What is the personal income tax rate on incomes from salaries and wages in Vietnam for 2024?
What is the personal income tax rate on incomes from salaries and wages in Vietnam for 2024?
Pursuant to Article 7 of Circular 111/2013/TT-BTC, the regulation on the personal income tax rate for 2024 from salary and wages is as follows:
The tax basis for income from business and income from salary and wages is taxable income and tax rate. Specifically:
- Taxable income is determined by taxable income as guided in Article 8 of Circular 111/2013/TT-BTC minus (-) the following deductions:
+ Personal deductions as guided in Clause 1, Article 9 of Circular 111/2013/TT-BTC.
+ Insurance premiums, voluntary retirement fund contributions as guided in Clause 2, Article 9 of Circular 111/2013/TT-BTC.
+ Donations, humanitarian, educational support contributions as guided in Clause 3, Article 9 of Circular 111/2013/TT-BTC.
- Tax Rate
The personal income tax rate for income from business, salary, and wages is applied according to the progressive tax rate detailed in Article 22 of the Personal Income Tax Law 2007, specifically:
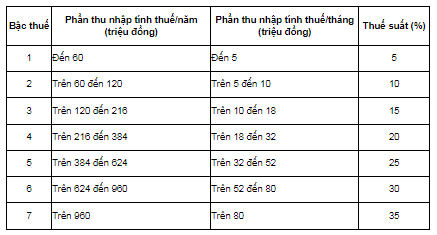
The personal income tax payable for individuals with income from salary and wages is calculated progressively. In other words, the higher the taxable income, the higher the tax liability (higher tax rate). To be specific: there are 07 tax brackets.
Calculation of personal income tax from salary and wages is as follows:
Personal Income Tax Payable = Taxable Income x Tax Rate
To calculate the tax payable, taxable income and tax rate need to be determined, specifically:
- Taxable Income:
Taxable Income = Taxable Income - Deductions
Where,
Taxable Income = Total Income - Exemptions
- Tax Rate: The tax rate from salary and wages is calculated according to the aforementioned table.
Therefore, the personal income tax rate for 2024 from salary will depend on the taxable income; the higher the taxable income, the higher the tax payable (higher tax rate) according to 7 brackets.

What is the personal income tax rate on incomes from salaries and wages in Vietnam for 2024? (Image from the Internet)
How much salary is subject to personal income tax in Vietnam?
Pursuant to Article 21 of the Personal Income Tax Law 2007 as amended by Clause 5, Article 1 of the Amended Personal Income Tax Law 2012 as follows:
Taxable Income
1. Taxable income for income from business, salary, and wages is the total taxable income specified in Articles 10 and 11 of this Law, minus social insurance, health insurance, unemployment insurance, professional liability insurance contributions for some professions and occupations that are required to participate in compulsory insurance, voluntary retirement contributions, and deductions specified in Articles 19 and 20 of this Law.
The Government of Vietnam prescribes the maximum deduction for voluntary retirement contributions stipulated in this clause.
2. Taxable income for income from capital investment, transfer of capital, transfer of real estate, winnings, royalties, franchising, inheritance, and gift is taxable income specified in Articles 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, and 18 of this Law.
Additionally, based on Article 1 of Resolution 954/2020/UBTVQH14, the regulation on personal deductions is as follows:
Personal Deductions
Adjust the personal deduction amount specified in Clause 1, Article 19 of the Personal Income Tax Law No. 04/2007/QH12 as amended and supplemented by Law No. 26/2012/QH13 as follows:
- The deduction for taxpayers is 11 million dong/month (132 million dong/year);
- The deduction for each dependent is 4.4 million dong/month.
Additionally, at Point i, Clause 1, Article 25 of Circular 111/2013/TT-BTC, the regulation on deducting personal income tax is as follows:
Tax Deduction and Tax Deduction Vouchers
1. Tax Deduction
Tax deduction involves the entity or individual paying income deducting tax from the taxpayer’s income before payment. Specifically:
...
i) Tax deduction for certain other cases
Organizations or individuals paying wages, remuneration, or other payments to residents who do not sign labor contracts (as guided in points c, d, clause 2, Article 2 of this Circular) or sign labor contracts under three (03) months with a total payment of two million (2,000,000) dong per time or more must deduct tax at the rate of 10% on income before paying it to the individual.
In cases where an individual’s only taxable income, as mentioned above, results in their total taxable income, after personal deductions, not reaching the taxable threshold, such individuals must make a commitment (using the form issued with the tax management guidelines document) and submit it to the income-paying organization, enabling the temporary non-deduction of personal income tax.
Based on the commitment of the income recipient, the income-paying organization will not deduct tax. At the end of the tax year, the income-paying organization must compile and submit a list of individuals whose incomes have not reached the tax deduction threshold to the tax authorities, using the form issued with the tax management guidelines document. Individuals who make commitments are responsible for their commitments and, if fraudulent practices are detected, they will be subject to penalties as prescribed by the Law on Tax Administration.
Individuals who make commitments as directed at this point must have taxpayer registration and a taxpayer identification number at the time of making the commitment.
...
and Article 4 of Circular 40/2021/TT-BTC, states:
Tax Calculation Principles
1. The tax calculation principles for household businesses or individual businesses are implemented according to current laws regarding VAT, personal income tax, and related legal documents.
2. Household businesses or individual businesses with annual revenue from production and business activities under 100 million dong are not subject to VAT and personal income tax according to tax regulations.
3. For household businesses or individual businesses formed as groups, the revenue threshold of 100 million dong/year to determine non-liability for VAT and personal income tax is set for one (01) representative of the group or family in the tax year.
Based on these provisions, individuals without dependents are required to pay income tax when their total income from salary and wages exceeds 11 million dong/month (132 million dong/year), after subtracting compulsory insurance contributions and other contributions, such as charity, humanitarian activities, and tax-exempt amounts.
Furthermore, certain cases, such as individuals not signing labor contracts or signing contracts under 03 months, with total payment from 2 million dong/payment or more, must pay personal income tax.
Additionally, personal income tax is applicable not only to individuals but also to household businesses. These businesses or individual businesses must have annual revenue from production and business activities exceeding 100 million dong in the calendar year.
Therefore, if an individual has an income from salary exceeding 11 million dong/month (132 million dong/year) after compulsory insurance and other contributions, such as charity and humanitarian activities, they must pay personal income tax.
Are income from prize winnings taxable in Vietnam?
Pursuant to Article 3 of the Personal Income Tax Law 2007, the types of income subject to personal income tax include:
- Income from business activities.
- Income from salary and wages.
- Income from capital investment.
- Income from capital transfer.
- Income from real estate transfers.
- Income from winnings.
- Income from royalties.
- Income from franchising.
- Income from inheritance, including securities, shares in economic organizations, business establishments, real estate, and other assets requiring registration of ownership or usage rights.
- Income from gifts, including securities, shares in economic organizations, business establishments, real estate, and other assets requiring registration of ownership or usage rights.
Therefore, according to the regulation, apart from salary income, winnings are also subject to personal income tax.

