What is the Cauchy-Schwarz inequality? When do students in Vietnam learn about the Cauchy-Schwarz inequality?
What is the Cauchy-Schwarz inequality?
The Cauchy-Schwarz inequality is an important inequality in mathematics that is often used to find the maximum and minimum values of an expression. It compares the arithmetic mean to the geometric mean of a set of non-negative numbers.
The Cauchy-Schwarz inequality is formulated as follows:
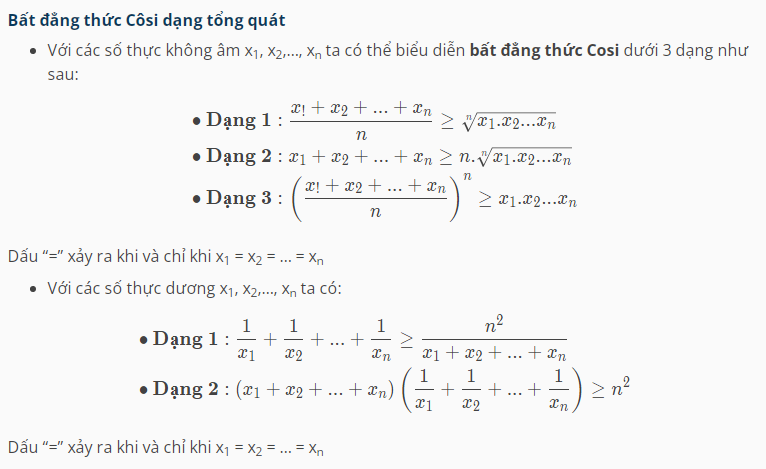
A special form of the Cauchy-Schwarz inequality is as follows:

*Note: Information is for reference only./.
What is the Cauchy-Schwarz inequality? When do students in Vietnam learn about the Cauchy-Schwarz inequality? (Image from the Internet)
When do students in Vietnam learn about the Cauchy-Schwarz inequality?
Additionally, based on Section V of the Mathematics Education Program issued together with Circular 32/2018/TT-BGDDT, it is evident that the grade 9 mathematics program requires the following:
In the section on first-degree polynomial inequalities in one variable, students will learn about: Inequalities and first-degree polynomial inequalities in one variable. Specifically, grade 9 students will learn to:
- Recognize the order in the set of real numbers.
- Recognize inequalities and describe some of the basic properties of inequalities (transitive property; the relationship between order and addition/multiplication).
- Recognize the concept of a first-degree polynomial inequality in one variable, and the solution of such inequalities.
- Solve first-degree polynomial inequalities in one variable.
Therefore, based on the above regulation, it can be seen that the Cauchy-Schwarz inequality will be taught in the 9th grade.
What educational content is required in the grade 9 mathematics curriculum in Vietnam?
According to Section V of the Mathematics Education Program issued along with Circular 32/2018/TT-BGDDT, the grade 9 mathematics curriculum requires the following educational content:
*For Core Content:
- The mathematics curriculum is integrated around three strands of knowledge: Numbers, Algebra and Some Analysis Elements; Geometry and Measurement; Statistics and Probability.
- Numbers, Algebra, and Some Elements of Analysis are the foundation for all further mathematical studies. They aim to form mathematical tools to solve problems in mathematics and related scientific fields, fostering students' deductive reasoning skills, logical thinking, mathematical creativity, and the ability to use algorithms.
Functions are also critical tools for building mathematical models of processes and phenomena in the real world.
- Geometry and Measurement are crucial components of mathematical education, essential for students to acquire knowledge about space and practical skills.
Geometry and Measurement provide tools to describe objects and entities in the surrounding world, equip students with basic mathematical knowledge and skills in Geometry and Measurement (with common measurement quantities), and foster deductive reasoning, the ability to conduct mathematical proofs, contributing to logical thinking and mathematical creativity, spatial imagination, and intuition.
Additionally, Geometry contributes to aesthetic education and enhances students' mathematical culture. The integration of Measurement and Geometry enhances the intuitiveness and practicality of mathematics teaching.
- Statistics and Probability are mandatory components of school mathematics education, enhancing the application and practical value of mathematical education.
Statistics and Probability enable students to perceive and analyze information presented in various forms, understand the probabilistic nature of many real-world dependencies, gain insights into the role of statistics as a critical source of information socially, and apply statistical thinking to data analysis.
From there, students' understanding and methodological research into the modern world are elevated.
- Moreover, the mathematics curriculum at each educational level allocates adequate time for practical and experiential activities, such as undertaking projects and studies in Math, especially on practical mathematical applications; organizing mathematics games, math clubs, forums, workshops, and competitions; publishing wall newspapers (or newsletters) on Mathematics; visiting math education and research institutions, and interacting with students skilled in and passionate about Math. These activities enable students to creatively apply accumulated mathematical knowledge, skills, attitudes, and personal experiences to real-life situations; develop organizational and management capabilities, self-awareness, and self-activation; help students identify their abilities and preferences early on to guide career choices and establish fundamental skills for future workers and responsible citizens.
*Regarding Study Themes
- In each grade during the career-oriented education phase, students (especially those oriented towards natural sciences and technology) can choose to study specific themes. These themes aim to:
- Provide additional knowledge and skills in Mathematics to meet deeper differentiation requirements (e.g., mathematical induction; systems of first-degree equations in three variables; discrete random variables and characteristic numbers of discrete random variables; plane transformations; technical drawing; some elements of graph theory); create opportunities for students to apply math to interdisciplinary and practical problems, forming a scientific basis for STEM education (e.g., knowledge about systems of first-degree equations allows solving some physics problems involving resistor calculations, current intensity in direct current,...; balancing reactions in some chemistry problems,...; some biology problems about mitosis, meiosis,...; knowledge about derivatives to solve optimization problems about distance, time, economics;...).
- Help students gain deeper understanding of the role and applications of Mathematics in reality; gain insights into careers related to Mathematics and its value as a basis for career guidance after high school.
- Create opportunities for students to recognize their talent, interests, develop enthusiasm and confidence in learning Mathematics; develop mathematical capabilities and the ability to explore issues related to Mathematics throughout their lives.

