What are the guidelines for proper handwriting practice? What are the teaching objectives for the 2nd-grade Vietnamese language subject?
What are the guidelines for proper handwriting practice in Vietnam?
The guidelines for proper handwriting practice in Vietnam provide specific and detailed instructions on how to hold a pen, proper sitting posture, how to write letters, and exercises to help learners achieve beautiful, clear, and aesthetically pleasing handwriting.
Students and teachers may refer to the guidelines for proper handwriting practice in Vietnam below:
|
Guidelines for proper handwriting practice in Vietnam 1. Choose Suitable Writing Tools |
Note: The above information is for reference only.
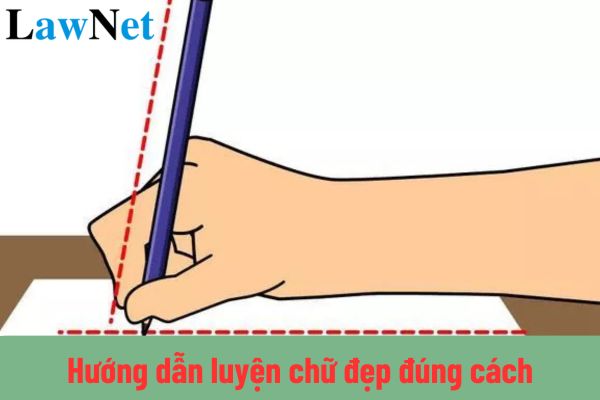
What are the guidelines for proper handwriting practice in Vietnam? What are the teaching objectives for the 2nd-grade Vietnamese language subject? (Image from the Internet)
What are the teaching objectives for the 2nd-grade Vietnamese language subject?
According to subheading 2, Section 3 of the general education program for Literature issued with Circular 32/2018/TT-BGDDT, the teaching objectives for the 2nd-grade Vietnamese language subject are as follows:
- Help students form and develop essential qualities with specific manifestations: love for nature, family, and homeland; awareness of their roots; appreciation for beauty and goodness, and healthy emotions; enthusiasm for learning and work; honesty and integrity in learning and life; awareness of responsibilities towards themselves, family, society, and the surrounding environment.
- Help students initially form general competencies, and develop language skills in all reading, writing, speaking, and listening at a basic level: correct and fluent reading of texts; understanding the main content and information of texts; relating and comparing outside texts; correct spelling and grammar; writing some sentences, short paragraphs, mainly stories, and descriptions; clear articulation; and understanding spoken opinions.
Develop literary competence with the requirement to distinguish between poetry and stories, know how to read poetry and stories; recognize the beauty of artistic language; have imagination, and understand and empathize with the beauty and goodness of people and the world reflected in literary texts.
What learning outcomes are required for specific competencies in the 2nd-grade Vietnamese language subject?
Under section 2.1, subheading 2, Section 4 of the general education program for Literature issued with Circular 32/2018/TT-BGDDT, the learning outcomes required for specific competencies in the 2nd-grade Vietnamese language subject are as follows:
* Language Competence
- Correctly, fluently, and expressively reading texts; understanding the main content of texts, mainly explicit content; initially understanding implicit content such as themes and lessons drawn from the texts read.
- Reading requirements include reading techniques and comprehension skills, focusing on reading correctly at an appropriate speed, and understanding the simple content of texts.
- Writing correct spelling, vocabulary, and grammar; writing some short sentences and paragraphs.
- Writing texts recounting stories read, witnessed, participated in, and stories imagined by students; describing familiar objects and phenomena; introducing objects and activities close to students' lives.
Writing paragraphs expressing the feelings and thoughts of students when reading a story, a poem, when witnessing an event that evokes many emotions; expressing opinions on a simple issue in study and life; writing some types of texts such as: autobiographies, messages, invitations, schedules, applications,...; initial understanding of writing processes; written work should have all three parts (introduction, body, conclusion).
- Clearly presenting ideas and emotions; initially knowing how to use appropriate gestures and posture when speaking; being able to clearly recount stories read or heard; sharing and exchanging emotions, attitudes, and thoughts regarding discussed topics; knowing how to explain a subject or a simple process.
- Listening with appropriate attitudes and grasping the main content; recognizing the emotions of the speaker; knowing how to respond to what has been heard.
* Literary Competence
- Distinguishing between prose and poetry (segment, prose, and segment, verse); recognizing the content of texts and the attitudes and emotions of the writer; initial understanding of the effect of some formal elements of literary texts (language, characters, plot, verse, comparisons, personification). Knowing how to associate, imagine, and express with literary attributes in both writing and speaking.
- Recognizing who or what a text talks about; identifying characters in stories, and rhymes in poetry; distinguishing between stories and poetry.

