What are the 1st-semester question papers and answers for 12th-grade History in Vietnam? What are the required specific competencies in the 12th-grade History curriculum?
What are the 1st-semester question papers and answers for 12th-grade History in Vietnam?
Students may refer to the following 1st-semester question papers and answers for 12th-grade History in Vietnam:
|
1st-semester question papers and answers for 12th-grade History
A. MULTIPLE CHOICE SECTION (7 points)
Question 1: Which of the following countries was not present at the Yalta Conference (February 1945)?
A. France.
B. The USA.
C. The UK.
D. The Soviet Union.
Question 2: What was the foremost urgent issue for the Allies at the Yalta Conference (February 1945)?
A. Reorganizing the world after the war.
B. Dividing the spoils of victory among the winning countries.
C. Resolving the issues of defeated fascist countries.
D. Quickly defeating the fascist countries completely.
Question 3: On what basis did the people of the Soviet Union quickly succeed in the 5-year economic recovery plan (1946 – 1950)?
A. Scientific and technological advancements.
B. Spirit of self-reliance and resilience.
C. Assistance from Eastern European countries.
D. Abundance of natural resources.
Question 4: What is the significance of the Soviet Union launching an artificial satellite in 1957?
A. It was the first country in the world to successfully launch an artificial satellite.
B. It marked the development of Soviet scientific and technological prowess.
C. It demonstrated the superiority of socialist policies compared to capitalist policies.
D. It heralded the start of the human space exploration era.
Question 5: Arrange the following events in the correct chronological order:
1. The founding of the People's Republic of China.
2. Two states formed on the Korean Peninsula.
3. Civil war between the Kuomintang and the Communist Party in China.
4. China regained control of Hong Kong and Macau.
A. 4, 2, 3, 1.
B. 3, 2, 4, 1.
C. 3, 1, 2, 4.
D. 3, 2, 1, 4.
Question 6: When did the trend of globalization start to appear?
A. Early 1980s.
B. Mid-1980s.
C. Late 1980s.
D. Early 1990s.
Question 7: Which countries participated in founding ASEAN?
A. Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore, Thailand, Philippines.
B. Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore, Thailand, Brunei.
C. Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore, Thailand, Cambodia.
D. Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore, Thailand, Myanmar.
Question 8: Who was the 10th member of ASEAN?
A. Laos.
B. Myanmar.
C. Cambodia.
D. East Timor.
Question 9: What was the primary reason for the rapid development of the US economy after World War II?
A. Adoption of scientific and technological achievements.
B. Selling weapons to warring countries.
C. Abundance of natural resources.
D. Capital and production concentration levels.
Question 10: What was the purpose of Japan signing the US-Japan security treaty?
A. The US wanted to make Japan a military base.
B. Japan hoped to utilize US capital and technology for economic development.
C. Creating a balance between the US and Japan.
D. Forming a US-Japan alliance against socialist countries.
Question 11: What is another name for the second scientific and technical revolution from the 1970s?
A. Scientific-technological revolution.
B. Industrial revolution.
C. Green revolution.
D. Intellectual revolution.
Question 12: What event marked the end of the Cold War?
A. Helsinki Accords were signed in 1975.
B. The US and USSR signed offensive weapons reduction treaties in the 1970s.
C. The US failed in the Vietnam War in 1975.
D. US and Soviet leaders met at Malta in 1989.
Question 13: The Communist Party's founding conference approved brief political theses and strategies drafted by Nguyen Ai Quoc, collectively known as
A. The Communist Party Manifesto.
B. The Political Thesis of the Communist Party.
C. The First Political Platform of the Communist Party.
D. The All-People Resistance Call of the Communist Party.
Question 14: What has been the strategic line of the Vietnamese revolution since the Communist Party's founding in 1930?
A. National independence linked with socialism.
B. National liberation and people's prosperity and happiness.
C. Rich people, strong country, fair, democratic, and civilized society.
D. National liberation and liberation of all classes from servitude.
Question 15: In March 1938, the Communist Party renamed the Indochinese Anti-Imperialist United Front to which front?
A. Indochinese Anti-Imperialist Front.
B. Indochinese Democratic Front.
C. Vietnam Independent Alliance Front.
D. Indochinese Anti-Imperialist United Front.
Question 16: The mass organizations within the Viet Minh Front were known as
A. Democratic associations.
B. Anti-Imperialist associations.
C. National salvation associations.
D. Lien Viet associations.
Question 17: From late September 1940 to March 1945, the Vietnamese people lived under the colonial rule of
A. France and the USA.
B. The UK and France.
C. Japan and France.
D. The Republic of China and France.
Question 18: The slogan "Expel the Japanese fascists" replaced "Expel the French and Japanese" in which document?
A. Communist Party's Central Executive Committee meeting in November 1939.
B. Communist Party's Central Executive Committee meeting in May 1941.
C. Directive "The Japanese-French Conflict and Our Actions" on March 12, 1945.
D. National Conference of the Communist Party on August 14-15, 1945.
Question 19: Which organization is considered the forerunner of the Vietnam People's Army?
A. National Salvation Army Platoon I.
B. Vietnam Liberation Army.
C. Vietnam National Salvation Army.
D. Vietnam Propaganda Liberation Army Unit.
Question 20: Which front played a direct role in preparing for the August Revolution of 1945?
