Latest periodic table of chemical elements and Guide on how to read it
Latest periodic table of chemical elements and Guide on how to read it
According to the regulations in Circular 38/2021/TT-BGDDT, the periodic table of chemical elements is one of the minimum teaching equipment for lower secondary education.
The structure of the periodic table of chemical elements consists of element boxes, periods, and groups. In the periodic table, the elements are arranged in ascending order of nuclear charge as follows:
Sample Periodic Table of Chemical Elements 1
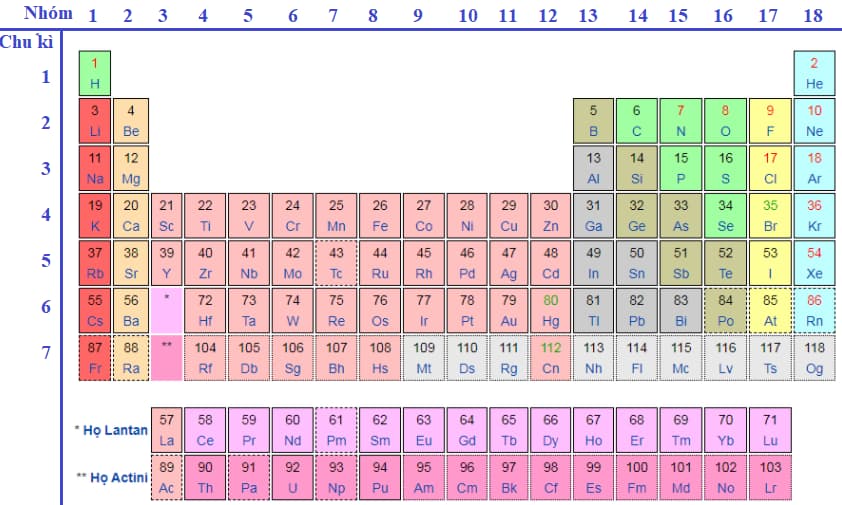
Sample Periodic Table of Chemical Elements 2
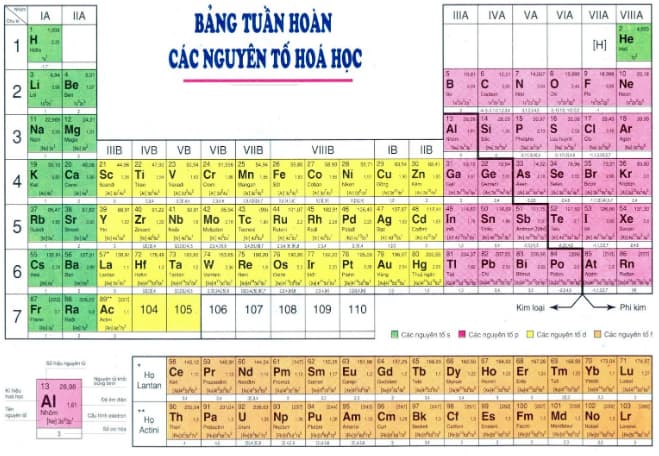
Sample Periodic Table of Chemical Elements 3
