What are the tasks and powers of enforcers in Vietnam? - Ngoc Tham (Dien Bien, Vietnam)
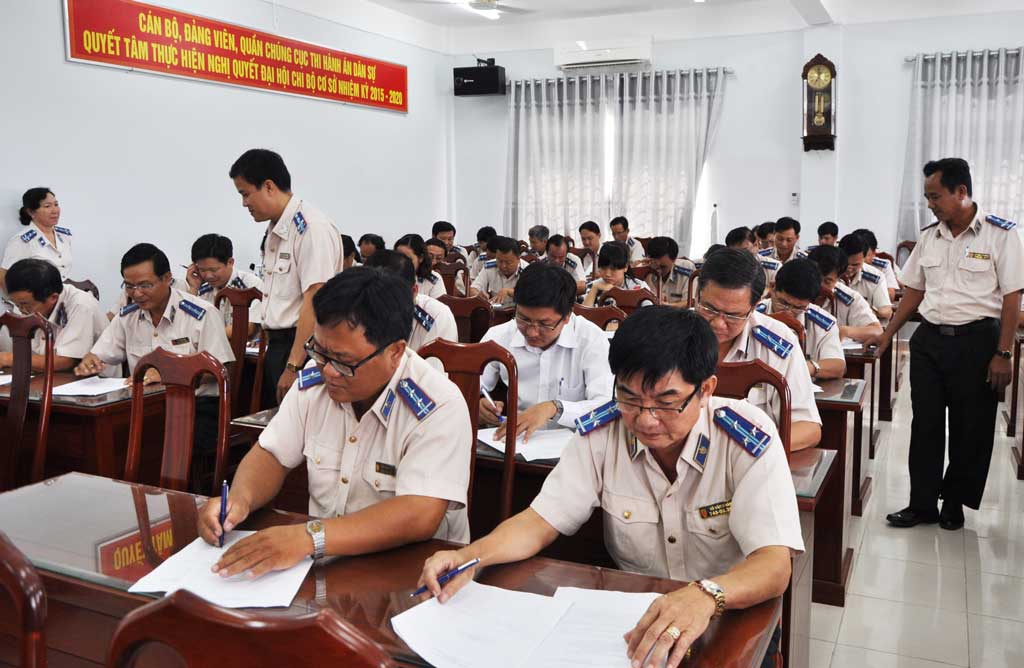

Tasks and powers of enforcers in Vietnam (Internet image)
1. Who are enforcers?
Article 17 of the Law on Enforcement of Civil Judgments 2008 stipulates enforcers as follows:
- Enforcers are persons tasked by the State to enforce judgments and rulings prescribed in Article 2 of this Law. Enforcers have three ranks: junior enforcer, intermediate-level enforcer and senior enforcer.
- Enforcers shall be appointed by the Justice Minister.
2. Criteria for appointment of enforcers in Vietnam
In Article 18 of the Law on Enforcement of Civil Judgments 2008, the criteria for appointment of enforcers are as follows:
- Vietnamese citizens who are loyal to the Fatherland, honest, non-corruptible, possess good ethical quality and a law bachelor or higher degree, and have good health to fulfill assigned tasks may be appointed as enforcers.
- Persons who fully satisfy the criteria specified in Clause 1 of Article 18 of the Law on Enforcement of Civil Judgments 2008, and the following conditions may be appointed as junior enforcers:
+ Having been engaged in legal work for 3 years or more;
+ Having been trained in civil judgment enforcement profession;
+ Passing the examination for selection of junior enforcers.
- Persons who fully satisfy the criteria specified in Clause 1 of Article 18 of the Law on Enforcement of Civil Judgments 2008 and the following conditions may be appointed as intermediate-level enforcers:
+ Having worked as junior enforcers for 5 years or more;
+ Passing the examination for selection of intermediate-level enforcers.
- Persons who fully satisfy the criteria specified in Clause 1 of Article 18 of the Law on Enforcement of Civil Judgments 2008, and the following conditions may be appointed as senior enforcers:
+ Having worked as intermediate-level enforcers for 5 years or more;
+ Passing the examination for selection of senior enforcers.
