What is the deadline for finalization of corporate income tax in Vietnam?
What is the deadline for finalization of corporate income tax (CIT) in Vietnam?
Based on Clause 2, Article 44 of the Law on Tax Administration 2019, the time limit for CIT finalization is specified as follows:
Deadline for submitting tax declaration dossiers
...
2. The deadline for submitting tax declaration dossiers for taxes determined on an annual basis is as follows:
a) No later than the last day of the third month from the end of the calendar year or fiscal year for annual tax finalization dossiers; no later than the last day of the first month of the calendar year or fiscal year for annual tax declaration dossiers;
b) No later than the last day of the fourth month from the end of the calendar year for personal income tax finalization dossiers submitted directly by individuals;
c) No later than December 15 of the preceding year for fixed tax returns of business households and individuals paying tax by the fixed method; in case of newly commenced business households and individuals, the deadline for submitting the fixed tax return is no later than 10 days from the start date of the business.
...
Thus, according to the above regulations, the deadline for CIT finalization is the last day of the third month from the end of the calendar year or fiscal year for the annual tax finalization dossier.
In summary, the deadline for CIT finalization is March 31 every year.
What is the form for finalization of corporate income tax in Vietnam?
According to Appendix 2 issued together with Circular 80/2021/TT-BTC, the form for CIT finalization declaration is Form 03/TNDN as follows:
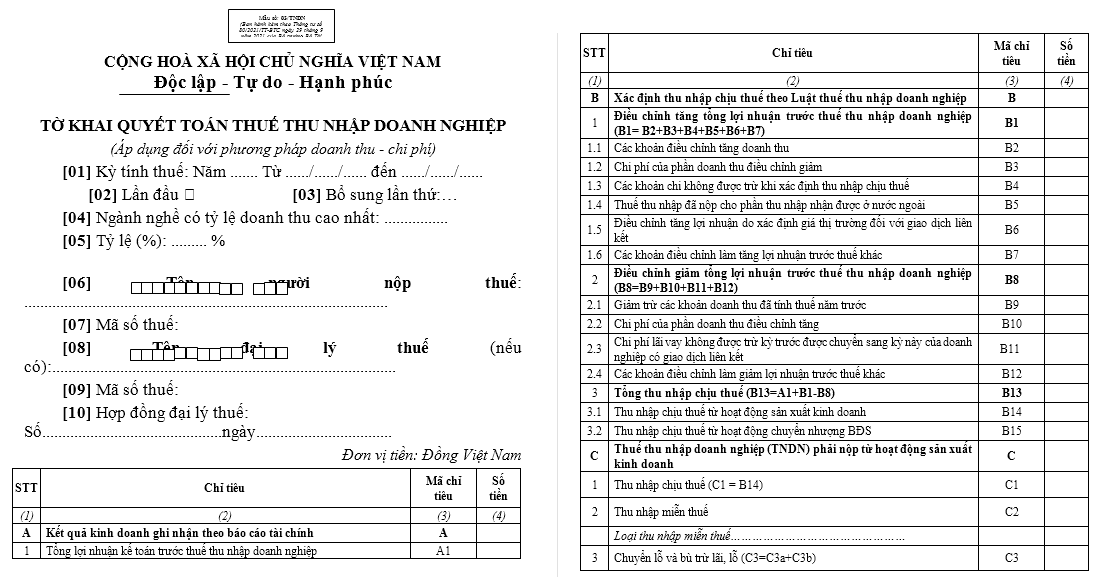
Download the Form 03/TNDN for CIT finalization declaration in 2024.

What is the deadline for finalization of corporate income tax (CIT) in Vietnam? (Image from the Internet)
When shall enterprises in Vietnam carry forward losses if CIT is finalized with a loss?
Based on Article 9 of Circular 78/2014/TT-BTC, the determination and carrying forward of losses are specified as follows:
Determination and carrying forward of losses
1. The loss incurred during the tax calculation period is the negative difference in taxable income not including the losses carried forward from previous years.
2. Enterprises that incur losses after finalizing taxes shall carry forward the entire and continuous loss amount to the taxable income (after subtracting tax-exempt income) of the following years. The continuous loss carry-forward period shall not exceed 5 years from the year following the year of the loss incurrence.
Enterprises temporarily carry forward losses to the income of the quarters of the following year based on the provisional quarterly declarations and officially in the following year based on the annual tax finalization declaration.
Example 12: In 2013, Enterprise A incurred a loss of VND 10 billion. In 2014, Enterprise A earned an income of VND 12 billion. Then, the entire loss of VND 10 billion incurred in 2013 must be carried forward to the income in 2014.
Example 13: In 2013, Enterprise B incurred a loss of VND 20 billion. In 2014, Enterprise B earned an income of VND 15 billion. Then:
+ Enterprise B must carry forward the entire loss amount of VND 15 billion to the income in 2014;
+ The remaining loss of VND 5 billion must be monitored and continuously carried forward according to the loss carry-forward principle stated above in subsequent years, but not exceeding 5 years from the year following the year of the loss incurrence.
- Enterprises with quarterly losses within the same fiscal year can offset the previous quarters' losses against the subsequent quarters' income within that fiscal year. When finalizing CIT, enterprises determine the annual loss amount and carry forward the entire and continuous loss amount to the taxable income of the years following the year of loss incurrence as per the aforementioned regulations.
- Enterprises self-determine the deductible loss amount based on the above principles. If additional losses occur during the continuous loss carry-forward period, the newly incurred loss amount (excluding the carried forward losses from previous periods) will be carried forward entirely and continuously for no more than 5 years from the year following the year of the new loss incurrence.
In cases where the competent authorities inspect and audit CIT finalization and determine a different loss amount from what the enterprise self-determines, the determined loss amount will follow the conclusions of the inspection and audit authorities, ensuring the entire and continuous loss carry-forward for no more than 5 years from the year following the year of the loss incurrence as regulated.
If the 5-year period following the year of loss incurrence expires and the loss amount has not been fully carried forward, it cannot be carried forward to the following years' income.
Thus, according to the above regulations, if an enterprise finalizes CIT with a loss, it should carry forward the loss amount to the income of the quarters of the following year based on the provisional quarterly declarations and officially in the next year based on the annual tax finalization declaration.

