What are the cases of using the VAT declaration form - Form 03/GTGT in Vietnam?
Which entities are required to pay VAT in Vietnam?
Under the provisions of Clauses 1 and 2, Article 2 of Decree 209/2013/ND-CP, value-added taxpayers include:
- Value-added taxpayers include organizations and individuals producing or trading in goods or services subject to value-added tax (below referred to as business establishments) and organizations and individuals importing goods subject to value-added tax (below referred to as importers).
- Vietnam-based production and business organizations and individuals that purchase services (including services associated with goods) from foreign organizations without permanent establishments in Vietnam or overseas individuals not residing in Vietnam shall be value-added taxpayers, unless they are not required to declare, calculate and pay value-added tax defined at point b Clause 3 of Article 2 of Decree 209/2013/ND-CP.
Note: Permanent establishments and overseas individuals being non-residents in this Clause must comply with the laws on enterprise income tax and personal income tax.

What are the cases of using the VAT declaration form - Form 03/GTGT in Vietnam? (Image from the Internet)
What are the cases of using the VAT declaration form - Form 03/GTGT in Vietnam?
The VAT declaration form for activities of buying, selling, and crafting jewelry applying the direct calculation method on the added value is specified in Form 03/GTGT issued with Circular 80/2021/TT-BTC, as follows:
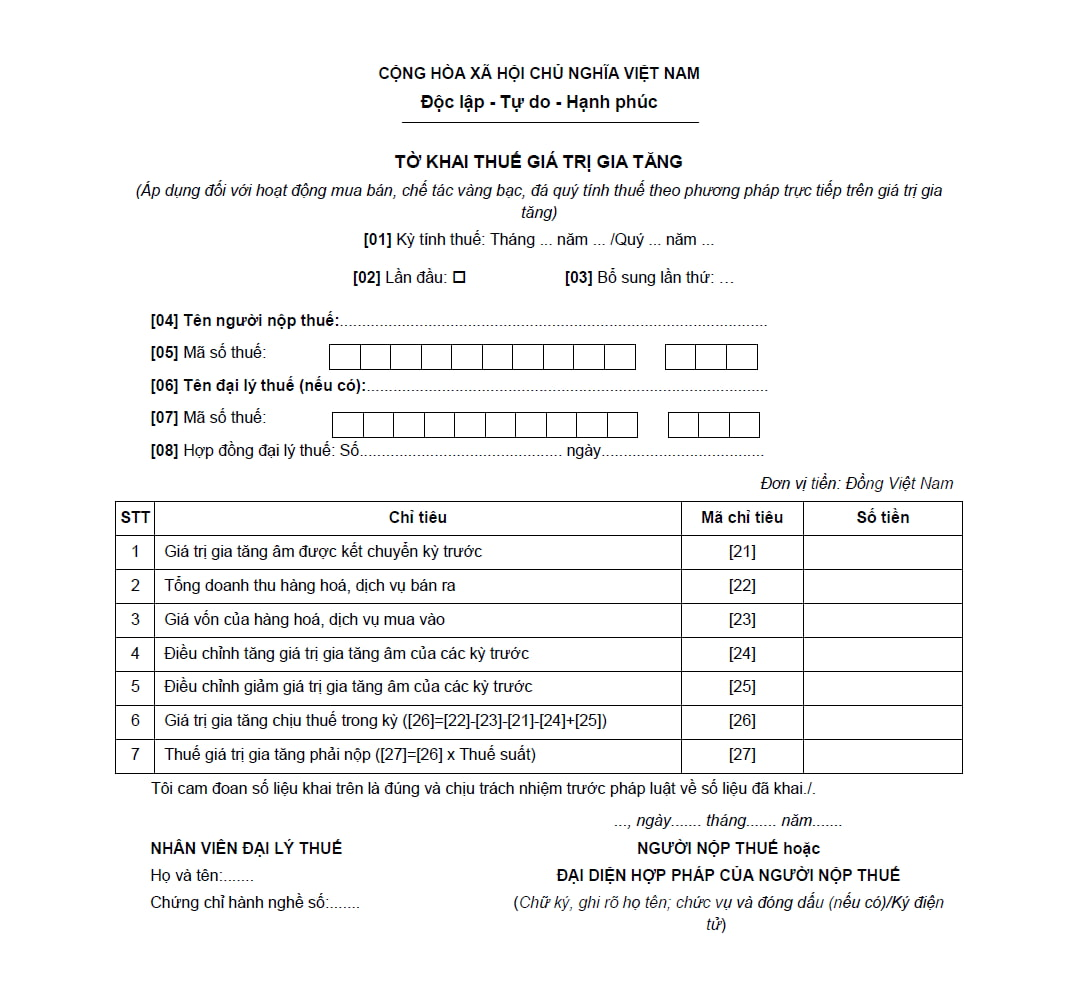
Download VAT declaration form - Form 03/GTGT: Here
How is the direct method on added value applied?
According to Article 13 of Circular 219/2013/TT-BTC (amended by Clause 4, Article 3 of Circular 119/2014/TT-BTC) that stipulates the direct method on added value as follows:
(1) VAT payable equals (=) value added multiplied by (x) VAT rate on jewelry trading.
Value added of jewelry equals (=) its selling price minus its buying price.
The selling price of jewelry is the price written on the invoice, inclusive of crafting cost, VAT, and surcharges to which the seller is entitled.
The buying price of jewelry is the VAT-inclusive value of jewelry purchased or imported for crafting or trading the jewelry sold.
In the tax period, any negative value added of jewelry shall be offset against its positive value added. If the positive value added is not available or not sufficient to completely offset against the negative value added, the negative value added shall transferred to the next period in the same year. At the end of the calendar year, any residual negative value added shall not be transferred to the next year
(2) Cases in which VAT is calculated by directly multiplying a rate (%) by the revenue (hereinafter referred to as direct VAT):
This method may be applied by the following entities:
- The operational companies and cooperatives that earn less than 1 billion VND in annual revenues, except for those that voluntarily apply credit-invoice method prescribed in Clause 3 Article 12 of Circular 219/2013/TT-BTC;
- The new companies and cooperatives, except for those that voluntarily apply credit-invoice method prescribed in Clause 3 Article 12 of Circular 219/2013/TT-BTC;
- Business households and businesspeople;
- The foreign entities doing business in Vietnam without following the Law on Investment; the organizations that fail to adhere to accounting and invoicing practice, except for those that provide goods and services serving petroleum exploration and extraction.
- The business organizations other than companies and cooperatives, except for those that voluntarily apply credit-invoice method.
Direct VAT rates applied to various business lines:
- From goods distribution or goods supply: 1%;
- From services or construction exclusive of building materials: 5%;
- Manufacturing, transport, services associated with goods, construction inclusive of building materials: 3%;
- Other lines of business: 2%.
The taxable revenue is the total revenue from selling goods and services, which is written on the sale invoice for taxable goods and services, inclusive of the surcharges to which the seller is entitled.
The rates above are not applied to the revenue from selling the goods and services that are not subject to VAT and revenue from exported goods and services.
If the taxpayer engages in various lines of business to which different rates are applied, they must be sorted by VAT rate. Otherwise, the highest rate among which shall apply.
(3) The direct VAT payable by a business household or businessperson that pays VAT at a flat rate depends on the declaration made by the taxpayer, the data of the tax authority, the result of the investigation into the taxpayer’s actual revenue, and opinions of the local Tax Advisory Council.
If the taxpayer that pays tax at a flat rate engages in multiple lines of business, the rate on the primary business line shall be applied.

