What are rules for placing tonal marks according to Vietnamese Language curriculum? When do students in Vietnam study tonal marks according to Vietnamese Language curriculum?
What are rules for placing tonal marks according to Vietnamese Language curriculum?
Tonal marks are a crucial feature of Vietnamese, helping to differentiate the meanings of words. Correctly placing tonal marks is essential for effective communication.
There are 5 main tonal marks and one unmarked tone:
Thanh ngang: This is the base tone without any mark, typically considered the root tone for comparison with others.
Thanh huyền: The grave mark (`) lowers the pitch of the syllable. For example: bà, nhà.
Thanh hỏi: The question mark (?) raises and then lowers the pitch of the syllable. For example: mẹ, bé.
Thanh ngã: The tilde (~) raises and then sharply lowers the pitch of the syllable. For example: ngã, lá.
Thanh sắc: The acute mark (´) raises the pitch of the syllable. For example: cá, gà.
Thanh nặng: The dot mark (.) lengthens and lowers the pitch of the syllable. For example: mật, mật ong.
Below are the basic rules for placing tonal marks:
| * Placement of tonal marks Single vowels: The tonal mark is usually placed directly on the vowel. For example: bàn, ghế, nhà, cây. Compound vowels: ia, ua, ưa: The tonal mark is usually placed on the first letter (i, u). For example: mía, mùa, lửa. iê, yê, uô, uơ: The tonal mark is usually placed on the second letter (ê, ơ). For example: biển, thuyền, buồm, vườn. Syllables with ending consonants: The tonal mark is usually placed on the final vowel. For example: bát, sách, bút. * Special Cases Compound words: The tonal mark is usually placed according to the root word. For example: nhà cửa (cửa is the root of cửa), sách vở (vở is the root of vở). Reduplicatives: The tonal marks are usually placed similarly in each syllable. For example: lung linh, xinh xắn. * Notes When Placing tonal marks Listening and Reading: The best way to learn how to place tonal marks is by listening to others speak and by reading many books and newspapers. Using Dictionaries: When uncertain about the tonal mark of a word, consult a dictionary. Frequent Practice: Write many exercises on placing tonal marks to hone the skill. |
Illustrative Example:
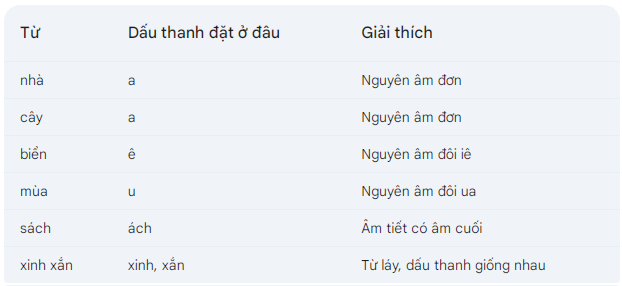
*Note: These are only basic rules. Vietnamese has many exceptions, so continuous learning and practice are crucial.

What are rules for placing tonal marks according to Vietnamese Language curriculum? When do students in Vietnam study tonal marks according to Vietnamese Language curriculum? (Image from the Internet)
When do students in Vietnam study tonal marks according to Vietnamese Language curriculum?
Pursuant to Section IV of the General Education Program in Literature, issued along with Circular 32/2018/TT-BGDDT, the specific requirements for Vietnamese language for Grade 1 in writing are as follows:
WRITING
WRITING TECHNIQUES
- Know how to sit correctly while writing: sit with a straight back; place both feet flat on the floor; one hand should rest on the corner of the notebook, the other hand should hold the pen; do not lean the chest on the edge of the desk; maintain a distance of about 25cm between the eyes and the notebook; hold the pen with three fingers (thumb, index finger, and middle finger).
- Write correctly in lowercase letters, numbers (from 0 to 9); know how to write uppercase letters.
- Place tonal marks in the correct position. Follow the rules for writing words that begin with c, k, g, gh, ng, ngh.
- Write a dictated poem or prose passage correctly with a length of about 30-35 characters in the forms of look-and-write (copying) and listen-and-write. Writing speed is about 30-35 characters in 15 minutes.
SENTENCE AND SHORT PARAGRAPH WRITING
Writing Process
Able to initially answer questions like: Who are you writing about? What are you writing about?
Writing Practice
- Fill in the missing information, write the answer, write a sentence under the picture that fits the content of the story read or heard.
- Fill in the missing information, write a sentence about the appearance or activities of characters under the picture in the story learned based on suggestions.
- Fill in the missing information, write an answer or rewrite a statement to introduce oneself based on suggestions.
Thus, according to the above regulations, one of the requirements for Vietnamese language for Grade 1 is to place tonal marks in the correct position.
What is the age of Grade 1 students in Vietnam?
According to Article 33 of the Primary School Regulation issued in conjunction with Circular 28/2020/TT-BGDDT on the age of primary school students:
Age of primary school students
1. The age for entering Grade 1 is 06 years old and is calculated by the year. Children with disabilities, those with physical or intellectual development delays, children in areas with particularly difficult socio-economic conditions, ethnic minority children, orphaned children without a caretaker, children returning from abroad, and children of foreigners studying or working in Vietnam may start Grade 1 at an older age but not more than 03 years older than the prescribed age. In case a child enters Grade 1 more than 03 years older than the prescribed age, it will be decided by the head of the Department of Education and Training.
2. Primary school students can be older than the prescribed age in case of grade repetition, children in areas with particularly difficult socio-economic conditions, ethnic minority children, children with disabilities, children with physical or intellectual development delays, orphaned children without a caretaker, children returning from abroad, and other cases as stipulated by law.
Thus, according to the above regulation, children 06 years old will enter Grade 1 (age calculated by year). However, the age for starting Grade 1 can be higher than 06 years but no more than 03 years for the following children:
- Children with disabilities, physical or intellectual development delays.
- Children in areas with particularly difficult socio-economic conditions.
- Ethnic minority children, orphaned children without a caretaker.
- Children returning from abroad, children of foreigners studying or working in Vietnam.
The case of children entering Grade 1 more than 03 years older than the prescribed age for Grade 1 will be decided by the head of the Department of Education and Training.

