What are conditions for physical facilities to ensure food safety in schools in Vietnam?
What are conditions for physical facilities to ensure food safety in schools in Vietnam?
Pursuant to subsection 1, Section 3 of the Guidance issued with Decision No. 2195/QD-BGDDT in 2022, the conditions for physical facilities to ensure food safety in schools in Vietnam are as follows:
- For preschool educational institutions:
+ Kitchen: Independent from other functional rooms; includes a preparation area, processing area, cooking area, and food distribution area; designed and organized for a one-way operational flow.
+ Kitchen storage: Separately divides food storage and ingredient storage; has convenient, independent entry and exit points and zones for different types of food; equipped with food preservation equipment; walls, ceilings, and floors in the storage area are impermeable, not cracked, and mold-free.
- For primary schools:
+ Kitchen: Independent from study and learning support blocks; follows a one-way operational process, maintaining hygiene.
+ Kitchen storage: Separately divides food storage and ingredient storage; has convenient, independent entry and exit points and zones for different types of food; equipped with food preservation equipment. Walls, ceilings, and floors in the storage area are impermeable, not cracked, and mold-free.
+ Dining hall (for schools with boarding facilities): Fully equipped to serve students.

What are conditions for physical facilities to ensure food safety in schools in Vietnam? (Image from the Internet)
What is the role of school meals in the health of students in Vietnam?
According to subsection 2, Section 1 of the Guidance issued with Decision No. 2195/QD-BGDDT in 2022, the role of school meals in the health of students is:
- Providing energy and nutrients to meet the requirements for learning and physical activities, fostering physical and mental development appropriate for their age.
- Ensuring food security and nutrition for students under policy support, who receive free school meals, helping children to develop healthily and have adequate energy for learning.
- Forming healthy eating habits beneficial to student health.
- Supporting the control of nutrition-related diseases, including malnutrition, micronutrient deficiencies, and obesity.
What are general principles in organizing school meals in Vietnam?
According to Section 1, Part 2 of the Guidance issued with Decision No. 2195/QD-BGDDT in 2022, the general principles for organizing school meals are as follows:
(1). Ensure Adequate Energy and Nutrient Supply
- For nursery children (<36 months)
* Energy recommendations for nursery children
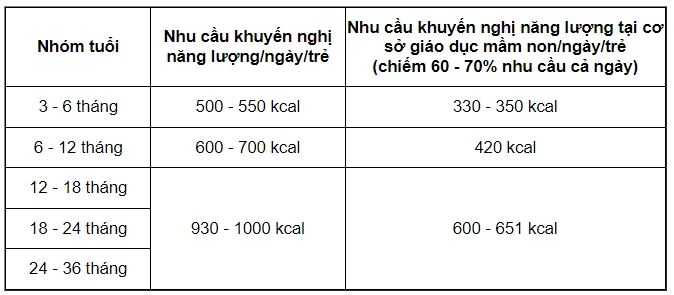
* Recommended energy-yielding nutrient ratios:
+ Protein provides about 13% - 20% of dietary energy.
+ Fat provides about 30% - 40% of dietary energy.
+ Carbohydrates provide about 47% - 50% of dietary energy.
- For kindergarten children (36 - 72 months)
* Energy and policy recommendations for kindergarten children
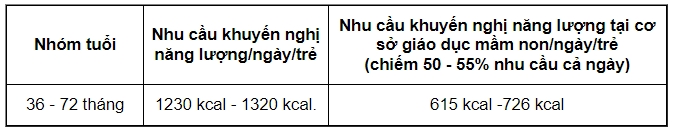
* Recommended energy-yielding nutrient ratios:
+ Protein provides about 13% - 20% of dietary energy.
+ Fat provides about 25% - 35% of dietary energy.
+ Carbohydrates provide about 52% - 60% of dietary energy.
- For primary school students (6 to 11 years old)
* Energy recommendations at school
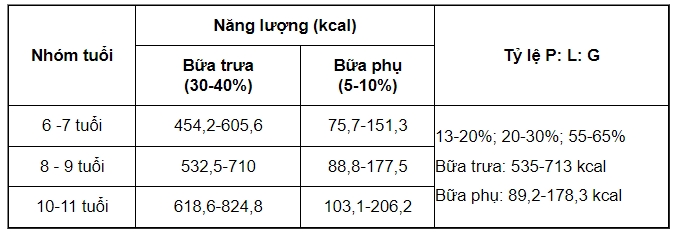
* Recommended energy-yielding nutrient ratios:
+ Protein provides about 13% - 20% of dietary energy.
+ Fat provides about 20% - 30% of dietary energy.
+ Carbohydrates provide about 55% - 65% of dietary energy.
In addition to energy, proteins, fats, and carbohydrates, it is essential to ensure adequate supply of important micronutrients such as calcium, iron, zinc, vitamin A, B vitamins, vitamin C, vitamin D, vitamin E, and fiber.
(2). Ensure the Energy Allocation Ratios of Meals for Students at School
The energy distribution of meals for students at school must adhere to the general ratios for daily meals by age group as follows:
* Energy distribution for the meals of nursery children (<36 months)
- Number of meals at preschool: Two main meals and one supplementary meal.
+ The lunch provides 30% to 35% of the daily energy.
+ The afternoon meal provides 25% to 30% of the daily energy.
+ The supplementary meal provides about 5% to 10% of the daily energy.
* Energy distribution for the meals of kindergarten children (36 - 72 months)
- Number of meals for kindergarten children at preschools: One main meal and one supplementary meal.
+ The main lunch provides 30% to 35% of the daily energy.
+ The afternoon meal provides 15% to 25% of the daily energy.
*Note: When conditions allow (parental needs, human resources, infrastructure, etc.), the institution may organize breakfast for children. However, it must be agreed upon by the principal, teaching staff, and parents. Breakfast provides about 10% - 15% of the daily energy requirement.
* Energy distribution for the school meals of primary students
- Number of meals for primary students at school: One main meal and one supplementary meal
+ Lunch provides 30-40% of the recommended daily energy requirement by age group.
+ The supplementary meal provides 5-10% of the daily energy requirement.
- For primary schools organizing four meals:
+ Breakfast provides 25-30% of the daily energy requirement.
+ Lunch provides 30-40% of the daily energy requirement.
+ The supplementary meal provides 5-10% of the daily energy requirement.
+ Dinner provides 25-30% of the daily energy requirement.
- For primary schools that do not organize school meals or provide meals without a supplementary meal: Ensure at least three main meals for students, and do not let them go to school without breakfast.
(3). Ensure the Development of a Scientific, Balanced, and Reasonable Meal Menu
- The school meal menu must ensure food variety. It should include stir-fried dishes, savory dishes, soups, and desserts. The menu should contain at least 10 different food items, with at least 5 out of the 8 food groups recommended by the World Health Organization, including a mandatory fat group. These include protein-rich foods (meat, fish, seafood, eggs, legumes…), fats (cooking oil, grease), carbohydrates (rice, noodles, pho, vermicelli…), vegetables, fruits, and milk.
- The menu should be feasible, reasonably prepared to ensure nutrition and food safety, compliant with the regulations and conditions of each facility.

