What is the cosine function theorem? What are the guidelines for proof of the cosine function theorem in Mathematics? What are the regulations on assessment of educational results for 9th-grade Mathematics in Vietnam?
What is the cosine function theorem? What are the guidelines for proof of the cosine function theorem in Mathematics?
The cosine function theorem is an incredibly useful tool in solving problems related to triangles. It helps us establish the relationship between the sides and angles of a triangle, thereby solving many complex problems.
Students can refer to the following information on the cosine function theorem and proof of the cosine function theorem in Mathematics below:
|
What is the cosine function theorem? What are the guidelines for proof of the cosine function theorem in Mathematics? The cosine function theorem is one of the important theorems in trigonometry, allowing us to establish the relationship between the lengths of the sides of a triangle with the cosine of the opposite angle. |
*Note: Information is for reference only./.
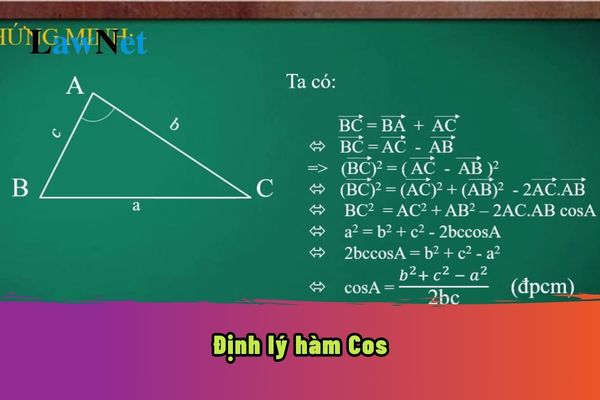
What is the cosine function theorem? What are the guidelines for proof of the cosine function theorem in Mathematics? What are the regulations on the assessment of educational results for 9th-grade Mathematics in Vietnam? (Image from the Internet)
In Vietnam, what is the grade at which the cosine function theorem is taught in the Mathematics curriculum?
Under Section 5 of the General education program in Mathematics issued along with Circular 32/2018/TT-BGDDT, the content in the 9th-grade Mathematics curriculum is as follows:
*Ratio of trigonometry in right triangles
Trigonometric ratios of acute angles. Some relationships about the sides and angles in a right triangle
- Recognize values of sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent of an acute angle.
- Explain the trigonometric ratios of special angles (30°, 45°, 60°) and of complementary angles.
- Calculate (precise or approximate) trigonometric ratios of an acute angle using a handheld calculator.
- Explain some relationships about the sides and angles in a right triangle (the leg is equal to the hypotenuse multiplied by the sine of the opposite angle or multiplied by the cosine of the adjacent angle; the leg is equal to the other leg multiplied by the tangent of the opposite angle or multiplied by the cotangent of the adjacent angle).
- Solve some real-world problems related to the trigonometric ratios of acute angles (e.g., calculate line lengths, angle magnitudes, and apply to solve right triangles, etc.).
Thus, according to the above regulation, the cosine function theorem will be taught in the 9th-grade Mathematics curriculum.
What are the regulations on the assessment of educational results for 9th-grade Mathematics in Vietnam?
Under Section 7 of the General education program in Mathematics issued along with Circular 32/2018/TT-BGDDT, the assessment of educational results for 9th-grade Mathematics in Vietnam is specified as follows:
The assessment of educational results for Mathematics aims to provide accurate, prompt, and valuable information on the development of student's abilities and progress based on the required achievements at each class level; adjust teaching activities to ensure each student's progress and enhance the quality of mathematics education and overall education quality.
Utilize a combination of various assessment forms (process assessment, periodic assessment), and numerous assessment methods (observation, documenting the process of implementation, oral response, objective tests, written tests, practical exercises, study projects/products, real-world tasks, ...) at appropriate times.
Process assessment (or regular assessment) is organized by the subject teacher, combined with assessments by other subject teachers, self-assessment by the assessed student, and by classmates or student parents. Process assessment aligns with students' learning activities, avoiding separation between teaching and assessment processes, ensuring the aim of assessing student's progress in learning.
Periodic assessment (or summative assessment) primarily aims to assess the achievement of learning objectives. Results from periodic and summative assessments are used to certify learning levels and acknowledge students' achievements. Periodic assessments are organized by the educational institution or via national assessments and examinations.
Periodic assessment is also used to manage teaching activities effectively, ensuring quality at educational institutions and contributing to mathematics curriculum development.
Assess student competence through evidence of results achieved during the execution of students' actions. The assessment process involves basic steps such as: determining the purpose of the assessment; identifying necessary evidence; selecting appropriate assessment methods and tools; collecting evidence; interpreting the evidence and making comments.
Focus on choosing methods and tools to assess components of mathematical competence. To be specific:
- Assess mathematical reasoning and argumentation competence: may use methods and tools such as questions (oral, written), and exercises,... requiring students to present, compare, analyze, aggregate, and systematize knowledge; to apply mathematical knowledge to explain and argue.
- Assess mathematical modeling competence: select practical situations that give rise to mathematical problems. From there, require students to identify mathematical models (including formulas, equations, charts, graphs,...) for the situation presented in the practical problem; solve mathematical issues in the established model; express and assess solutions in the practical context and improve the model if the solution is unsuitable.
- Assess problem-solving competence in mathematics:
+ Be able to use methods such as requesting the learner to identify the situation, detect and present the problem to be solved; describe, and explain initial information, goals, and expectations of the problem situation being considered;
+ Gather, select, arrange information and connect it with existing knowledge; use questions (requiring oral or written responses) that require learners to apply knowledge to solve problems, particularly real-world issues; use observation methods, observe learners during problem-solving; assess through learners' practical products; pay reasonable attention to integrated assessment tasks.
- Assess mathematical communication competence: can use methods such as requesting learners to listen, read, write (summarize), analyze, select, extract fundamental, focal mathematical information in spoken or written text; use mathematical language combined with ordinary language in presenting, expressing, questioning, discussing, debating mathematical content, ideas, solutions in interaction with others.
- Assess the competence to use tools and means of learning mathematics: can use methods such as requiring learners to recognize names, functions, usage regulations, preservation methods, advantages, and limitations of mathematical learning tools and means; present reasonable usage of tools and means to perform learning tasks or to explain mathematical reasoning and proofs.
When teachers plan lessons, they should establish criteria and assessment methods to ensure that at the end of each lesson, students achieve basic requirements based on the stated criteria before undertaking subsequent learning activities.
>> View the General education program in Mathematics issued with Circular 32/2018/TT-BGDDT: Download

