What is the formula to find a common denominator for grade 4 students in Vietnam?
What is the formula to find a common denominator for grade 4 students in Vietnam?
Equalizing the denominators of several fractions involves transforming those fractions into equivalent fractions with the same denominator.
| 1. The formula for equalizing denominators for two fractions is as follows:
- Multiply the numerator and the denominator of the first fraction by the denominator of the second fraction.
- Multiply the numerator and the denominator of the second fraction by the denominator of the first fraction.
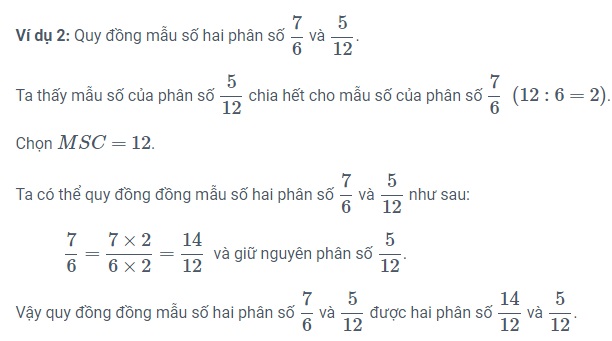
2. If the denominator of the second fraction is divisible by the denominator of the first fraction, the formula for equalizing denominators for the two fractions is as follows:
- Take the common denominator as the denominator of the second fraction.
- Find the corresponding factor by dividing the second denominator by the first denominator.
- Multiply both the numerator and the denominator of the first fraction by the corresponding factor.
- Keep the second fraction unchanged.
Note: Typically, the common denominator is the smallest non-zero natural number that is divisible by all denominators.
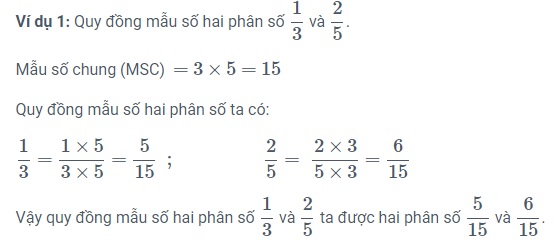
 || --- |
|| --- |

What is the formula to find a common denominator for grade 4 students in Vietnam? (Image from Internet)
What are the expected outcomes for studying numbers and calculations in grade 4 math in Vietnam?
Based on the General Education Program for Mathematics issued along with Circular 32/2018/TT-BGDDT, the expected outcomes for studying numbers and calculations in grade 4 math are as follows:
Number and decimal structure of a number
- Read and write numbers with many digits (up to millions class).
- Recognize the decimal structure of a number and the positional value of each digit in a number.
- Identify even numbers and odd numbers.
- Acquaintance with the natural number sequence and its characteristics.
Comparing numbers
- Recognize how to compare two numbers within the millions range.
- Perform arranging numbers in order (from smallest to largest or vice versa) in a group of no more than 4 numbers (within the millions range).
Rounding numbers
- Round numbers to the nearest ten, hundred, thousand, ten thousand, hundred thousand (e.g., rounding 12,345 to the nearest hundred gives 12,300).
Addition and subtraction
- Perform addition and subtraction of natural numbers with many digits (with up to three carries and not consecutive).
- Apply the commutative and associative properties of addition and the relationship between addition and subtraction in calculation practice.
Multiplication and division
- Calculate the average of two or more numbers.
- Perform multiplication with numbers having up to two digits.
- Perform division by numbers having up to two digits.
- Perform multiplication by 10; 100; 1000; ... and division by 10; 100; 1000; ...
- Apply the commutative and associative properties of multiplication and the relationship between multiplication and division in calculation practice.
Mental arithmetic
- Apply the properties of operations to compute mentally and find the most convenient calculation methods.
- Estimate results in simple calculations (e.g., dividing 572 by 21 results in a quotient that cannot be 30).
Numeric and literal expressions
- Get acquainted with expressions containing one, two, or three letters and compute the value of these expressions in simple cases.
- Apply the distributive property of multiplication over addition to compute the value of expressions.
Practice solving problems related to the learned calculations
- Solve problems involving solving up to two or three calculation steps (within the learned numbers and operations) related to the components and results of operations; related to direct comparative relationships or direct, simple-dependent relationships (e.g., problems involving finding the average of two numbers; finding two numbers when their sum and difference are known; problems involving unit conversion).
Initial concept of fractions
- Recognize the initial concept of fractions, numerators, and denominators.
- Read and write fractions.
Basic properties of fractions
- Recognize the basic properties of fractions.
- Perform simplifying fractions in simple cases.
- Perform equalizing denominators for two fractions in cases where one denominator is divisible by the other.
Comparing fractions
- Compare and arrange the order of fractions in the following cases: fractions with the same denominator; one denominator divisible by the others.
- Identify the largest and smallest fractions (in groups of no more than 4 fractions) in the following cases: fractions with the same denominator; one denominator divisible by the others.
Addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division of fractions
- Perform addition and subtraction of fractions in the following cases: fractions with the same denominator; one denominator divisible by the others.
- Perform multiplication and division of two fractions.
- Solve problems involving solving up to two or three calculation steps related to the 4 operations with fractions (e.g., problems involving finding the fraction of a number).
What are the practical and experiential activities in grade 4 math in Vietnam?
According to the General Education Program for Mathematics issued along with Circular 32/2018/TT-BGDDT, schools organize the following activities for students and may supplement other activities depending on specific conditions.
Activity 1: Practice applying mathematical knowledge to practical and interdisciplinary topics, such as:
- Practice activities related to calculation, measurement, and estimation such as: calculating and estimating the perimeter, area, angle of some practical shapes related to learned shapes; calculating and estimating weight, volume, etc.; determining the year, century marking the birth (occurrence) of some scientific inventions, cultural-social events, history, etc.
- Practice collecting, analyzing, and representing statistical data (through simple situations linked to economic, social development issues or global issues such as climate change, sustainable development, financial education, sea and island sovereignty, borders, STEM education, etc.).
- Practice buying, selling, and exchanging currency.
Activity 2: Organize extracurricular activities (e.g., math games, or activities “Learning is fun – Fun is learning”; games related to buying, selling, exchanging goods; assembling, folding, arranging shapes; tossing coins, rolling dice, etc.) related to reviewing, reinforcing math knowledge or solving problems arising in practical situations.
Activity 3 (if the school is capable of implementing): Organize exchanges with students who are talented in math within the school and with other schools.

