What are the 1st-semester question papers and answers for 6th-grade History and Geography? What are the requirements on contents for lower secondary education in Vietnam?
What are the 1st-semester question papers and answers for 6th-grade History and Geography in Vietnam?
Students can refer to the following 1st-semester question papers and answers for 6th-grade History and Geography in Vietnam:
|
Department of Education and Training ...
1st-semester question paper - Knowledge Connection
2024 - 2025 Academic Year
Subject: 6th-grade History and Geography
Duration: 45 minutes
(Question paper No. 1)
Part 1. Multiple Choice (5.0 points)
Question 1. Which of the following is the oldest poetry collection in China, consisting of many folk compositions, collected and edited by Confucius?
A. Li Tao.
B. Book of Songs.
C. Heaven's Questions.
D. Chu Ci.
Question 2. Qin Shi Huang unified the territory of China (in 221 BC) through which method?
A. War.
B. Diplomacy.
C. Law.
D. Cultural assimilation.
Question 3. Who is the author of the epics Iliad and Odyssey?
A. Homer.
B. Polybius.
C. Herodotus.
D. Pythagoras.
Question 4. A representative architectural work in ancient Rome is
A. Parthenon Temple.
B. Babylon City.
C. Colosseum.
D. Great Wall.
Question 5. When did the early Southeast Asian countries emerge?
A. Second millennium BC.
B. From the seventh century BC to the seventh century.
C. Seventh century BC.
D. Tenth century BC.
Question 6. Southeast Asia holds a very important geographical position because this region
A. is the center of the world.
B. borders China.
C. is the "crossroads" of the world.
D. borders India.
Question 7. Which feudal state in Southeast Asia developed significantly through maritime trade?
A. Champa.
B. Au Lac.
C. Van Lang.
D. Sri Vijaya.
Question 8. What famous commodities were the feudal states of Southeast Asia known for?
A. Spices.
B. Grapes.
C. Dates.
D. Olives.
Question 9. How did the trade interaction affect the economic development of feudal kingdoms in Southeast Asia?
A. Southeast Asian economies became heavily dependent on foreign countries.
B. The feudal kingdoms in Southeast Asia only traded with Indian merchants.
C. Southeast Asia exported many key products like wheat, grapes, olives…
D. Many bustling ports emerged in Southeast Asian kingdoms.
Question 10. Which religion from India fused with indigenous beliefs in Southeast Asia?
A. Hinduism and Christianity.
B. Buddhism and Christianity.
C. Hinduism and Buddhism.
D. Hinduism and Islam.
Question 11. Which ancient Indian literary work exerted widespread influence in many Southeast Asian countries?
A. Ramayana.
B. Mahabharata.
C. Shakuntala.
D. Vedas.
Question 12. Which statement below is incorrect when assessing Southeast Asian culture?
A. Indigenous beliefs merged with imported religions.
B. Southeast Asian inhabitants did not develop their own script.
C. Indian literature had a strong influence on Southeast Asian literature.
D. Temple-mountain architecture is a typical Hindu style in Southeast Asia.
Question 13. What is the first step when interpreting the content of any map?
A. Read the legend.
B. Determine orientation.
C. Check the map scale.
D. Study contour lines.
Question 14. What shape is the Earth?
A. Circular.
B. Square.
C. Spherical.
D. Oval.
Question 15. The alternation of day and night results from the
A. Earth's orbit around the Sun.
B. Earth's rotation on its axis.
C. Earth's orbit around other planets.
D. Earth's orbital movement around the Sun.
Question 16. During which season of the year do days become shorter and nights longer?
A. Spring.
B. Autumn.
C. Winter.
D. Summer.
Question 17. What is the highest temperature in the Earth's core?

Question 18. The main energy source for endogenic processes is not
A. the decomposition of radioactive substances.
B. energy from nuclear tests.
C. energy from chemical reactions.
D. movement of material flows.
Question 19. Most of the Mantle layer provides energy for which activities?
A. Earthquakes, volcanoes.
B. Tsunamis, sea-level rise.
C. Volcanoes, tsunamis.
D. Earthquakes, ravines.
Question 20. Which type of terrain is favorable for cultivating food and livestock crops?
A. Plateau.
B. Plain.
C. Hill.
D. Mountain.
Part 2. Script (5.0 points)
Question 1 (3.0 points). What are the advantages and disadvantages of the natural conditions in ancient Greece and Rome for the formation and development of civilizations there?
Question 2 (2.0 points). State the differences in thickness, state, and temperature among the Earth's crust, mantle, and core (a comparison chart can be used).
|
ANSWER KEY
Part 1. Multiple Choice (5.0 points)
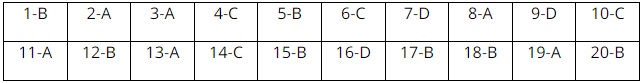
Part 2. Script (5.0 points)
Question 1 (3.0 points).
(1) Advantages:
- Rich in mineral resources and especially having a convenient geographical position (coastal) which promotes the development of handicrafts and trade (especially maritime trade).
- Favorable geographical location for cultural exchange, learning, and adoption.
(2) Disadvantages:
- Due to poor arable land, stone and bronze tools were ineffective. It wasn't until the advent of iron tools that agriculture became efficient => leading to surplus production, which caused private ownership and class division in society. Consequently, ancient states emerged in the West around the first millennium BC (later than in the East).
- As the territory was fragmented, it was challenging to concentrate large populations. When class societies formed, each region, each peninsula became a state, thus each had a relatively small area.
Question 2 (2.0 points):
| Layer |
Earth's Crust |
Mantle Layer |
Core Layer |
| Thickness |
5km - 70km. |
2900km. |
3400km. |
| State |
- Outer thin hard layer.
- Composed of different rock layers.
- Divided into continental and oceanic crust.
- Exists in a solid state. |
Divided into 2 sections:
- Upper mantle in a viscous state.
+ Lower mantle in a solid state. |
- Divided into 2 sections:
+ Outer core in a liquid state.
+ Inner core in a solid state.
- Mainly composed of heavy metals Ni, Fe (also called Nife core). |
| Temperature |
Temperature increases with depth, maximum up to 1000°C. |
From 1500°C to 4700°C. |
About 5000°C. |
Note: Information is for reference purposes only!

What are the 1st-semester question papers and answers for 6th-grade History and Geography? What are the requirements on contents for lower secondary education in Vietnam? (Image from Internet)
What does the History curriculum benefit students in Vietnam?
According to Section 3 of the General Education Program for History included with Circular 32/2018/TT-BGDDT, the objectives of the History curriculum are as follows:
- The History curriculum helps students develop historical competence, a manifestation of scientific capabilities formed at the secondary school level; contributes to nurturing national spirit, patriotism, and the good traditional values of the nation and human cultural essences, characteristics, and competencies of Vietnamese citizens and global citizens in line with contemporary development trends;
- The History curriculum helps students access and clearly understand the role and characteristics of historical science and the connection between history and various scientific fields and professions, providing a foundation for students to orient their future careers.
What are the requirements on contents for lower secondary education in Vietnam?
According to Article 30 of the Education Law 2019, the requirements on contents for lower secondary education in Vietnam are as follows:
- The contents of general education must ensure the popular, basic, comprehensive, career-orienting, and systematic characteristics; linking with the realities of life, appropriate to the psycho-physiological characteristics of students, meeting the objectives of education at each level.
- Lower secondary education shall consolidate and develop the contents learned in primary education, guarantee students the basic general knowledge in Vietnamese, mathematics, national history, other knowledge in social sciences, natural sciences, law, informatics, foreign languages; with introductory understanding on techniques and career-orientation.




