What is the record form for fixed asset handover in Vietnam according to Circular 200?
What is the record form for fixed asset handover in Vietnam according to Circular 200?
The template of the record for fixed asset handover according to Circular 200/2014/TT-BTC is applicable to:
- Enterprises of all sectors and all types of economic components.
- Small and medium enterprises implementing accounting according to the accounting regime applicable for small and medium enterprises may utilize the provisions of Circular 200/2014/TT-BTC to suit their business characteristics and management needs.
The template for the fixed asset handover record is form number 01-TSCD issued along with Circular 200/2014/TT-BTC.
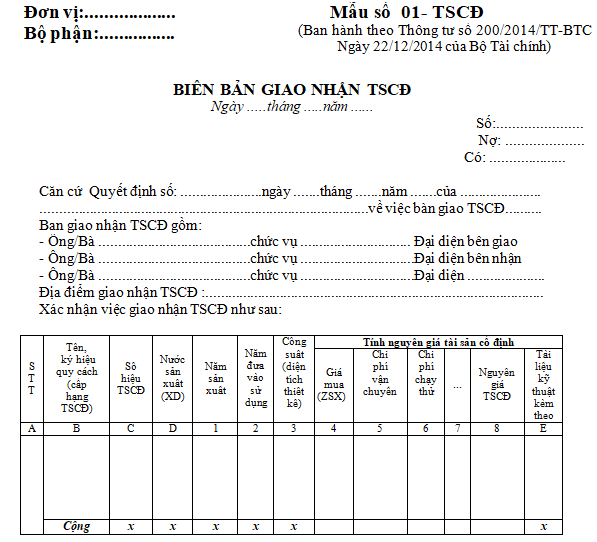
Download the template for fixed asset handover record according to Circular 200 here.

What is the record form for fixed asset handover in Vietnam according to Circular 200? (Image from the Internet)
What is the classification of enterprise fixed assets in Vietnam?
Based on Article 6 of Circular 45/2013/TT-BTC amended by Clause 2, Article 1 of Circular 147/2016/TT-BTC, enterprises classify fixed assets based on their usage purposes according to the following criteria:
- Fixed assets for business purposes are those managed and used by the enterprise for its business operations.
+ For tangible fixed assets, enterprises classify as follows:
Type 1: Buildings and architectural structures: These are fixed assets of the enterprise formed after construction processes such as office buildings, warehouses, fences, water towers, yards, decorative constructions for buildings, roads, bridges, railways, airport runways, docks, harbors, and slipways.
Type 2: Machinery and equipment: This includes all machinery and equipment used in the business activities of the enterprise such as specialized machinery, work equipment, drilling rigs in the oil and gas sector, cranes, technological lines, and standalone machines.
Type 3: Transportation means, transmission equipment: Includes transportation means such as rail, water, road, air, pipeline transit, and transmission equipment such as information systems, electrical systems, water pipelines, conveyors, and gas pipelines.
Type 4: Management equipment and tools: These are tools and equipment used in the management of business operations such as computers for management, electronic devices, measurement and testing tools, dehumidifiers, vacuum cleaners, and pest control tools.
Type 5: Perennial gardens, working animals, and/or product-producing animals: Includes perennial gardens like coffee, tea, rubber gardens, orchards, lawns, and turf; working animals and/or livestock such as elephants, horses, buffaloes, and cattle.
Type 6: Fixed assets are major infrastructural constructions invested with state budget funds assigned to economic organizations for management and exploitation:
++ Fixed assets are machinery, production lines, assets built from concrete and earth serving direct water irrigation and drainage (such as lakes, dams, canals, ditches); Water pumps with a capacity of 8,000 m3/hour or above with architectural structures for operating the engineering work handed over to one-member limited liability companies owned 100% by the state to manage, exploit hydraulic projects for organizing business and providing public utility services;
++ Fixed assets are infrastructural works in industrial zones invested by the state for common use of the industrial zone such as: internal roads, lawns, green trees, lighting systems, drainage and waste treatment systems...;
++ Fixed assets are railway, urban railway infrastructure (tunnels, elevated structures, rail tracks…).
Type 7: Other fixed assets: Including all other fixed assets not listed in the six categories above.
+ Intangible fixed assets: land use rights as specified in point đ Clause 2 Article 4 Circular 45/2013/TT-BTC, issuance rights, patents, literary, artistic, scientific works, products, results of art performances, audio recordings, video recordings, broadcast programs, encrypted satellite signals carrying programs, industrial designs, layout designs of semiconductor integrated circuits, trade secrets, trademarks, trade names, geographical indications, plant varieties and breeding materials.
- Fixed assets used for welfare, career, security, and national defense purposes are fixed assets managed by the enterprise for these purposes within the enterprise. These assets are also classified according to the aforementioned regulations.
- Fixed assets kept, safeguarded on behalf of another are those fixed assets that enterprises safeguard or shelter for other units, or store for the state based on the regulations of competent state agencies.
- Depending on the management requirements of each enterprise, enterprises can further classify their fixed assets into more detailed groups as appropriate.
Are corporate income tax deductions allowed for fixed assets ưithout oroof of ownership in Vietnam?
Based on Article 6 of Circular 78/2014/TT-BTC amended by Article 4 of Circular 96/2015/TT-BTC, the regulation states:
Expenses entitled to deduction and non-deduction when determining taxable income
...
2. Expenses not entitled to deduction when determining taxable income include:
...
2.2. Depreciation expenses of fixed assets in the following cases:
a) Depreciation for fixed assets not used for production, business of goods, services.
Specifically for fixed assets serving employees at the enterprise such as: mid-shift restrooms, canteens, changing rooms, toilets, medical rooms to diagnose and treat diseases, training facilities, libraries, nurseries, sports areas, and equipment and furniture qualified as fixed assets installed in these facilities; clean water storage tanks, parking lots; transport vehicles for transporting employees, direct housing for employees; construction costs of facilities, purchase costs of machines, equipment as fixed assets used for organizing vocational education included as deductible expenses when determining taxable income.
b) Depreciation for fixed assets without proof of ownership by the enterprise (except financial leasing fixed assets).
c) Depreciation for fixed assets not managed, monitored, accounted in the accounting books of the enterprise according to current fixed asset management policies and accounting.
In the case where fixed assets lack proof of ownership by the enterprise, they will not be eligible for corporate income tax deduction.
Except for financial leased fixed assets, which are not required to have proof of ownership.

