What is a rectangular prism? What is the formula for calculating the volume of a rectangular prism? Which skills does the Mathematics subject in upper secondary school help students in Vietnam to develop?
What is a rectangular prism?
- A rectangular prism is a three-dimensional shape comprised of 6 faces, all of which are rectangles.
+ The rectangular prism has 12 edges, 8 vertices, and 6 faces.
+ The diagonals with endpoints as opposite vertices of the rectangular prism converge at a single point.
+ The area of the two opposite faces of a rectangular prism is equal.
+ The perimeter of the two opposite faces of a rectangular prism is equal.
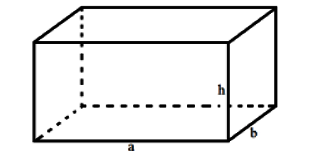
What is the formula for calculating the volume of a rectangular prism?
- The volume of a rectangular prism is equal to the area of the base times its height.
V = a.b.h
Where:
+ V is the volume
+ a and b are the length and width of the base, respectively.
+ h is the height of the rectangular prism.
*Note: Information is for reference only./.
What is a rectangular prism? What is the formula for calculating the volume of a rectangular prism? Which skills does the Mathematics subject in upper secondary school help students in Vietnam to develop? (Image from the Internet)
Which skills does the Mathematics subject in upper secondary school help students in Vietnam to develop?
Based on the Mathematics curriculum for general education issued with Circular 32/2018/TT-BGDDT:
General objectives
The Mathematics curriculum helps students achieve the following primary objectives:
a) Form and develop mathematical skills, including the following core components: the ability to think and reason mathematically; the ability to model mathematically; the ability to solve mathematical problems; the ability to communicate mathematically; the ability to use mathematical tools and means.
b) Contribute to forming and developing in students the main qualities and general skills at the levels appropriate to the subject and educational level stipulated in the Overall Program.
c) Possess popular, basic, and essential mathematical knowledge and skills; develop the ability to solve integrated problems involving Mathematics and other subjects such as Physics, Chemistry, Biology, Geography, Informatics, Technology, History, Art,...; create opportunities for students to experience and apply mathematics to real life.
d) Have a relatively general understanding of the usefulness of mathematics in different related professions to serve as a career orientation basis and have minimum capacity to self-learn mathematical issues throughout life.
Thus, according to the above regulations, the objective of the Mathematics subject in the 2018 general education program helps develop mathematical skills including:
- The ability to think and reason mathematically;
- The ability to model mathematically;
- The ability to solve mathematical problems;
- The ability to communicate mathematically;
- The ability to use mathematical tools and means.
What are the primary objectives of the Mathematics subject in upper secondary school?
Based on Subsection 4, Section 3 of the Mathematics curriculum for general education issued with Circular 32/2018/TT-BGDDT, the upper secondary school mathematics aims to help students achieve the following primary objectives:
(1) Contribute to forming and developing mathematical skills with the requirements to be achieved: pose and answer questions when reasoning and problem-solving; use reasoning, induction, and deduction methods to understand the different approaches in problem-solving;
Establish mathematical models to describe situations, thereby proposing solutions to the mathematical problems set out in the established model; execute and present problem-solving solutions and evaluate the solution, reflect on the value of the solution, generalize for similar problems; use tools and means to learn mathematics in learning, exploration, and mathematical problem-solving.
(2) Hold basic, essential mathematical knowledge and skills regarding:
- Algebra and some elements of calculus: Calculate and use calculation tools; use algebraic language and symbols; transform algebraic and transcendental expressions (trigonometric, exponential, logarithmic), equations, systems of equations, inequations; recognize basic elementary functions (power, trigonometric, exponential, logarithmic); investigate functions and draw function graphs using calculus tools;
- Use function language, function graphs to describe and analyze some real-world processes and phenomena; use integration for calculating the area of flat shapes and volume of solids in space.
- Geometry and Measurement: Provide knowledge and skills (at a logical reasoning level) about geometric relations and some familiar plane and solid figures; algebraic methods (vectors, coordinates) in geometry; develop spatial imagination; solve simple practical problems associated with Geometry and Measurement.
- Statistics and Probability: Perfect the ability to collect, classify, represent, analyze, and process statistical data; use statistical data analysis tools through characteristic numbers measuring central tendency and level of dispersion for ungrouped and grouped data samples; use statistical rules in practice; recognize random models, basic concepts of probability, and the significance of probability in practice.
(3) Help students have a relatively general understanding of professions associated with Mathematics and its value; provide a foundation for career orientation after upper secondary school; have the minimum capacity to self-inquire into mathematical issues throughout life.

