What are guidelines on 2 methods for calculating personal income tax (PIT) from salaries and wages according to the latest progressive tax table in Vietnam?
What are guidelines on 2 methods for calculating personal income tax (PIT) from salaries and wages according to the latest progressive tax table in Vietnam?
Based on the provisions of Articles 7 and 8 of Circular 111/2013/TT-BTC, PIT from the salary and wages of a resident individual is determined by the following formula:
PIT from salary and wages = Taxable income from salary and wages x Tax rate
Where:
(1) Taxable income = Taxable income - Deductions
Taxable income = Total income - Exemptions
(2) Tax rates as specified in Clause 2, Article 7 of Circular 111/2013/TT-BTC
However, Appendix 01/PL-TNCN enclosed with Circular 111/2013/TT-BTC guides 02 methods for calculating tax according to the progressive tax table for income from salaries and wages, specifically as follows:
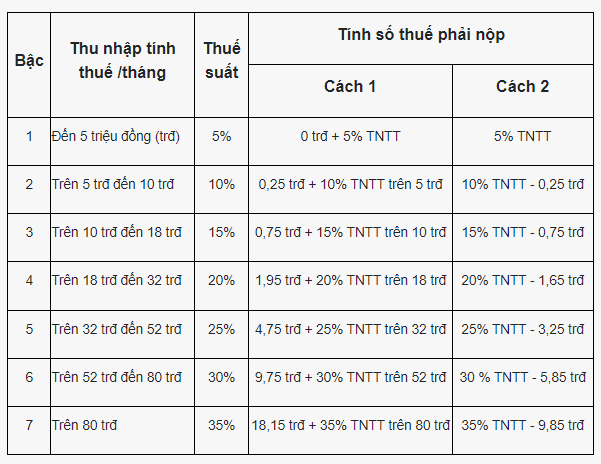
Note: The above guidance applies to income from salaries and wages of resident individuals.
According to Article 18 of Circular 111/2013/TT-BTC, PIT from salaries and wages of non-resident individuals is determined as follows:
PIT from salary and wages = Taxable income from salary and wages x PIT rate of 20%

What are guidelines on 2 methods for calculating personal income tax (PIT) from salaries and wages according to the latest progressive tax table in Vietnam? (Image from the Internet)
At what salary level is personal income tax payable in Vietnam?
Based on Article 2 of Circular 111/2013/TT-BTC, it is specified as follows:
Taxable income items
…
2. Income from salaries and wages
Income from salaries and wages is the income an employee receives from an employer, including:
a) Salaries, wages, and other earnings of similar nature in cash or in kind.
b) Allowances and subsidies, except for the following allowances and subsidies:
b.1) Monthly preferential allowances and lump-sum subsidies as stipulated by the law for individuals with merit.
b.2) Monthly and lump-sum subsidies for individuals involved in resistance, national defense, international missions, and youth volunteers who have completed their tasks.
b.3) Defense and security allowances; subsidies for armed forces personnel.
b.4) Hazardous and dangerous allowances for sectors, occupations, or jobs in hazardous or dangerous workplaces.
b.5) Attraction allowances and regional allowances.
b.6) Unexpected hardship subsidies, work accident subsidies, occupational disease subsidies, Lump-sum subsidies for childbirth or adoption, maternity regime allowances, nursing and recuperation after childbirth subsidies, subsidies for reduced working capacity, Lump-sum retirement subsidies, monthly survivor pensions, severance allowances, job-loss allowances, unemployment allowances and other allowances as stipulated by the Labor Code and Social Insurance Law.
b.7) Subsidies for individuals who receive social protection according to the law.
b.8) Service allowances for high-ranking leaders.
…
Additionally, based on Article 1 of Resolution 954/2020/UBTVQH14, it is regulated as follows:
Personal deduction levels
Adjusting the personal deduction levels specified in Clause 1, Article 19 of the Personal Income Tax Law No. 04/2007/QH12, as amended and supplemented by Law No. 26/2012/QH13, as follows:
1. The deduction for the taxpayer is 11 million VND/month (132 million VND/year);
2. The deduction for each dependent is 4.4 million VND/month.
Thus, for an individual without dependents, personal income tax is payable when the total income from salaries and wages exceeds 11 million VND/month.
What allowances and subsidies are exempt from personal income tax in Vietnam?
Based on Point b, Clause 2, Article 3 of Decree 65/2013/ND-CP, as amended by Clause 3, Article 2 of Decree 12/2015/ND-CP, the following allowances and subsidies are exempt from PIT:
- Monthly preferential allowances and lump-sum subsidies as stipulated by the law for individuals with merit;
- Monthly and lump-sum subsidies for individuals involved in resistance, national defense, international missions, and youth volunteers who have completed their tasks;
- Defense and security allowances; subsidies for armed forces personnel;
- Hazardous and dangerous allowances for sectors, occupations, or jobs in hazardous or dangerous workplaces;
- Attraction allowances and regional allowances;
- Unexpected hardship subsidies, work accident subsidies, occupational disease subsidies, Lump-sum subsidies for childbirth or adoption, subsidies for reduced working capacity, Lump-sum retirement subsidies, monthly survivor pensions, severance allowances, job-loss allowances, unemployment allowances and other allowances as stipulated by the Labor Code and Social Insurance Law;
- Subsidies for individuals who receive social protection according to the law;
- Service allowances for high-ranking leaders;
- Lump-sum allowances for individuals transferring to work in areas with especially difficult socio-economic conditions, Lump-sum support for officials working on marine sovereignty according to the law. Relocation allowances for foreign individuals residing in Vietnam, Vietnamese individuals working abroad, and Vietnamese individuals who have been abroad for a long-term returning to work in Vietnam;
- Allowances for village health workers;
- Special occupational allowances.
These allowances and subsidies not counted as taxable income must be regulated by competent state authorities.

