What are the details of National Standard TCVN 13781:2023 on methods for determining the energy of natural gas in Vietnam?
- What are the details of National Standard TCVN 13781:2023 on methods for determining the energy of natural gas in Vietnam?
- What are the general principles for determining the energy of natural gas in Vietnam according to National Standard TCVN 13781:2023?
- What are the regulations on the measurement of natural gas volume specified in National Standard TCVN 13781:2023?
What are the details of National Standard TCVN 13781:2023 on methods for determining the energy of natural gas in Vietnam?
National Standard TCVN 13781:2023 is compiled by the National Technical Committee of Standards TCVN/TC193 Gas products, proposed by the Directorate of Standards, Metrology and Quality, and published by the Ministry of Science and Technology.
Accordingly, this National Standard includes 11 reference annexes.
National Standard TCVN 13781:2023 provides methods for determining the energy of natural gas by measurement or by calculation and describes relevant techniques and measures to be taken. The calculation of thermal energy is based on the measurement of the individual quantity, by mass or by volume, of the transferred gas and the calculated or measured calorific value. This National Standard TCVN 13781:2023 also provides general methods for calculating uncertainty.
This National Standard TCVN 13781:2023 describes only the systems currently in use.
Note: The use of these systems in commercial or official transactions may require approval from national authorities and need to comply with legal regulations.
This National Standard TCVN 13781:2023 applies to any gas measuring station from domestic transmission to large-scale high-pressure transmission.
New techniques can also be used, as long as the proven effectiveness is equal to or better than the techniques mentioned in this National Standard TCVN 13781:2023.

What are the general principles for determining the energy of natural gas in Vietnam according to National Standard TCVN 13781:2023?
Under Section 5 of National Standard TCVN 13781:2023, the general principles for determining the energy of natural gas in Vietnam are specified as follows:
- The energy fraction, E, contained in a certain amount of gas, Q, is calculated by calorimetric multiplication, H, by the corresponding amount of gas.
- Energy can be directly measured as follows:
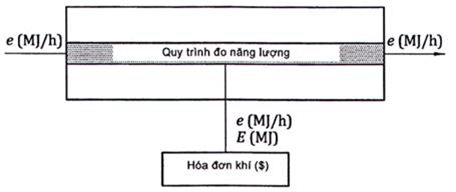
Or calculated from the quantity and calorific value of the gas as follows:
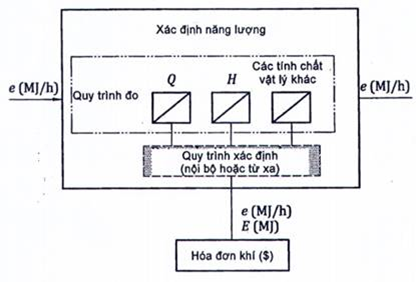
Typically, the amount of gas is expressed in volume and calorific value on a volume-based basis. To achieve accurate measurements of energy, both gas volume and calorific value must be at the same reference conditions. The determination of energy is based on the accumulation over time of the calculated results from successive sets of calorific values and simultaneous flow values or on the multiplication of the total volume and representative calorific values (assigned) for that period.
Especially in situations where different calorific values are present and when the flow rate is determined at a location other than the (representative) calorific measurement position, the effect on accuracy due to the difference in time between the determination of flow and calorific value must be considered (see Article 11).
The volume of gas can be measured and reported as volume under standard reference conditions as recommended by ISO or measured under some other conditions and converted to equivalent volume under standard reference conditions as recommended by ISO, Use the appropriate volume conversion method.
The volume conversion method used at a particular gas volume measurement station may require gas quality data to be determined at other locations. For this standard, the standard reference conditions as recommended by ISO of 288.15 K and 101.325 kPa should be used, as specified in TCVN 12548 (ISO 13443).
NOTE: For gas supplies, other conditions may be used, corresponding to applicable standards or regulations. Methods for converting between different conditions for dry natural gas are outlined in TCVN 12548 (ISO 13443).
The calorific value can be measured at the gas measuring station or at some other representative point and assigned to the gas measuring station. It is also possible to express the amount of gas and calorific value in terms of mass.
This general principle of determination of energy is extended in Article 10 to cases when the amount of gas is calculated by volume or by volume.
To calculate the amount of energy of a gas passing through a gas measuring station over a period, the energy determination methods from Articles 7 to 10 are applied. These methods involve integration at intervals; That integration can be of energy flow, or gas flow over time to obtain the amount of gas, which is then multiplied by the representative calorific value.
The method of integration may depend on contractual agreements or applicable regulations.
The general principles of energy determination in Articles 7 to 10 do not depend on the method of conducting integration. The integrated method affects the uncertainty of the specified energy; these impacts are considered in Article 11.
What are the regulations on the measurement of natural gas volume specified in National Standard TCVN 13781:2023?
According to subsection 6.2, section 6 of National Standard TCVN 13781:2023, the measurement of natural gas volume is specified as follows:
The volumetric flow measurement system of a natural gas measuring station consists of one or more meters. Typically, gas volumetric flow meters under real operating conditions. There are standards for hole plate gauges [TCVN 8113-1 (ISO 5167-1)] and turbine meters [TCVN 8115 (ISO 9951)].
The choice of flow measurement system for a particular application depends at least on the following:
- conditions of flow;
- flow measurement range;
- operating conditions, especially operating pressure;
- acceptable pressure losses;
- required accuracy.
For volumetric flow measurement of natural gas, the instruments primarily used at delivery points 1 to 6 (see 7.1) are outlined in Appendix A.
LawNet