What are the 03 sets of 1st end-of-semester question papers and answers for 11th-grade History? What competencies are developed through the 11th-grade History curriculum in Vietnam?
What are the 03 sets of 1st end-of-semester question papers and answers for 11th-grade History in Vietnam?
Students can refer to the following sets of 1st end-of-semester question papers and answers for 11th-grade History in Vietnam in preparation for the upcoming exams:
|
Department of Education and Training .....
1st end-of-semester question papers for 11th-grade History
2024 - 2025 Academic Year
Test: 11th-grade History
Time:.. minutes
(Excluding distribution time)
(Question paper No. 1)
Question 1. The most aggressive competitor in the colonial scramble among imperial nations at the end of the 19th century - beginning of the 20th century was:
A. France.
B. Germany.
C. England.
D. United States.
Question 2. After the 1905 - 1907 Revolution, Russia remained a:
A. autocratic monarchy.
B. constitutional monarchy.
C. parliamentary republic.
D. aristocratic republic.
Question 3. The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics was established in the month of:
A. October 1922.
B. November 1922.
C. December 1922.
D. January 1924.
Question 4. Which sector of Japan's economy was most affected by the Great Depression (1929 - 1933)?
A. Agriculture.
B. Military industry.
C. Financial banking.
D. Trade and business.
Question 5. During the years 1918 - 1939, reactionary and militant forces in Germany consolidated in which organization?
A. Nazi Party.
B. Communist Party of Germany.
C. German Social Democratic Party.
D. National Union Party.
Question 6. According to the Russian calendar, the day of victory of the October Socialist Revolution in Russia is:
A. October 24, 1917.
B. October 20, 1917.
C. October 7, 1917.
D. October 25, 1917.
Question 7. Which Austrian genius composer made significant contributions to the art of choral music?
A. Mozart.
B. Beethoven.
C. Tchaikovsky.
D. Bertolt Brecht.
Question 8. To maintain a new world order and protect their interests, in early 1920, capitalist countries established:
A. United Nations.
B. League of Nations.
C. Vienna Conference.
D. International Union League.
Question 9. Which foreign policy did the United States implement in the Latin American region during the years 1934 - 1939?
A. "Neighbor Diplomacy."
B. "Commitment and Expansion."
C. "Friendly Neighbor."
D. "Rising Peacefully."
Question 10. In Japan, the economic crisis (1929 - 1933) was most severe in the year:
A. 1929.
B. 1930.
C. 1931.
D. 1932.
Question 11. Lenin's report to the Bolshevik Party Central Committee (April 1917) outlined the goals and direction of transforming from a bourgeois democratic revolution to:
A. a revolutionary civil war.
B. a socialist revolution.
C. a new type of bourgeois revolution.
D. bourgeois democratic revolution.
Question 12. The only person in American history to be elected President four consecutive times is:
A. George Washington.
B. Franklin D. Roosevelt.
C. Bill Clinton.
D. Abraham Lincoln.
Question 13. At the dawn of the modern age, literature, art, and thought played an important role in:
A. serving as a bridge to expand exchanges between countries and nations.
B. promoting values and teachings of Christianity, protecting the autocratic feudal order.
C. attacking the rising bourgeois ideology, protecting the feudal ideology.
D. attacking the stronghold of feudal policies; forming bourgeois class ideology.
Question 14. In the years 1921 - 1941, the recognition and establishment of diplomatic relations with the Soviet Union by many countries demonstrated what?
A. The Soviet Union had strong economic and defense potential.
B. The Soviet Union became a potential market for major countries.
C. The reputation of the Soviet Union in the international arena was increasingly enhanced.
D. The contradictions and hostility between imperial countries and the Soviet Union ended.
Question 15. Which sign indicated that at the end of the 19th century - beginning of the 20th century, international relations among European imperial nations were increasingly tense?
A. The formation of the fascist axis alliance (Axis powers).
B. The emergence of two opposing imperial blocs: the Entente - the Alliance.
C. The formation of economic alliances among imperial nations.
D. The United States increased influence and deeply intervened in European political life.
Question 16. The cause leading to the economic crisis (1929 - 1933) was:
A. the impact of World War I (1914 - 1918).
B. the impact of the revolutionary surge of 1918 - 1923 in European capitalist countries.
C. unresolved conflicts of interest among capitalist countries.
D. capitalist countries produced in mass, leading to "supply" exceeding "demand.".
Question 17. Which factor strongly influenced world cultural circumstances from the beginning of the modern period to the end of the 19th century - early 20th century?
A. The blending of various cultures.
B. The emergence of many great writers, poets, and artists.
C. The strong development of the capitalist economic system.
D. Historical fluctuations from the beginning of the modern age to the end of the 19th century - early 20th century.
Question 18. In March 1921, the Bolshevik Party decided to implement the New Economic Policy (NEP) in Russia in the context of:
A. having completed the task of industrialization.
B. feudal production relations still dominated.
C. having completed agricultural collectivization.
D. the economy being severely damaged.
Question 19. To escape the economic crisis (1929 - 1933), the ruling class in Germany:
A. implemented economic reforms: renewing the production process, organization, management, etc.
B. implemented freedoms and democratic rights.
C. fascistized the state machinery, establishing openly dictatorial and terrorist policies.
D. continued to maintain a bourgeois parliamentary republic policy.
Question 20. Hitler's government openly terrorized the Communist Party of Germany because the Communist Party:
A. was the largest political party in Germany.
B. resolutely opposed fascism.
C. opposed the Weimar Republic.
D. openly sabotaged bourgeois republic policies.
Question 21. What was the socialist industrialization strategy in the Soviet Union from 1925 to 1941?
