What are the 2nd mid-semester question papers and answers for 7th-grade Mathematics in 2025? What are the characteristics of 7th-grade Mathematics in Vietnam?
What are the 2nd mid-semester question papers and answers for 7th-grade Mathematics in 2025?
2nd mid-semester question papers and answers for 7th-grade Mathematics
Question paper No. 1:
Question 1. Replace the ratio 1.25 : 3.45 with a ratio between integers to get
A. 12.5 : 34.5;
B. 29 : 65;
C. 25 : 69;
D. 1 : 3.
Question 2. Given 7x = 4y and y – x = 24. Then, the values of x, y are
A. x = −56, y = −32;
B. x = 32, y = 56;
C. x = 56, y = 32;
D. x = 56, y = −32.
Question 3. Knowing that y is directly proportional to x with a ratio coefficient k = 2. When x = –3, what is the value of y?
A. –6;
B. 0;
C. –9;
D. –1.
Question 4. Given that x and y are inversely proportional quantities and when x = –12 then y = 8. When x = 3, y is:
A. –32;
B. 32;
C. –2;
D. 2.
Question 5. The algebraic expression for “The square of the sum of two numbers x and y” is
A. x^2 − y^2;
B. x + y;
C. x^2 + y^2;
D. (x + y)^2.
Question 6. The constant term of the polynomial M = 8x^2 – 4x + 3 – x^5 is
A. 1;
B. 4;
C. 3;
D. 5.
Question 7. Given two polynomials P(x) = 6x^3 − 3x^2 − 2x + 4 and G(x) = 5x^2 − 7x + 9. The value of P(x) − G(x) is
A. x^2 − 9x + 13;
B. 6x^3 − 8x^2 + 5x − 5;
C. x^3 − 8x^2 + 5x − 5;
D. 5x^3 − 8x^2 + 5x + 13.
Question 8. The result of the multiplication (5x − 2)(2x + 1) is which polynomial among the following?
A. 10x^2 − 3x − 2;
B. 10x^2 − x + 4;
C. 10x^2 + x − 2;
D. 10x^2 − x − 2.
Question 9. In triangle MNP with: ˆN=65°; ˆP=55°. Which of the following statements is true?
A. MP < MN;
B. MP = MN;
C. MP > MN;
D. Insufficient data to compare.
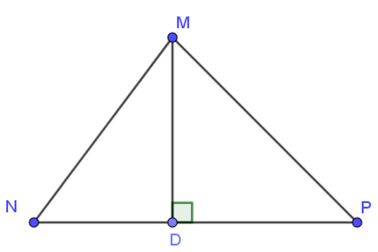
Question 10. In triangle MNP with: MN < MP, MD ⊥ NP. Which of the following statements is true?
A. DN = DP;
B. MD < MP;
C. MD > MN;
D. MN = MP.
Question 11. Which set of line segment lengths below cannot form a triangle?
A. 15cm; 25cm; 10cm;
B. 5cm; 4cm; 6cm;
C. 15cm; 18cm; 20cm;
D. 11cm; 9cm; 7cm.
Question 12. Given that G is the centroid of triangle MNP with median MK. Which of the following statements is true?
A. GM/MK=1/3;
B. GK/MK=1/3;
C. MG/GK=3;
D. GK/MG=2/3.
II. ESSAY SECTION (7.0 points)
Problem 1. (1.5 points) Find the rational number x in the following proportions:
a) 56/56: x = 20 : 3;
b) 9x−19=53;
c) x+11*(4−x)=23.
Problem 2. (1.0 point) A car departs from A at 8 o'clock. At 9 o'clock, another car departs from A. The first car arrives at B at 2 PM. The second car arrives at B half an hour earlier than the first car. Calculate the speed of each car, knowing that the speed of the second car is 20 km/h faster than the speed of the first car.
Problem 3. (2.0 points) Given two polynomials: P(x) = x^3 – 2x^2 + x – 2;
Q(x) = 2x^3 – 4x^2 + 3x – 6.
a) Calculate P(x) – Q(x).
b) Prove that x = 2 is a solution of both polynomials P(x) and Q(x).
