What is the Cosine formula? What are some examples of applying the Cosine formula? What is the grade whose Mathematics curriculum in Vietnam covers the Cosine formula?
What is the Cosine formula? What are some examples of applying the Cosine formula?
The Cosine formula is a useful tool for solving problems related to triangles. Mastering this formula will help you solve geometric problems more quickly and accurately.
|
In geometry, the Cosine formula is a relationship between the sides of a triangle. It allows us to calculate the length of one side of a triangle when the lengths of the other two sides and the included angle are known.
|
*Note: The information is for reference only./.
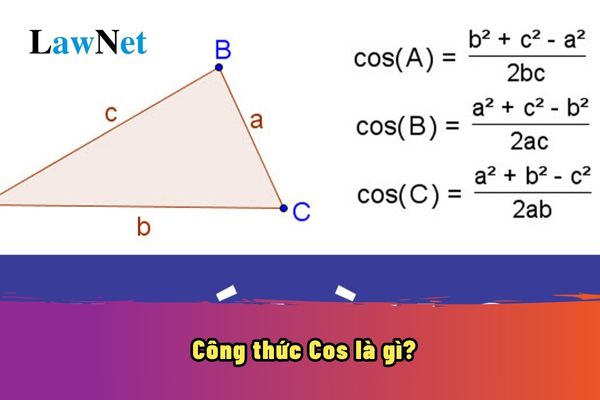
What is the Cosine formula? What are some examples of applying the Cosine formula? What is the grade whose Mathematics curriculum in Vietnam covers the Cosine formula? (Image from the Internet)
What is the grade whose Mathematics curriculum in Vietnam covers the Cosine formula?
Under Section 5 of the General education program in Mathematics issued with Circular 32/2018/TT-BGDDT, the content in the 9th-grade Mathematics curriculum is as follows:
*Trigonometric Ratios in Right Triangles
Trigonometric ratios of acute angles. Some relationships regarding sides and angles in right triangles
- Recognize the values of sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent of acute angles.
- Explain the trigonometric ratios of specific acute angles (30°, 45°, 60°) and complementary angles.
- Calculate the trigonometric ratios of acute angles, either exactly or approximately, using a handheld calculator.
- Explain some relationships regarding sides and angles in right triangles (e.g., the length of a leg is equal to the hypotenuse times the sine of the opposite angle or the cosine of the adjacent angle; the length of a leg is equal to the other leg times the tangent of the opposite angle or the cotangent of the adjacent angle).
- Solve some practical problems associated with the trigonometric ratios of acute angles (e.g., calculating segment lengths, angle magnitudes, and applying right triangle problems, etc.).
Therefore, according to the above regulations, the 9th-grade Mathematics curriculum covers the Cosine formula.
What are the regulations on assessing the educational outcomes for 9th-grade Mathematics in Vietnam?
Under Section 7 of the General education program in Mathematics issued with Circular 32/2018/TT-BGDDT, the assessment of educational outcomes for 9th-grade Mathematics in Vietnam is as follows:
The goal of assessing the educational outcomes of Mathematics is to provide accurate, prompt, and valuable information on students' capacity development and progress based on the requirements for each grade and level of education; adjusting teaching activities, ensuring each student's progress, and enhancing the quality of Mathematics education in particular and overall educational quality.
Combine multiple assessment forms (process assessment, periodic assessment), multiple assessment methods (observation, recording the implementation process, oral questioning, objective tests, essays, written exams, practical exercises, study projects/products, real-world task execution,...) and at appropriate times.
Process assessment (or continuous assessment) is organized by the subject teacher, combined with assessments by other subject teachers, self-assessment by the assessed student, and assessments by other students in the group, class, or by parents. Process assessment goes hand in hand with the learning activities of students, avoiding separation between teaching and assessment processes, and ensuring the assessment goal of student progress in learning.
Periodic assessment (or final assessment) primarily aims to assess the achievement of learning goals. Periodic and final assessment results are used to certify learning levels and recognize student achievements. Periodic assessments are organized by educational institutions or through national examinations and assessments.
Periodic assessments are also used to manage teaching activities, ensuring quality in educational institutions and supporting the development of the Mathematics program.
Assess student capacity through evidenced outcomes during the execution of student actions. The assessment process includes basic steps such as: determining assessment purposes; identifying necessary evidence; selecting appropriate methods and tools; collecting evidence; interpreting evidence and providing remarks.
Focus on selecting methods and tools to assess components of mathematical capability. To be specific:
- Assess mathematical thinking and reasoning skills: use methods and tools such as questions (spoken, written), exercises,... that require students to present, compare, analyze, aggregate, and systematize knowledge; apply mathematical knowledge to explain and reason.
- Assess mathematical modeling capabilities: select real-life situations that give rise to mathematical problems. From there, require students to identify the mathematical model (including formulas, equations, tables, graphs,...) for real-world situations; solve mathematical problems within the established model; represent and assess solutions in practice and improve the model if the resolution is unsuitable.
- Assess problem-solving capabilities in mathematics:
+ Use methods that require learners to identify situations, detect and present problems to be solved; describe, explain initial information, objectives, and expectations of the context;
+ Collect, select, organize, and connect information with existing knowledge; use questions (which may require oral or written responses) that require learners to apply knowledge to solve problems, especially practical ones; use observation methods, observe learners during problem-solving; assess through learners' practice products; reasonably consider integrated assessment tasks.
- Assess mathematical communication skills: use methods such as requiring learners to understand, read, take notes (summarize), analyze, select, and extract key mathematical information in spoken or written texts; use mathematical language combined with regular language to present, express, ask questions, discuss, and debate mathematical content, ideas, and solutions while interacting with others.
- Assess the ability to use tools and means for learning mathematics: use methods such as requiring learners to recognize the name, usage, form, maintenance, advantages, and limitations of mathematical learning tools and means; present the (appropriate) use of tools and means for learning mathematics to perform learning tasks or explain mathematical reasoning and proofs.
When preparing lesson plans, they must set assessment criteria and methods to ensure students achieve basic requirements based on given criteria before proceeding with further learning activities.
>> See the General education program in Mathematics issued with Circular 32/2018/TT-BGDDT: Download