- Persons who fully satisfy the criteria specified in Clause 1 of Article 18 of the Law on Enforcement of Civil Judgments 2008 and are in-service army officers may be appointed as military enforcers.
Criteria for persons to be appointed as military primary-level enforcers, intermediate- level enforcers and high-level enforcers are prescribed in Clauses 2, 3 and 4 of Article 18 of the Law on Enforcement of Civil Judgments 2008.
- Incumbent judges, procurators and investigators who are transferred to civil judgment enforcement agencies or those who have once act as enforcers but are now assigned to perform other tasks and fully satisfy the criteria specified in Clause 1 of Article 18 of the Law on Enforcement of Civil Judgments 2008 may be appointed as enforcers of equivalent ranks without having to pass an examination.
- In special cases due to the demand for appointment of heads and deputy heads of civil judgment enforcement agencies, persons who fully satisfy the criteria specified in Clause 1 of Article 18 of the Law on Enforcement of Civil Judgments 2008,
And have been engaged in legal work for 5 years or more, 10 years or more or 15 years or more may be appointed as primary-level, intermediate-level or high-level enforcers, respectively, without having to pass an examination.
3. Tasks and powers of enforcers in Vietnam
In Article 20 of the Law on Enforcement of Civil Judgments 2008, the tasks and powers of enforcers are as follows:
- To promptly organize the enforcement of judgments or rulings assigned to them; to issue judgment enforcement decisions according to their competence.
- To strictly enforce contents of judgments or rulings; to correctly apply legal provisions on the order of and procedures for judgment enforcement, ensuring the interests of the State and the rights and legitimate interests of involved parties and persons with related interests and obligations; and to strictly observe regulations on standard professional ethics of enforcers.
- To summon involved parties and persons with related interests and obligations for judgment enforcement.
- To verify assets and judgment execution conditions of judgment debtors; to request concerned agencies, organizations and individuals to supply documents for the verification of addresses and assets of judgment debtors or coordinate with concerned agencies in handling material evidence, assets and other matters related to judgment enforcement.
- To decide on the application of measures to secure judgment enforcement and coercive measures to enforce judgments; to work out plans on coercive judgment enforcement; and to confiscate assets for judgment enforcement.
- To request under law police offices to detain persons resisting the judgment enforcement.
- To make written records of violations of the law on judgment enforcement; to impose administrative sanctions according to their competence; to propose competent agencies to discipline or administratively sanction violators or examine violators for penal liability.
- To decide on the application of coercive measures to recover money and assets already paid to involved parties in contravention of law, collect judgment enforcement charges and other amounts payable by involved parties.
- To use support tools while on duty under the Governments regulations.
- To perform other tasks assigned by heads of judgment enforcement agencies.
When performing their tasks or exercising their powers, enforcers shall comply with law and take responsibility before law for judgment enforcement and have their lives, health, honor, dignity and prestige protected by law.
4. Prohibitions on enforcers in Vietnam
Pursuant to Article 21 of the Law on Enforcement of Civil Judgments 2008 stipulates the prohibitions on enforcers as follows:
- Prohibitions on civil servants as prescribed by law.
- Providing advice to involved parties and persons with related interests and obligations, leading to unlawful judgment enforcement.
- Illegally intervening in the handling of cases subject to judgment enforcement or abusing one’s influence to affect persons responsible for judgment enforcement.
- Illegally using material evidence, money and assets involved in judgment enforcement.
- Enforcing judgments related to their own rights and interests and those of the following persons:
+ Their spouses, blood children or adopted children;
+ Their blood parents, adoptive parents, paternal or maternal grandparents, uncles, aunts, and blood siblings or those of their spouses;
+ Nephews and nieces whose blood parents are their blood siblings.
- Using their enforcer cards, uniforms and badges or support tools in conducting activities beyond their assigned tasks and vested powers.
- Harassing or troubling individuals, agencies or organizations in the course of judgment enforcement.
- Intentionally enforcing judgments or rulings in violation of their contents; delaying or prolonging the enforcement of judgments assigned to them without adequate legal grounds.
Ngoc Nhi
- Key word:
- enforcers in Vietnam
 Article table of contents
Article table of contents






.Medium.png)
.Medium.png)
.Medium.png)
.Medium.png)
