What are the guidelines for proving an isosceles triangle for 7th-grade students in Vietnam? What are the cases of the adjustment of the assessment levels for continuing education students at the lower secondary level in Vietnam?
What are the guidelines for proving an isosceles triangle for 7th-grade students in Vietnam?
In geometry, an isosceles triangle is a special type of triangle with two equal sides, and the angles opposite these sides are also equal.
Students can refer to the following simple way to prove an isosceles triangle:
| I. THEORY 1. Definition of an Isosceles Triangle An isosceles triangle is a triangle with two equal sides, referred to as the legs. The vertex of an isosceles triangle is the intersection of the two legs. The angle at the vertex is called the vertex angle, and the remaining two angles are called base angles. 2. Properties of an Isosceles Triangle An isosceles triangle has the following four properties: Property 1: In an isosceles triangle, the base angles are equal. Property 2: A triangle with two equal angles is an isosceles triangle. Property 3: In an isosceles triangle, the perpendicular bisector of the base is also the angle bisector, median, and altitude of that triangle. Property 4: In a triangle, if a median is also a perpendicular bisector, then the triangle is an isosceles triangle. 3. Signs to Recognize an Isosceles Triangle An isosceles triangle can be recognized by 2 signs: Sign 1: If a triangle has two equal sides, it is an isosceles triangle. Sign 2: If a triangle has two equal angles, it is an isosceles triangle. 4. Area of an Isosceles Triangle The area of an isosceles triangle is equal to the product of the height from the vertex to the base, divided by 2. - Formula for the area of an isosceles triangle: S = (a x h)/2 Where: a: Length of the base of the isosceles triangle (the base is one of the three sides of the triangle) h: Height of the triangle (the height is the line segment dropped from the vertex to the base). II. METHODS TO PROVE AN ISOSCELES TRIANGLE 1. Method of Solution To identify and prove a triangle is isosceles, we use one of the following two methods: Method 1: Prove that the triangle has two equal sides. Then the triangle is isosceles at the intersection of those two sides; Method 2: Prove that the triangle has two equal angles. Then the triangle is isosceles at the remaining vertex. Note: When proving a triangle is isosceles, specify which vertex isosceles. For example, ∆ABC is isosceles at A, ∆MNP is isosceles at N,... 2. Illustrative Examples Example 1: In triangle ABC, Δ ABD = Δ ACD. Prove that triangle ABC is isosceles. 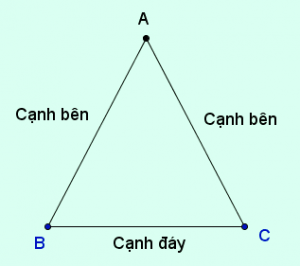 + Proof by Method 1: According to the problem, we have: Δ ABD = Δ ACD => AB = AC => Triangle ABC is isosceles at A + Proof by Method 2: According to the problem, we have: ∆ ABD = ∆ ACD => Angle B = C => Triangle ABC is isosceles at A Example 2: Given triangle ABC and M is the midpoint of segment BC. a) Suppose AM is perpendicular to BC. Prove that triangle ABC is isosceles at A. b) Suppose AM is the bisector of angle BAC. Prove that triangle ABC is isosceles at A. Answer Hint a) 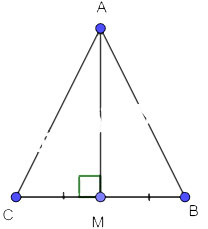 Consider two right triangles AMC and AMB with: AM in common BM=CM (given) => ∆ AMB = ∆ AMC (SAS) => AM=BM (two corresponding sides) => Triangle ABM is isosceles at A b) 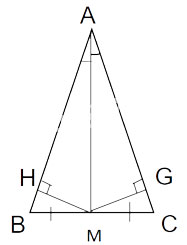 Draw MH perpendicular to AB (H belongs to AB) MG perpendicular to AC (G belongs to AC) Consider two right triangles AHM and AGC with: Angle HAM = Angle GAM AM in common => ∆ AHM = ∆ AGC (hypotenuse – acute angle) => HM=GM (two corresponding sides) Consider two right triangles BHM and CGM with: BM=CM (given) MH=MG (proved above) => ∆ BHM = ∆ CGM (hypotenuse – leg) => Angle BMH = Angle CMH (two corresponding angles) => Triangle ABC is isosceles at A. |
Note: The content is for reference only.

What are the guidelines for proving an isosceles triangle for 7th-grade students in Vietnam? What are the cases of the adjustment of the assessment levels for continuing education students at the lower secondary level in Vietnam? (Image from the Internet)
What are the cases of the adjustment of the assessment levels for continuing education students at the lower secondary level in Vietnam?
Under Clause 3, Article 9 of Circular 43/2021/TT-BGDDT, the adjustment of the assessment levels for continuing education students at the lower secondary level is regulated as follows:
Assessment of students' academic outcomes
...
3. Adjustment the level of assessment of academic outcomes
If the assessment level of the academic outcomes of the semester or the whole school year is lower by 02 (two) levels or more compared to the assessment level specified at point a, point b, clause 2 of this Article only due to the assessment result of only one (one) subject, the assessment of the academic outcomes of that semester and the whole school year will be adjusted to the adjacent level.
Thus, if the assessment level of the academic outcomes of the semester or the whole school year is lower by 02 (two) levels or more compared to the specified assessment level only due to the assessment result of only one (one) subject, the assessment of the academic outcomes of continuing education students at the lower secondary level will be adjusted to the adjacent level.
What are the regulations on the assessment of the academic outcomes in the whole school year of continuing education students at the lower secondary level in Vietnam?
Under Clause 2, Article 9 of Circular 43/2021/TT-BGDDT, the academic outcomes in the whole school year of continuing education students at the lower secondary level in Vietnam are assessed by 04 levels:
- Good: All subjects have semester average scores and whole year average scores of 6.5 or higher, of which at least 05 subjects have semester average scores and whole year average scores of 8.0 or higher.
- Fair: All subjects have semester average scores and whole year average scores of 5.0 or higher, of which at least 05 subjects have semester average scores and whole year average scores of 6.5 or higher.
- Passed: At least 05 subjects (five) have scores of 5.0 or higher, no subjects have semester average scores or whole year average scores of below 3.5.
- Failed: The remaining cases.