Problem 4. (2.0 points) Given triangle ABC with D being the midpoint of AC. On segment BD, take point E so that BE = 2ED. Point F lies on the opposite ray of DE so that BF = 2BE. Let K be the midpoint of CF and G be the intersection of EK and AC.
a) Prove that G is the centroid of triangle EFC.
b) Calculate the ratios GE/GK;GC/DC.
Problem 5. (0.5 points) Given the proportion a/b=c/da/cd. Prove that a−2b/b=c−2d/d.
Question paper No. 2:
Question 1. Statistical data as a number is also called a
A. figure;
B. data;
C. number;
D. Both A, B, and C are incorrect.
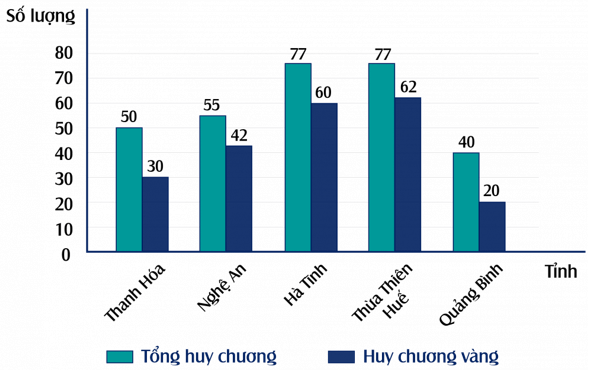
Question 2. Given the chart below
The statistical subject is
A. Number of medals;
B. Number of gold medals;
C. Provinces: Thanh Hoa, Nghe An, Ha Tinh, Thua Thien Hue, Quang Binh;
D. Both A, B, and C are incorrect.
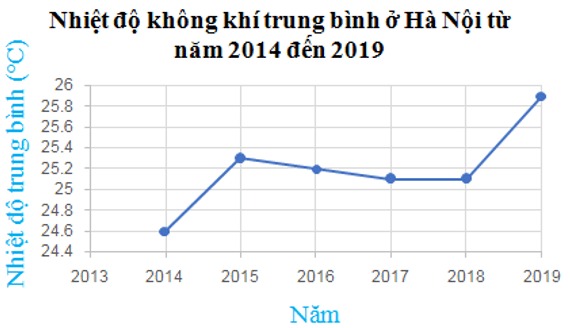
Question 3. Given the segment line chart as shown.
The chart above has 6 points, and each point is determined by
A. Statistical year;
B. Statistical year and average air temperature in Hanoi that year;
C. Average air temperature in Hanoi;
D. Both A, B, and C are incorrect.
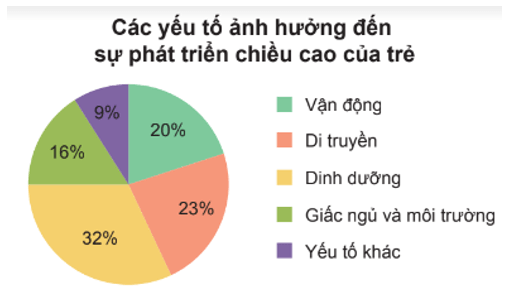
Question 4. Given the following chart.
In the above chart, the factor affecting 23% of children's height development is
A. Exercise;
B. Sleep and environment;
C. Nutrition;
D. Genetics.
Question 5. The probability of an event in a dice game is
A. the product of the number of favorable outcomes for the event and the number of possible outcomes for the face appearing on the dice;
B. the ratio of the number of possible outcomes for the face appearing on the dice to the number of favorable outcomes for the event;
C. the difference in the number of possible outcomes for the face appearing on the dice and the number of favorable outcomes for the event;
D. the ratio of the number of favorable outcomes for the event to the number of possible outcomes for the face appearing on the dice.
