What is the Form 01/GTGT on VAT declaration in Vietnam according to Circular 80?
What is the Form 01/GTGT on VAT declaration in Vietnam according to Circular 80?
The latest VAT declaration form is stipulated in Form 01/GTGT in Appendix 2 issued with Circular 80/2021/TT-BTC as follows:
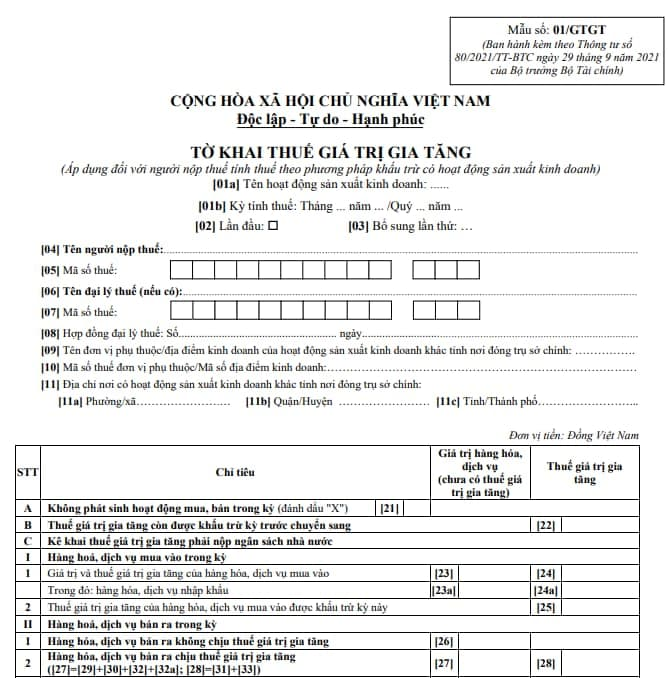
Download the 01/GTGT tax declaration form: Here

What is the Form 01/GTGT on VAT declaration in Vietnam according to Circular 80? (Image from Internet)
What are cases where VAT is declared monthly in Vietnam?
According to Clause 1, Article 8 of Decree 126/2020/ND-CP, it is regulated as follows:
Types of taxes declared monthly, quarterly, annually, on each time of tax obligation arising, and final tax settlement
1. Types of taxes and other state budget revenues managed by tax authorities that must be declared monthly include:
a) Value-added tax, personal income tax. In cases where taxpayers meet the criteria stipulated in Article 9 of this Decree, they can choose to declare quarterly.
b) Special consumption tax.
c) Environmental protection tax.
d) Resource tax, except resource tax specified at point e of this clause.
...
Value-added tax is a type of tax that organizations and individuals declare monthly; however, in cases where taxpayers meet the conditions to declare tax quarterly, they can choose either monthly or quarterly tax declaration.
What are principles of tax declaration in Vietnam?
According to the provisions of Article 42 of the Tax Administration Law 2019 on the principles of tax declaration and tax calculation, it is regulated as follows:
- Taxpayers must accurately, honestly, and fully declare the contents in the tax declaration forms as prescribed by the Minister of Finance and submit all documents and papers required in the tax declaration dossier to the tax authorities.
- Taxpayers should self-calculate the amount of tax payable, except in cases where the tax is calculated by the tax authorities as prescribed by the Government of Vietnam.
- Taxpayers declare tax and calculate tax at the local tax authority with jurisdiction where their headquarters are located.
In the case where the taxpayer centralizes accounting at the main office and has dependent units in administrative units at different provincial levels from where the main office is located, then:
Taxpayers declare tax at the main office and calculate tax, allocate the tax obligation payable to each locality where the revenue resource is enjoyed by the state budget.
- For e-commerce business activities, business based on digital platforms, and other services performed by overseas suppliers without a permanent establishment in Vietnam:
The overseas supplier is required to directly or authorize the implementation of taxpayer registration, tax declaration, and tax payment in Vietnam in accordance with the regulations of the Minister of Finance.
- The principles of declaration, and determination of tax pricing in related-party transactions are specified as follows:
+ Declare, and determine the price of related-party transactions based on the principle of analysis, comparison with independent transactions, and the principle of substance over form in determining tax obligations as if it were an independent transaction;
+ Adjust the price of related-party transactions to independent transactions to declare, and determine the amount of tax payable based on the principle that it does not reduce taxable income;
+ Small-scale taxpayers with low tax risk are exempt from the provisions in points a and b, Clause 5, Article 42 of the Tax Administration Law 2019 and apply simplified mechanisms in declaring and determining transfer pricing.
- The principles of tax declaration for advance pricing agreement mechanisms are defined as follows:
+ The application of advance pricing agreement mechanisms is based on the taxpayer’s proposal, agreement between the tax authority and the taxpayer through unilateral, bilateral, and multilateral agreements among tax authorities, taxpayers, and relevant foreign tax authorities;
+ The application of advance pricing agreement mechanisms must be based on the taxpayer’s information, commercial databases ensuring legal compliance;
+ The application of advance pricing agreement mechanisms must be approved by the Minister of Finance before implementation;
For bilateral and multilateral agreements involving foreign tax authorities, implementation is subject to international treaties and international agreements.

