What is the direction of the prevailing wind in Vietnam during the summer season? What are regulations on evaluation by scores for continuing education students at lower secondary level in Vietnam?
What is the direction of the prevailing wind in Vietnam during the summer season?
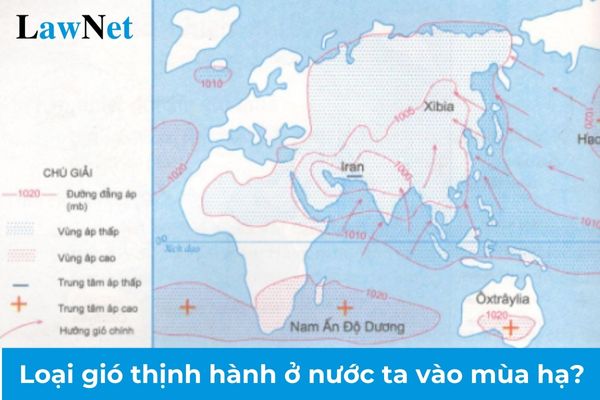
During the summer, due to geographical position and changes in air pressure, our country is primarily influenced by the southwest monsoon, including the particularly distinctive southern foehn wind (Laos wind). These winds bring distinct characteristics in terms of direction and nature, contributing to the formation of the rainy season and various weather phenomena across regions.
1. Southwest Monsoon
- Wind Direction: The wind blows from the southwest direction.
- Origin: The southwest monsoon forms from the high-pressure area over the Indian Ocean and its surrounding seas (primarily the Bay of Bengal) blowing towards the tropical low-pressure area over the Asian continent.
- Characteristics:
+ The southwest monsoon carries moisture from the Indian Ocean and the Bay of Bengal. When it reaches Vietnam through the Gulf of Thailand and the East Sea, it causes significant rainfall, especially in the South, Central Highlands, and parts of the Central region.
+ It is the main cause of the rainy season in these areas, particularly in the Central Highlands, providing abundant water resources for agricultural production and daily life.
+ The southwest monsoon typically prevails from May to October, resulting in continuous heavy rains in the South and Central Highlands.
2. Southern Foehn Wind (Laos Wind)
- Wind Direction: Also primarily southwest.
- Origin: The southwest wind from the Indian Ocean blows through the Bay of Bengal and Laos before crossing the Truong Son Mountains to reach Vietnam.
- Formation Process:
+ As the southwest wind blows over the Truong Son Mountains, its moisture is retained on the western side of the mountains (the territory of Laos). Consequently, the air becomes dryer and hotter after crossing the mountain peaks to reach Central Vietnam.
- Characteristics:
+ The southern foehn wind causes severe drought and extreme heat in the North Central Coast and Central coastal provinces like Thanh Hoa, Nghe An, Ha Tinh, Quang Binh, Quang Tri, Thua Thien - Hue.
+ This wind typically occurs from May to July, sometimes extending into August, subjecting the region to harsh heat, drought, and water shortages, hindering agricultural production as well as daily activities.
Explanation of the Prevalence of Southwest Wind in Summer
- Influence of low and high pressure:
+ In summer, when the sun shines most intensely in the Northern Hemisphere, the Asian continent (especially Southeast Asia) heats up significantly, forming a large low-pressure area.
+ Meanwhile, the Indian Ocean, Bay of Bengal, and East Sea maintain high-pressure areas. This pressure difference creates a wind flow from the high-pressure area of the Indian Ocean to the low-pressure area over the Asian continent and Vietnam.
+ Southeast Asia Monsoon System: Vietnam is located in the area influenced by the Southeast Asia monsoon. In summer, the southwest monsoon from the Indian Ocean combines with air masses from the East Sea, creating the prevailing wind during this period.
+ The role of the Truong Son Mountains: The Truong Son Mountains act as a barrier and alter the characteristics of the southwest winds. As they cross the mountains, these winds lose moisture and become dry and hot, causing the foehn effect in the North Central Coast and Central regions.
Impact of the Southwest Monsoon and Southern Foehn Wind
- Southwest Monsoon:
+ It brings substantial rainfall to the South and Central Highlands, helping to replenish water resources for agricultural production, irrigation, and hydroelectric development.
+ Plays a crucial role in forming the rainy season, helping to alleviate the heat in the southern region.
- Southern Foehn Wind (Laos Wind):
+ Causes arid conditions, extreme heat in the North Central Coast and Central coastal regions, increasing the risk of forest fires, droughts, and adversely affecting crops.
+ At the same time, the hot dry weather also increases the demand for water in daily and production activities, placing significant pressure on water resources in this area.
Conclusion
Thus, the prevailing winds in Vietnam during the summer are the southwest monsoon and the southern foehn wind. The southwest monsoon brings heavy rains, cooling temperatures, and nourishing crops in the South and Central Highlands, while the southern foehn wind (Lao Wind) causes severe dryness in the Central region. The presence of these winds not only reflects the tropical monsoon climate characteristics of Vietnam but also greatly impacts the life, production, and activities of the population.
Note: The content is for reference purposes only.
What is the direction of the prevailing wind in Vietnam during the summer season? What are regulations on evaluation by scores for continuing education students at lower secondary level in Vietnam? (Image from the Internet)
What are regulations on evaluation by scores for continuing education students at lower secondary level in Vietnam?
Pursuant to Clause 2, Article 5 of Circular 43/2021/TT-BGDDT, the regulations on evaluation by scores for continuing education students at lower secondary level in Vietnam are as follows:
- Teachers use scores to evaluate the results of students' practice and study.
- The assessment by scores is utilized in regular evaluations, periodic evaluations through forms of testing, and assessing the performance of practice and study tasks suitable to the specific characteristics of the subject.
What are regulations on evaluation of the practice result of continuous education students at the lower secondary level in each semester in Vietnam?
Pursuant to Clause 2, Article 8 of Circular 43/2021/TT-BGDDT, the practice results of continuous education students at the lower secondary level each semester are evaluated according to four levels as follows:
- Good Level: Meets the required standards of qualities stipulated in the continuous education curriculum and demonstrates many outstanding traits.
- Fair Level: Meets the required standards of qualities stipulated in the continuous education curriculum and shows outstanding traits but has not reached the Good level.
- Pass Level: Meets the required standards of qualities stipulated in the continuous education curriculum.
- Not Pass Level: Does not meet the required standards of qualities stipulated in the continuous education curriculum.