Question 6. The quarterfinals of the swimming competition involve six schools with 8 participating representatives:
Nguyen Hue Secondary School: Kiet;
Nguyen Khuyen Secondary School: Long;
Chu Van An Secondary School: Nguyen and Dang;
Nguyen Binh Khiem Secondary School: Minh;
Luu Van Liet Secondary School: Thanh;
Nguyen Du Secondary School: Kha and Binh.
Consider the event “The winner is a student from Nguyen Hue Secondary School or Nguyen Du Secondary School.” Calculate the probability of this event.
A. 1/14;
B. 3/38;
C. 1/13;
D. 1/16.
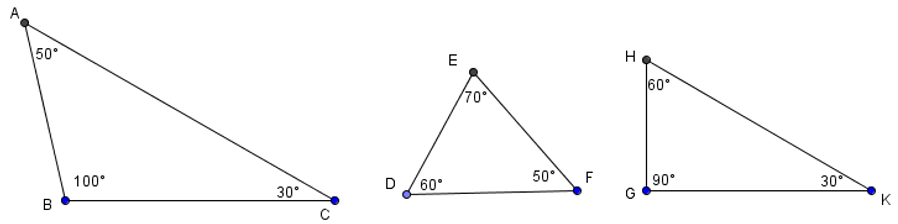
Question 7. Given the triangles below (diagram).
The obtuse triangle is
A. Triangle GHK;
B. Triangle DEF;
C. Triangle ABC;
D. Both A and C.
Question 8. Given triangle MNP with ˆM=80° and ˆN=50°. Compare the lengths of NP and MP:
A. NP > MP;
B. NP = MP;
C. NP < MP;
D. Insufficient condition to compare.
Question 9. Given ∆ABC = ∆MNP. Among the following statements, which is incorrect?
A. ˆB=ˆN;
B. BC = MP;
C. ˆP=ˆC;
D. AB = MN.
Question 10. Given triangle ABC and triangle MNP with AB = MP, AC = NM, BC = NP. Which statement below is correct?
A. ∆ABC = ∆MNP;
B.∆ABC = ∆NMP;
C.∆ABC = ∆PMN;
D.∆ABC = ∆MPN.
Question 11. The correct statement is
A. If two sides and the included angle of one triangle are equal to two sides and the included angle of another triangle, then the two triangles are congruent;
B. If two sides and one angle of one triangle equal two sides and one angle of another triangle, then the triangles are congruent;
C. If two sides of one triangle are equal to two sides of another triangle, then the triangles are congruent;
D. If one angle of one triangle is equal to one angle of another triangle, then the triangles are congruent.
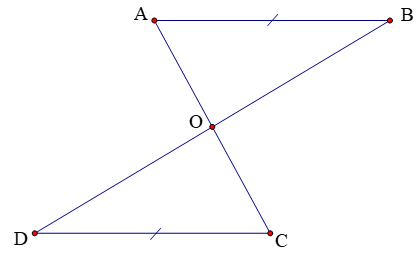
Question 12. Given the figure below, where AB // CD, AB = CD.
The correct statement is
A. OA = OD;
B. ˆBAO=ˆCDO;
C. O is the midpoint of AC;
D. ∆AOB = ∆DOC.
II. ESSAY SECTION (7.0 points)
Problem 1. (2.0 points) The results of the inquiry about the academic classification of 7th graders are given by the statistical table below:
| Academically Classified 7th Graders | ||||
| Type | Excellent | Good | Average | Weak |
| Number of Students | 120 | 285 | 150 | 25 |
a) Classify the data in the statistical table above based on qualitative and quantitative criteria.
Qualitative data: Type of academic classification (Excellent, Good, Average, Weak).
Quantitative data: Number of students (120, 285, 150, 25).
b) Does the above data represent the academic performance of 7th grade students? Why?
The data can represent the academic performance of 7th grade students if it is collected from a large enough sample and reflects the correct distribution of academic performance within the grade. If the students in the statistical table are a representative sample of all 7th graders, then this can be considered representative data.
