Which indicator on Form 01/GTGT is declaration of interest income from bank deposits in Vietnam?
Which indicator on Form 01/GTGT is declaration of interest income from bank deposits in Vietnam?
Based on the provisions in Article 5 of Circular 219/2013/TT-BTC as follows:
Cases not subject to VAT declaration, calculation, and payment
1. Organizations and individuals receiving monetary compensation (including compensation for land and assets on the land when being recovered following the decision of a competent State authority), bonuses, support money, transfer of emission rights, and other financial receipts.
When a business receives compensation money, bonuses, or support, transfers of emission rights, and other financial receipts, they must record the receipts according to regulations. For businesses disbursing money, they must create payment documents according to the purpose of the transaction.
In cases of compensation in goods or services, the compensating entity must issue invoices and declare, calculate, and pay VAT as for the sale of goods and services; the compensated party declares and deducts according to regulations.
If a business receives money from an organization or individual to provide services like repairs, warranties, promotions, advertising for that entity, it must declare and pay tax according to regulations.
Interest income from bank deposits is regarded as other financial receipts for businesses and is not subject to VAT declaration, calculation, and payment.
Specifically, Official Dispatch 53004/CTHN-TTHT 2024 from the Hanoi Tax Department guides as follows:
If a company has interest income from bank deposits classified as other financial receipts, it is not subject to VAT declaration, calculation, and payment as per Clause 1, Article 5, Circular No. 219/2013/TT-BTC dated December 31, 2013, of the Ministry of Finance. When filling out the VAT return form No. 01/GTGT issued with Circular No. 80/2021/TT-BTC dated September 29, 2021, of the Ministry of Finance, the company should declare this interest income under indicator [32a] on the VAT return.
Input VAT on goods and services used in activities not subject to VAT declaration, calculation, and payment is fully deductible if it meets the input VAT deduction criteria stated in Article 15 of Circular No. 219/2013/TT-BTC dated December 31, 2013, by the Ministry of Finance (amended and supplemented according to Clause 10 Article 1 of Circular No. 26/2015/TT-BTC, and Article 1 of Circular No. 173/2016/TT-BTC).
Thus, interest income from bank deposits is not subject to VAT declaration, calculation, and payment. However, when preparing the VAT return form No. 01/GTGT, the company must declare such interest income under indicator [32a] on the VAT return.
Furthermore, input VAT on goods and services used in activities not subject to VAT declaration, calculation, and payment is fully deductible if the conditions for input VAT deduction are met.
If enterprises incur input VAT on goods, services (including fixed assets) used concurrently for producing, trading goods, and services subject to VAT and not subject to VAT, the deductible VAT amount is determined as per the guidance in point a Clause 9, Article 1 of Circular 26/2015/TT-BTC.

Which indicator on Form 01/GTGT is declaration of interest income from bank deposits in Vietnam? (Image from Internet)
What is Form 01/GTGT VAT return in Vietnam according to Circular 80?
The latest VAT return form is specified in Form 01/GTGT in Appendix 2 issued together with Circular 80/2021/TT-BTC as follows:
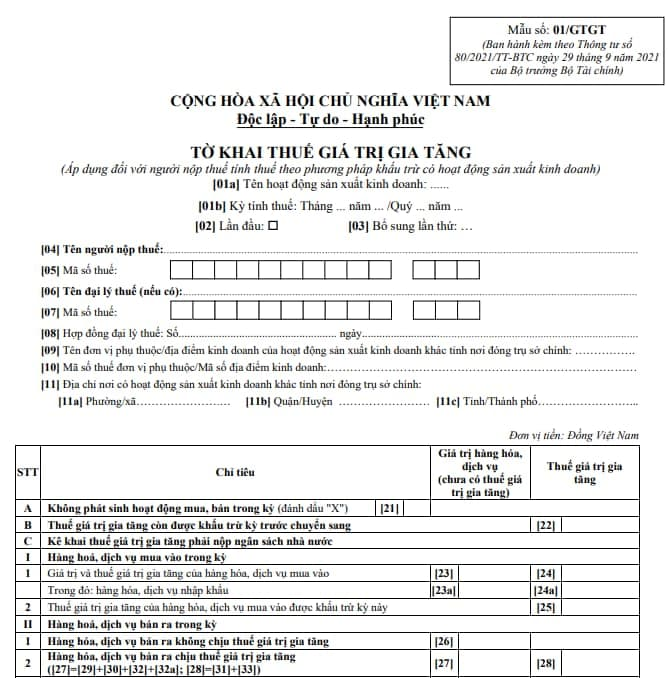
Download the 01/GTGT tax return form: Here
What are the regulations on tax declaration principles in Vietnam?
According to Article 42 of the Law on Tax Administration 2019, the principles of tax declaration and calculation are stipulated as follows:
- Taxpayers must accurately, honestly, and fully declare all contents in the tax return form as prescribed by the Minister of Finance and submit all documents and materials required in the tax dossier to the tax administration.
- Taxpayers self-calculate the amount of tax payable, except where the tax calculation is performed by the tax administration according to the regulations of the Government of Vietnam.
- Taxpayers declare and calculate tax at the local tax office with jurisdiction over where their headquarters are located.
In case the taxpayer centralizes accounts at the headquarters, with dependent units in different provincial administrative units from where the headquarters are located:
Taxpayers declare tax at the headquarters and calculate, allocate the tax obligation to be paid to each locality where the state budget revenue source is entitled.
- For e-commerce business activities, business based on digital platforms, and other services conducted by foreign providers without permanent establishments in Vietnam:
Overseas providers have the obligation to directly or authorize performing taxpayer registration, tax declaration, and tax payment in Vietnam according to the guidelines of the Minister of Finance.
- The principles for declaring and determining taxable prices for related-party transactions are regulated as follows:
+ Declare, determine transaction prices according to the principle of analysis, comparison with independent transactions, and the principle that the substance of activities and transactions determines tax obligations to identify the tax payable as in conditions of transactions between independent parties;
+ Related-party transaction prices are adjusted according to independent transactions to declare and determine the tax payable based on the principle of not reducing taxable income;
+ Taxpayers who are small in scale and low tax risk are exempt from implementing the provisions of point a, point b Clause 5 Article 42 of the Law on Tax Administration 2019 and are allowed to apply simplified mechanisms in declaring and determining related-party transaction prices.
- The principles of tax declaration for the advance pricing agreement mechanism are regulated as follows:
+ The application of the advance pricing agreement mechanism is based on the taxpayer's proposal, the consensus between the tax authority and the taxpayer through unilateral, bilateral and multilateral agreements between the tax authority, the taxpayer and foreign tax authorities and relevant territories;
+ The application of the advance pricing agreement mechanism must be based on the taxpayer’s information and commercial databases with verified legal compliance;
+ The application of the advance pricing agreement mechanism must be approved by the Minister of Finance before implementation;
For bilateral and multilateral agreements involving foreign tax authorities, implementation is according to the provisions of laws on international treaties and agreements.