A. Indochinese Anti-Imperialist United Front.
B. Indochinese Democratic Front.
C. Viet Minh Front.
D. Lien Viet Front.
Question 21: During the National Salvation Movement against the Japanese in 1945, the movement "Breaking graineries to solve famine" mainly occurred in the provinces
A. Northern Region.
B. Central Region.
C. Northern and North Central Regions.
D. Central and Southern Regions.
Question 22: What did we concede to France in the provisional agreement signed on September 14, 1946?
A. Economic and political interests.
B. Economic and cultural interests.
C. Economic, political, and cultural interests.
D. Economic and financial interests.
Question 23: To address the bare state of the budget for the Government of Vietnam after the August Revolution of 1945, the people responded to the movement?
A. "Independence Fund".
B. "Unity Day".
C. "Increase Production".
D. "Not a Single Inch of Land Left Unused".
Question 24: Who was the main enemy of the Vietnamese people after the August Revolution of 1945?
A. Republic of China.
B. Japanese fascists.
C. The USA and British colonists.
D. French colonists.
Question 25: What lesson was learned from the National Assembly election on January 6, 1946, of the Democratic Republic of Vietnam after the August Revolution?
A. Promoting the people's leadership in the country.
B. Understanding how to isolate and divide the enemy.
C. Being flexible in the strategy of struggle.
D. Compromising with limits and principles.
B. SCRIPT SECTION (3 points)
Question 1. (3 points) Discuss the common reasons for the economic development of the USA – Western Europe – Japan after World War II? Lessons learned for Vietnam from this development?
|
ANSWERS
A. MULTIPLE CHOICE SECTION
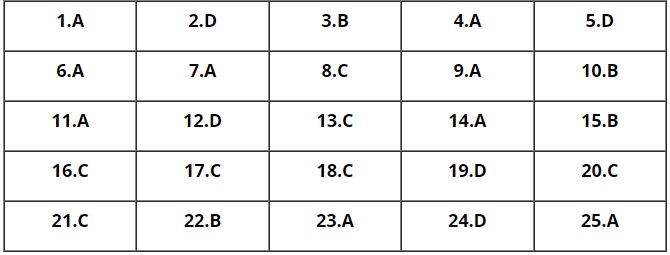
B. SCRIPT SECTION
Question 1
(1) Common reasons leading to the economic development of the USA - Western Europe - Japan:
- Relying on scientific and technological achievements, adjusting production structures, improving technology, increasing productivity, reducing costs.
- High levels of capital concentration and production concentration enabled significant production and competition.
- Effective state regulatory roles.
(2) Lessons for Vietnam:
- Learn from and apply scientific and technological achievements in production, and learn management experiences from developed countries.
- The state needs to implement reasonable policies and promptly adjust to match global and domestic changes.
- Enhance the economy's competitiveness by improving product quality and updating designs; expand the market economy to boost trade and exchange among countries.
Note: Information is for reference only!

What are the 1st-semester question papers and answers for 12th-grade History in Vietnam? What are the required specific competencies in the 12th-grade History curriculum? (Image from the Internet)
What are the objectives of the History curricula in Vietnam?
According to the general education program for History issued with Circular 32/2018/TT-BGDDT, the specific objectives of the History curricula in Vietnam are as follows:
- The history curriculum helps students develop historical competence, manifested as scientific competence, which was formed at the secondary education level; it contributes to educating the national spirit, patriotism, traditional values, and the quintessence of human culture, and qualities and competencies of Vietnamese citizens and global citizens consistent with the modern era's development trend;
- The history subject helps students understand the role and characteristics of historical science and the connection between history and other scientific fields and professions, forming a basis for students to orient their future careers.
What are the required specific competencies in the 12th-grade History curriculum in Vietnam?
Under Section 4, the general education program for History at the upper secondary level issued with Circular 32/2018/TT-BGDDT (as amended by Article 2 Circular 13/2022/TT-BGDDT), the required specific competencies in the 12th-grade History curriculum in Vietnam are as follows:
The history curriculum helps students develop historical competence on the foundation of basic and advanced knowledge of world history, regional history, and Vietnam's history through thematic and specialized topics related to political, economic, social, cultural, and civilization history. The components of historical competence include: exploring history; understanding and historical reasoning; and applying learned knowledge and skills. Specific expressions of historical competence are presented as follows:
- Exploring history:
+ Identifying types of historical documents; understanding, exploiting, and utilizing historical documents in learning.
+ Recreating and presenting the progression of events, figures, and historical processes verbally or in writing, from simple to complex; determining historical events within specific spatial and temporal contexts.
- Understanding and historical reasoning:
+ Explaining origins and developments of historical events, from simple to complex; identifying historical progression in chronological and synchronous contexts; comparing similarities and differences between historical events; rationalizing causal relationships in historical progress.
+ Offering personal opinions, comments, and assessments on historical events, figures, and processes based on historical understanding and reasoning; understanding the continuity and change of history; contemplating various perspectives in examining, evaluating, or seeking answers to a historical event, figure, or process.
- Applying learned knowledge and skills:
Drawing historical lessons and applying historical knowledge to explain real-life issues; on this foundation, having the capability to independently comprehend historical issues, develop creative capabilities, access, and process information from various sources, and have the consciousness and ability to self-learn history throughout life.