Problem 2. (1.0 point) A group of 11 tourists from the following countries: England; France; the United States; Thailand; Belgium; India; Netherlands; Cuba; South Africa; Japan; Brazil. Randomly select one person from the above group of tourists. Calculate the probability of the event "The selected tourist is from Europe."
Tourists from Europe: England, France, Belgium, Netherlands.
Total number of tourists: 11.
Number of tourists from Europe: 4.
Probability = 4/11
Problem 3. (3.0 points) Given the straight angle xOy with bisector Ot. On ray Ot, take two points A, B (A is between O and B). Select point C ∈ Ox such that OC = OB, select point D ∈ Oy such that OD = OA.
a) Prove that AC = BD and AC ⊥ BD.
b) Let M, N be the midpoints of AC and BD, respectively. Prove that OM = ON.
c) Calculate the angles of triangle MON.
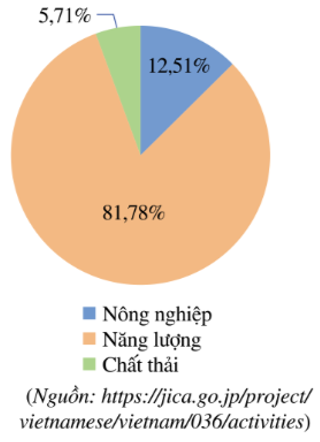
Problem 4. (1.0 point) The pie chart below represents greenhouse gas emissions in three sectors: Agriculture, Energy, and Waste in Vietnam in 2020 (calculated in percentage terms).
Based on the chart above, answer the following questions:
a) Calculate the greenhouse gas emissions generated in the Energy and Waste sectors in Vietnam in 2020. Knowing that the total greenhouse gas emissions in the above three sectors of Vietnam in 2020 is 466 million tons of carbon dioxide equivalent (meaning other greenhouse gases are converted to carbon dioxide for calculating mass).
Total greenhouse gas emissions is 466 million tons CO₂.
Emissions from Energy and Waste will be calculated from the percentage in the chart.
b) State two measures the Vietnamese government has proposed to reduce emissions and mitigate the impact of greenhouse gases.
Develop renewable energy (wind, solar).
Promote the reduction of energy consumption and the use of clean technology.
*Note: Information is for reference only./.
What are the 2nd mid-semester question papers and answers for 7th-grade Mathematics in 2025? What are the characteristics of 7th-grade Mathematics? (Image from the Internet)
What are the characteristics of 7th-grade Mathematics in Vietnam?
Under the Appendix of the General Education Program for Mathematics issued with Circular 32/2018/TT-BGDDT, the 7th-grade Mathematics curriculum is specifically developed as follows:
Mathematics increasingly has more applications in life, and basic math knowledge and skills have helped people systematically and accurately solve real-life problems, contributing to societal development.
Math at secondary schools contributes to forming and developing essential qualities, general competencies, and mathematical competencies for students; it develops key knowledge and skills and creates opportunities for students to experience and apply mathematics in practical situations; it establishes connections between mathematical ideas, between Mathematics and reality, between Mathematics and other subjects and educational activities, especially with Science, Natural Science, Physics, Chemistry, Biology, Technology, and Informatics to implement STEM education.
Mathematics inherently has logical, abstract, and general properties. Therefore, to understand and learn Mathematics, the secondary school Math program needs to ensure a balance between "learning" the knowledge and "applying" the knowledge to solve specific problems.
During the learning and application of mathematics, students always have the opportunity to use technological tools, modern teaching aids, especially electronic calculators and handheld calculators to support the representation, exploration, and discovery of knowledge, as well as the solving of mathematical problems.
In the general education program, Mathematics is a compulsory subject from grade 1 to grade 12. The mathematics education content is divided into two phases:
- Basic education phase: Mathematics helps students systematically understand the most essential mathematical concepts, principles, and rules necessary for everyone, laying the foundation for further academic study or daily life usage.
