, the seller may deliver the goods according to the contract.
4. The seller shall not be liable for defects of goods which the purchaser or the purchaser’s representative has known or should have known but failed to notify them to the seller within a reasonable time limit after the examination of goods.
5. The seller shall be liable for defects of goods already examined by the purchaser or the purchaser’s representative if the defects of the goods cannot be detected in the course of examination through common measures and the seller knew or should have known such defects but failed to notify them to the purchaser.
Thus, according to the above provisions in the contract for purchase and sale of goods before delivery, the responsibility for defects of the goods is as follows:
- The seller shall not be liable for defects of goods which the purchaser or the purchaser’s representative has known or should have known but failed to notify them to the seller within a reasonable time limit after the examination of goods.
- The seller shall be liable for defects of goods already examined by the purchaser or the purchaser’s representative if the defects of the goods cannot be detected in the course of examination through common measures and the seller knew or should have known such defects but failed to notify them to the purchaser.
LawNet