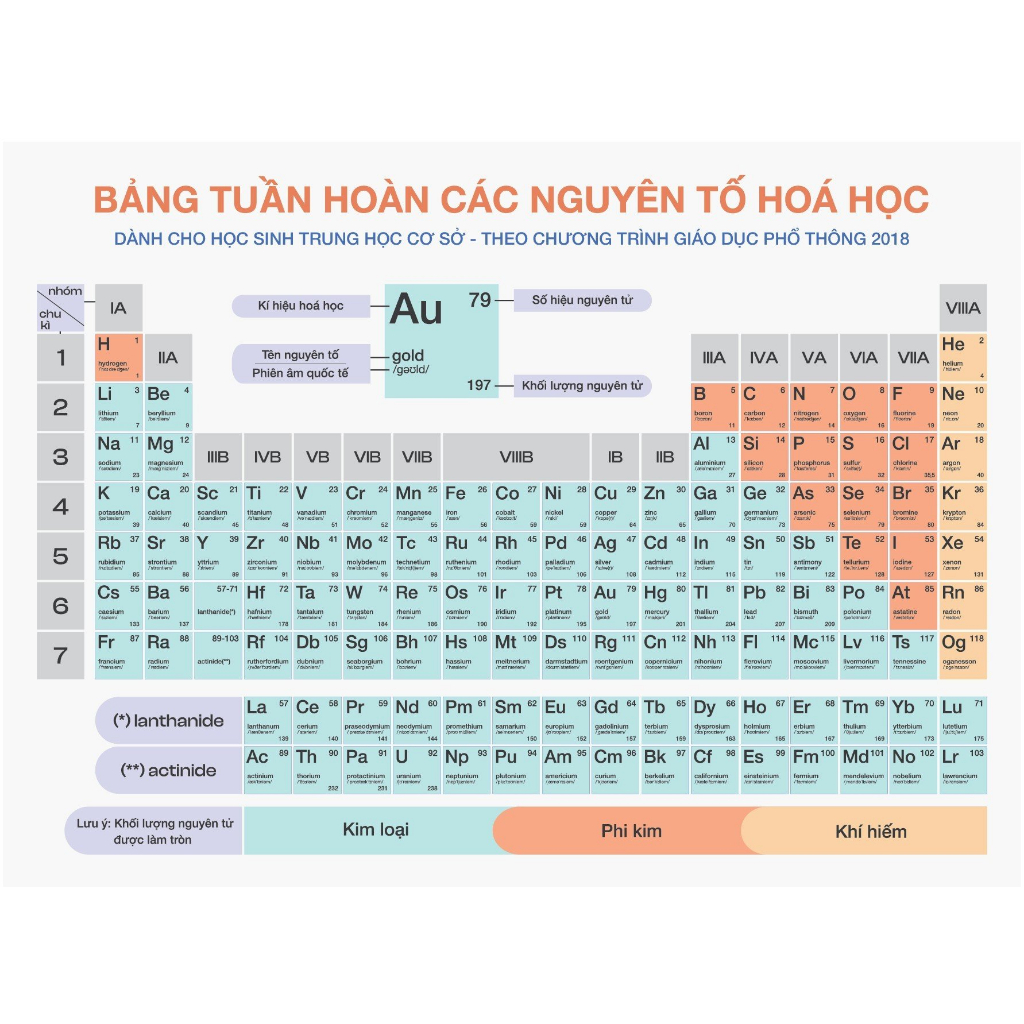
To read the periodic table of chemical elements, one needs to understand the details of an element box in the periodic table:
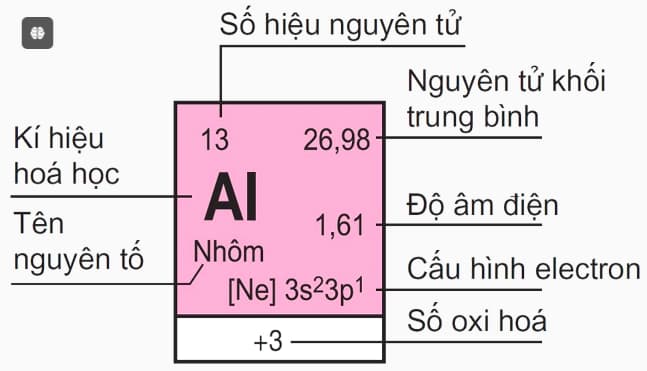
The terms in an element box in the periodic table of chemical elements are as follows:
- Element Name: Consisting of only one type of atom, distinguished based on the atomic number.
- Chemical Symbol: The shorthand name of the chemical element, consisting of 1 or 2 Latin letters. The first letter is usually capitalized.
- Atomic Number: Also known as the proton number of the chemical element. The atomic number equals the number of electrons in a neutral atom. Specifically, the atomic number uniquely identifies a chemical element.
