Which petroleum products are subject to the environmental protection tax in Vietnam?
Which petroleum products are subject to the environmental protection tax in Vietnam?
According to Article 3 of the Law on Environmental Protection Tax 2010, it is stipulated as follows:
Taxable objects
1. Gasoline, oil, lubricants, including:
a) Gasoline, excluding ethanol;
b) Jet fuel;
c) Diesel oil;
d) Kerosene;
dd) Mazut oil;
e) Lubricating oil;
g) Lubricating grease.
2. Coal, including:
a) Brown coal;
b) Anthracite coal;
c) Fat coal;
d) Other types of coal.
3. Hydro-chloro-fluoro-carbon (HCFC) solutions.
4. Nylon bags subject to tax.
5. Herbicides restricted from use.
6. Termiticides restricted from use.
7. Wood preservatives restricted from use.
8. Warehouse disinfectants restricted from use.
9. If it is deemed necessary to supplement other taxable objects to suit each period, the Standing Committee of the National Assembly shall consider and prescribe them.
the Government of Vietnam stipulates the details of this Article.
Currently, the types of oils subject to environmental protection tax are Gasoline, excluding ethanol; Diesel oil; Kerosene; Mazut oil; Lubricating oil.
How long is the duration of 50% reduction in the environmental protection tax on petroleum products in Vietnam?
Based on Resolution 42/2023/UBTVQH15 regarding the environmental protection tax rates on gasoline, oil, and lubricants.
To be specific:
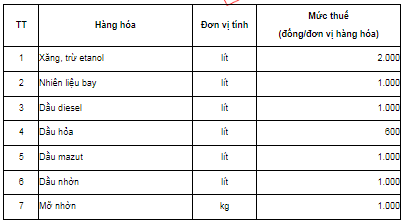
- Gasoline - excluding ethanol: 2,000 VND/liter.- Jet fuel, diesel oil, mazut oil, lubricating oil: 1,000 VND/liter.- Lubricating grease: 1,000 VND/kg.- Kerosene: 600 VND/liter.
*Note: The environmental protection tax rates on gasoline, oil, and lubricants from January 1, 2025, will continue to be applied according to the provisions at Section I, Clause 1, Article 1 of Resolution 579/2018/UBTVQH14 dated September 26, 2018, by the Standing Committee of the National Assembly on the Environmental Protection Tax Schedule.

Which petroleum products are subject to the environmental protection tax in Vietnam? (Image from the Internet)
How to determine the tax base for petroleum-based blended fuel in Vietnam?
According to Article 6 of the Law on Environmental Protection Tax 2010, it is stipulated as follows:
Tax base
1. The tax base for environmental protection is the quantity of taxable goods and the absolute tax rate.
2. The quantity of taxable goods is specified as follows:
a) For domestically produced goods, the quantity of taxable goods is the quantity of goods produced and sold, exchanged, internally consumed, donated;
b) For imported goods, the quantity of taxable goods is the quantity of imported goods.
Referring to Article 5 of Circular 152/2011/TT-BTC, it specifically guides that if the goods are petroleum-based blended fuel, the tax base is determined as follows:
- For goods being petroleum-based blended fuel containing fossil fuel-based gasoline, oil, lubricants, and biofuel, the quantity of taxable goods in the period is the quantity of fossil fuel-based gasoline, oil, lubricants in the quantity of blended fuel imported or produced and sold, exchanged, donated, put into internal consumption converted into the unit of measurement prescribed for the corresponding taxable goods.
The determination is as follows:
The quantity of taxable fossil fuel-based gasoline, oil, lubricants = Quantity of blended fuel imported, produced and sold, consumed, exchanged, donated x Percentage (%) of fossil fuel-based gasoline, oil, lubricants in the blended fuel.
Based on the technical standards for processing blended fuel approved by the competent authority (including the case of changing the percentage (%) of fossil fuel-based gasoline, oil, lubricants in the blended fuel), the taxpayer calculates, declares, and pays the environmental protection tax for the quantity of fossil fuel-based gasoline, oil, lubricants.
At the same time, they are responsible for notifying the tax authority of the percentage (%) of fossil fuel-based gasoline, oil, lubricants in blended fuel and submitting the declaration along with the tax return of the month following the month in which the blended fuel start being sold (or the percentage changes).
Is the environmental protection tax refundable for blended fuel temporarily imported to introduce new products in Vietnam?
According to Article 8 of Circular 152/2011/TT-BTC, the tax refund is specified as follows:
Tax refund
Taxpayers who have paid the environmental protection tax are entitled to a tax refund in certain cases as follows:
1. Imported goods still in storage, warehousing at the port, and under the supervision of the Customs office for re-export abroad.
2. Imported goods for delivery, sale to foreign countries through agents in Vietnam; gasoline, oil sold to foreign vehicles on the Vietnamese port route or Vietnamese vehicles on international transport routes as prescribed by law.
3. Goods temporarily imported for re-export under temporary import for re-export business are entitled to a refund of the paid environmental protection tax corresponding to the quantity of re-exported goods.
4. Imported goods re-exported by the importer (including returned goods) abroad are entitled to a refund of the paid environmental protection tax for the re-exported goods.
5. Goods temporarily imported for fairs, exhibitions, and product introductions are entitled to a refund of the paid environmental protection tax corresponding to the quantity of goods re-exported abroad.
The environmental protection tax refund under this Article is only applicable to actually exported goods. Procedures, documents, order, and authority to handle environmental protection tax refunds for exported goods are performed according to regulations similar to the handling of import tax refunds under the law on export and import tax.
Accordingly, under the above regulation, blended fuel temporarily imported to introduce new products that have paid environmental protection tax is eligible for a VAT refund.

