What are sources of initial healthcare care funds for lower secondary school students in Vietnam?
What are sources of initial healthcare care funds for lower secondary school students in Vietnam?
Concerning issues related to school healthcare, specifically healthcare in lower secondary schools, these are regulated in Article 3 of Joint Circular 13/2016/TTLT-BYT-BGDDT as follows:
Funding Sources
1. The funding sources for school healthcare work include:
a) Annual healthcare, education, and training budget funds according to the current budget decentralization of the units;
b) Student health insurance funds as per current regulations;
c) Sponsorship and support from domestic and foreign organizations, individuals according to the law, and other legitimate income sources.
2. School healthcare funds must be used for the right purposes and policies according to current state regulations.
3. Preparing budget estimates, implementing, and finalizing the healthcare funding for schools should comply with current regulations.
Thus, the funding for implementing healthcare tasks in lower secondary schools will come from healthcare careers and student health insurance funds.
Additionally, according to Article 34 of Decree 146/2018/ND-CP, managing and using the health insurance fund stipulates the conditions and content of expenditures as well as the process of settling costs for initial healthcare that lower secondary schools need to meet as follows:
[1] A lower secondary school (educational institution) must have at least one person qualified in medical examination and treatment according to the law on medical examination and treatment to work full-time or part-time in the initial healthcare task;
[2] A lower secondary school (educational institution) must have a medical room or a separate workspace to perform first aid, initial handling for subjects managed by the educational or vocational education institution, agencies, organizations, enterprises in case of injuries or common diseases during the time they study or work there.
* Note: Funding from the health insurance fund for medical examination and treatment in initial healthcare only applies to the lower secondary school (educational institution) as stipulated in point b, clause 1, Article 31 of Decree 146/2018/ND-CP.
Except in cases where the educational institution or vocational educational institution, agency, organization, enterprise has signed a contract for medical examination and treatment under health insurance as regulated in Article 19 of Decree 146/2018/ND-CP.
* When considering additional funding, the authority assessing the request for funding for the lower secondary school must also consider the following content of expenditures:
{1} Expenditure on purchasing medicines, medical supplies serving first aid, initial handling for children, students, and subjects managed by agencies, organizations, enterprises in case of injuries or common diseases during the period of study or work at educational or vocational institutions, agencies, organizations, enterprises;
{2} Expenditure on purchasing and repairing common medical equipment serving initial healthcare, health record management cabinets at educational or vocational institutions, agencies, organizations, enterprises;
{3} Expenditure on office supplies serving the medical examination and treatment activities in initial healthcare work.
* The payment and settlement of funds when lower secondary schools are provided with funding will be as follows:
(1) For public educational institutions or vocational institutions, expenses on medical examination and treatment in initial healthcare are accounted into healthcare tasks costs, and settled with the higher management unit as per current regulations;
(2) For private educational or vocational institutions, expenses on medical examination and treatment in initial healthcare are accounted into the institution's costs, and settled with the higher unit (if any);
(3) For businesses and economic organizations, separate accounting books should be opened to reflect the receipt and usage of funds, not included in the general cost settlement of businesses, economic organizations;
(4) For other agencies and units, expenses on medical examination and treatment in initial healthcare are accounted for as healthcare tasks costs of the agency or unit and settled with the direct higher management agency (if any) or the financial agency of the same level per current regulations.
**Note: lower secondary schools receiving funding for medical examination and treatment in initial healthcare as regulated in Decree 146/2018/ND-CP are responsible for using it for initial healthcare tasks only, not for other purposes.
Unused funds at the end of the year can be carried over to the next year without settling with the social insurance agency.
Thus, simply put, the expenditure from health insurance funds for initial healthcare for lower secondary school students requires the school to comply with and meet all conditions and suitable expenditure content.
Only then can they be funded from the health insurance funds for implementing medical examination and treatment in initial healthcare.

What are sources of initial healthcare care funds for lower secondary school students in Vietnam? (Image from Internet)
What are conditions for lower secondary school classroom healthcare in Vietnam?