- Career-oriented education phase: Mathematics provides students with a relatively comprehensive view of Mathematics, understanding its roles and applications in practical situations, and professions related to Mathematics, enabling students to have a basis for career orientation and the ability to independently explore mathematics-related issues throughout their life.
Besides the core educational content, each academic year, students (especially those oriented towards natural sciences and technology) can choose to study certain learning topics.
These topics aim to enhance mathematical knowledge, the ability to apply math knowledge to practice, meeting students' preferences, needs, and career orientations.
The Mathematics curriculum in both educational phases has a linear structure combined with "concentric spiral" (concentric, expand, and progressively escalate), revolving around and integrating three strands of knowledge: Numbers, Algebra and some elements of Calculus; Geometry and Measurement; Statistics and Probability.
What are the requirements regarding teaching equipment for Mathematics in Vietnam?
Under the Appendix of the General Education Program for Mathematics issued with Circular 32/2018/TT-BGDDT, the requirements regarding teaching equipment for Mathematics in Vietnam are as follows:
- Math teaching equipment contains and describes knowledge that can support teachers and help students focus on specific mathematical subjects (concepts, relationships, mathematical properties,...) to discover, explore, and reinforce knowledge during Mathematics learning.
- The use of Math teaching equipment should ensure the following requirements:
+ The teaching equipment should serve the teaching objectives of Mathematics, suitable to the learning content and student groups, supporting innovative teaching methods, and should not increase teaching content, teacher work, and incur unnecessary costs.
+ Use at the right time, in the right place, avoid forms or abuse causing counterproductive effects, reducing the effectiveness of the teaching process; create conditions for students to actually practice, manipulate training devices, thereby helping students actively and positively explore, discover knowledge, and develop "the ability to use tools and means of learning math."
+ Encourage the use of audiovisual means, modern technical means supporting the teaching process, while valuing the use of traditional means. When conditions permit, teachers guide students on how to search for information and materials on the Internet or reputable educational television programs to expand understanding and self-study skills.
+ Enhance self-made teaching equipment: Besides the minimum teaching equipment specified in the list issued by the Ministry of Education and Training, initiatives and creativity of students, teachers, and parents should be mobilized in exploiting, designing, and using self-made teaching equipment.
+ Flexibly coordinate the use of types of teaching equipment: Each type of device has certain advantages and limitations, so depending on the lesson content, teaching methods, different types of teaching equipment may be combined and coordinated reasonably, scientifically, and vividly.
- Based on the objectives and required outcomes of the Math program, the Ministry of Education and Training issues a list of minimum teaching equipment ensuring adequate quantity and types. Specifically:
+ Primary level:
++ Numbers and Calculations: Includes sets of teaching equipment about Natural Numbers and calculations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division) with natural numbers; Fractions and calculations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division) with fractions; Decimals and Calculations about decimals; Percentage.
++ Geometry and Measurement: Includes sets of teaching equipment for recognizing, describing shapes and features of some flat shapes and solids; practicing measuring, drawing, assembling, creating shapes (corresponding to the Math program of each grade); practical weighing, measuring, counting, checking time, buying and selling.
++ Elements of Statistics and Probability: Includes sets of teaching equipment about Reading, describing, representing data in tables, and statistical graphs; and familiarizing with the possibility of an event occurring.
+ Lower secondary level:
++ Numbers and Algebra: Includes sets of teaching equipment about Integers and Calculations with integers; Percentage; Functions and Graphs.
++ Geometry and Measurement: Teaching equipment sets for recognizing, and describing shapes and features of some flat shapes and solids; concerning practical measurement, drawing, creating shapes associated with learned flat shapes and solids.
++ Some elements of Statistics and Probability: Teaching equipment sets for Statistics and Probability.
+ Upper secondary level:
++ Algebra and some elements of Calculus: Teaching and learning device sets about Functions and Graphs.
++ Geometry and Measurement: Teaching equipment sets for Recognizing, describing pyramid, prism, cone, sphere, cylinder shapes, conic curves.
++ Statistics and Probability: Teaching equipment sets for Statistics and Probability.