- Average Atomic Mass: Most chemical elements are mixtures of different isotopes with specific atom percentage ratios. Hence, the atomic mass of these elements is calculated as the average atomic mass of the isotope mixture based on the percentage ratio of corresponding atoms.
- Electron Configuration: The distribution of electrons in different energy states in the atomic shell or places where they are present.
- Electronegativity: The ability to attract electrons during the formation of a chemical bond. Specifically, the higher the electronegativity of an element, the stronger the non-metallic property, and vice versa.
- Oxidation Number: A number used for one or a group of atoms to determine the number of electrons exchanged during a reaction.
Note: The content is for reference purposes only!

Latest periodic table of chemical elements and Guide on how to read it (Image from the Internet)
What are specifications for chemistry subject-based classrooms in Vietnam?
Based on Article 5 of the Regulations on subject-based classroom of general educational institutions promulgated together with Circular 14/2020/TT-BGDDT:
Specifications for Subject-based Classrooms
1. The minimum working area of subject-based classrooms is calculated based on the minimum working area for one student.
...
c) Upper secondary schools:
For subject-based classrooms in Physics, Chemistry, Biology, Informatics, Foreign Languages, and Multi-function rooms, the minimum working area for one student is 2.00m2, and each classroom has an area not less than 60m2;
For subject-based classrooms in Technology, Music, and Art, the minimum working area for one student is 2.45m2, and each classroom has an area not less than 60m2;
Subject-based classrooms for Social Sciences (used for subjects such as History, Geography, Economic and Legal Education) have a minimum working area for one student of 1.50m2, and each classroom has an area not less than 60m2.
d) Schools with multiple education levels should determine the minimum working area for subject-based classrooms based on the regulations in points a, b, and c, clause 1 of this Article.
2. Dimensions of subject-based classrooms:
a) The width of subject-based classrooms (measured perpendicular to the hallway adjacent to the subject-based classroom): For primary level, not less than 5.70m; for secondary and high school levels, not less than 7.20m;
b) The length of subject-based classrooms (measured along the hallway adjacent to the subject-based classroom) should not exceed 2 times the width;
c) The height of subject-based classrooms (measured from the floor to the ceiling) should be from 3.30m or higher. In cases using a false floor to arrange technical systems, the height from the floor to the ceiling should be no less than 2.80m.
3. Subject-based classrooms for Natural Sciences, Technology, Physics, Chemistry, Biology, and some subjects with extensive practical equipment must have a preparation room. The preparation room should be adjacent, with a connecting door to the subject-based classroom and an area from 12m2 to 27m2.
Thus, the specifications for chemistry subject-based classrooms are as follows:
The minimum working area for subject-based classrooms calculated on a per-student basis is 2.00m2, and each room's area is not less than 60m2;
The dimensions of the subject-based classrooms should ensure:
- The width of the subject-based classroom (measured perpendicular to the hallway adjacent to the subject-based classroom): For primary level, not less than 5.70m; for secondary and high school levels, not less than 7.20m;
- The length of the subject-based classroom (measured along the hallway adjacent to the subject-based classroom) should not exceed 2 times the width;
- The height of the subject-based classroom (measured from the floor to the ceiling) should be from 3.30m or higher. In cases using a false floor to arrange technical systems, the height from the floor to the ceiling should be no less than 2.80m.
- A preparation room should be adjacent, with a connecting door to the subject-based classroom, and an area from 12m2 to 27m2.
What are regulations on water supply and drainage system of the chemistry subject-based classroom in Vietnam?
Based on Article 11 of the Regulations on subject-based classrooms of general educational institutions promulgated together with Circular 14/2020/TT-BGDDT:
The water supply and drainage system in the chemistry subject-based classroom should be independently arranged, embedded in the walls, floor, or within technical boxes. The valves placed in the technical boxes should have inspection doors for convenient management and repair.
The chemistry subject-based classroom should be equipped with a sink system, water faucets, and water supply and drainage lines attached to the laboratory, practical tables.