Based on Article 4 of Joint Circular 13/2016/TTLT-BYT-BGDDT, classroom healthcare for lower secondary schools must ensure the following conditions:
* Classroom
- Lower secondary schools, lower secondary school classes must meet the design requirements specified in section 5.2 of the Vietnamese Standard (TCVN 8794: 2011) issued under Decision 2585/QD-BKHCN in 2011 as follows:
** Classroom Block
- The classroom block includes classrooms and subject classrooms.
NOTE: Subject classrooms are rooms equipped and installed with suitable tools and equipment for teaching, specifically for one or several subjects. Subject classrooms serve as both teaching rooms and laboratories, for both theoretical and practical purposes.
- The number of classrooms is to be built corresponding to the number of classes (2 sessions/day) of the school. The classroom area is determined based on the area criterion per student, the number of students, and the minimal area needed for the arrangement of teaching tools and equipment.
- The number of subject classrooms is determined based on the education program and plan issued by the Ministry of Education and Training. For each subject, the number of subject classrooms is calculated from the total number of experimental and practical sessions for all grades.
- Subject classrooms are used for lessons that include experiments and practical work.
NOTE: Schools with the conditions may build additional laboratories for experiments related to the lessons.
- The area standard for classrooms and subject classrooms is specified in Table 2.
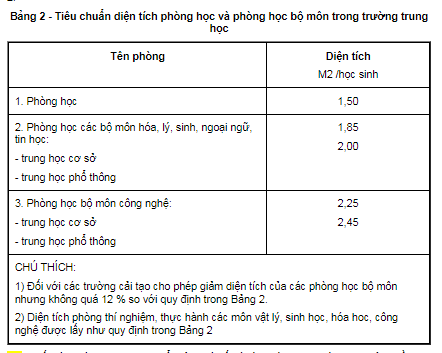
- For upper secondary schools with practice and labor rooms, the area standard is from 1.5 m² to 2.0 m² per student. For specialized technical practice workshops (tailor workshop, carpentry workshop, mechanical workshop, electrical workshop), the area standard is from 3.0 m² to 6.0 m² per student.
NOTE: The areas mentioned above are calculated based on the number of students in a lesson. They can be combined with local vocational training centers.
- The width of classrooms and subject classrooms must not be less than 7.20 m. The ratio of length to width of subject classrooms must not exceed 2.
- Subject classrooms must have preparation rooms with areas from 12 m² to 27 m², placed adjacent and accessible from the subject classrooms.
- The size of desks and chairs must comply with the regulations in TCVN 7490. The height of the desk for students with disabilities is from 700 mm to 750 mm; the chair height is from 400 mm to 500 mm.
Under the desk, there should not be sharp or rough surfaces, with space for knee clearance and footrest for wheelchair users.
- The arrangement of desks and chairs in the classroom must comply with TCVN 7491.
NOTE: Seats for students with disabilities should be placed at the front, near the classroom entrance.
The seating plan should be accessible by students with disabilities: maximum reach height of 1.20 m, forward reach over an obstruction of 0.4 m, horizontal unobstructed reach to the sides of 0.5 m.
In classrooms with students with disabilities, there should be no teacher’s podium.
- Desks and chairs in physics, chemistry, biology, and technology subject classrooms should be specialized to meet the particular requirements of each subject.
- The height from the floor to the bottom edge of the board should not be less than 0.8 m and not more than 1.0 m.
NOTE: If conditions allow, the board should be designed to move vertically to accommodate students with disabilities. The bottom edge of the board should not be less than 0.40 m.
- Classrooms should be designed with two entrances, one at the front and one at the back of the classroom.
- Doors should be double-leaf, at least 1.0 m wide, and open towards the corridor.
NOTE: In inclusive classrooms for students with disabilities, the clear width of the entrance should not be less than 1.20 m.
What are regulations on school sanitation regarding lower secondary school healthcare tasks in Vietnam?
Based on Article 2 of Joint Circular 13/2016/TTLT-BYT-BGDDT, the definition of school sanitation is as follows:
Explanation of Terms
In this Joint Circular, the following terms are understood as:
1. School sanitation refers to the conditions ensuring the environment, physical facilities of schools, classroom equipment, policies for teaching, studying, physical exercise, sports, and healthcare in schools.
...
Thus, according to the above regulations, school sanitation is understood as conditions ensuring the environment, physical facilities of schools, classroom equipment, policies for teaching, studying, physical exercise, sports, and healthcare in lower secondary schools.