A. Investing in the simultaneous development of all industrial sectors.
B. Strengthening investment in agriculture, creating prerequisites for industrial development.
C. Prioritizing the development of heavy industry, focusing on: machinery manufacturing, agricultural tools...
D. Prioritizing the development of light industry, creating prerequisites for the development of other economic sectors.
Question 22. The most developed industrial sector in Germany during 1933 - 1939 was:
A. military industry.
B. machinery and agricultural tool manufacturing.
C. light industry.
D. mining and metallurgy industries.
Question 23. After World War I ended, capitalist countries organized the Versailles and Washington Peace Conferences to:
A. discuss ways to counter the Soviet Union.
B. discuss ways to recover and develop the European economy.
C. sign peace treaties and agreements on dividing interests.
D. establish political-military alliances in Europe.
Question 24. Agriculture was the sector most severely affected during the economic crisis (1929 – 1933) in Japan because:
A. remnants of feudal production relations.
B. it was a key economic sector.
C. reliance on external markets.
D. harsh natural conditions.
Question 25. The most important act in the U.S.'s "New Deal" policy was:
A. Banking Act.
B. Agricultural Adjustment Act.
C. Industrial Recovery Act.
D. Social Security Act.
Question 26. Which content is not a cause of the economic crisis (1929 - 1933) in the U.S.?
A. Excess goods, "supply" exceeding "demand.".
B. The bourgeoisie produced in mass, chasing profits.
C. Public purchasing power decreased.
D. The decline in global crude oil prices.
Question 27. The October Russian Revolution was:
A. a new type of bourgeois democratic revolution.
B. the first proletarian revolution in the world.
C. a thorough bourgeois democratic revolution.
D. the first proletarian revolution globally to succeed.
Question 28. The essence of the "New Deal" policy proposed and implemented in the U.S. by President Franklin D. Roosevelt was:
A. allowing the economy to be adjusted freely by the market.
B. enhancing the role of the government in regulating and managing the economy.
C. the state having a central role in regulating the entire economy.
D. completely eliminating the state’s role in managing and regulating the economy.
Question 29. What measure did England, France, and the U.S. apply to escape the economic crisis (1929 - 1933)?
A. Establish fascist dictatorships.
B. Political reforms, increasing government power.
C. Economic-social reforms.
D. Launching invasion wars to expand territory.
Question 30. Which content does not accurately reflect the achievements the Soviet Union achieved in culture and education during the early socialist construction period (1925 – 1941)?
A. Eliminating illiteracy.
B. Completing universal primary education.
C. Building a unified education system.
D. Completing universal higher education.
Question 31. What was the most serious consequence of the economic crisis (1929 - 1933)?
A. Severe destruction of capitalist countries' economies.
B. Pushing hundreds of millions into unemployment and poverty.
C. The emergence of fascism and the looming threat of a new world war.
D. Instability in capitalist societies due to strikes and protests by the unemployed.
Question 32. The October 1917 Russian Revolution:
A. led to the coexistence of two governments.
B. helped Russia achieve its goal of building socialism.
C. empowered the Russian people to determine their destiny.
D. helped Russia repel external and internal enemies.
Question 33. Which idea does not accurately reflect the consequences of World War I (1914 - 1918)?
A. Over 10 million dead, over 20 million injured.
B. Many cities, villages, bridges, and factories destroyed.
C. Imperial countries' war expenses amounted to 85 billion dollars.
D. Over 60 million dead, over 90 million injured.
Question 34. Which content does not accurately reflect the errors and limitations in building socialism in the Soviet Union from 1925 – 1941?
A. Implementing political pluralism and opposition multi-party system.
B. Building a highly centralized, rigid, and sluggish planned economy.
C. Ineffectively implementing the voluntary principle in agricultural collectivization.
D. Not paying adequate attention to improving people's living standards.
Question 35. Why did Germany, Italy, and Japan choose to fascistize their governance systems to escape the economic crisis (1929 - 1933)?
A. Having colonies, they could offload the crisis burden onto the colonial peoples.
B. Lacking or having very few colonies, lacking capital, raw materials, and narrow markets.
C. Less affected by the global economic crisis (1929 - 1933).
D. The vigorous democratic struggle movements in Germany, Italy, and Japan.
Question 36. What is the similarity between the February and October revolutions in Russia in 1917?
A. The revolution succeeded, and the tsarist regime was overthrown.
B. Leading Russia to develop along the capitalist path.
C. Conducted under the leadership of the Russian Bolshevik Party.
D. The revolution succeeded, steering Russia towards capitalism.
Question 37. Who is the author of the famous quote: "I hope that humanity will draw more good from scientific inventions than bad"?
A. Victor Hugo.
B. Albert Einstein.
C. Alfred Nobel.
D. Lomonosov.
Question 38. In the January 27, 1924 issue of the Truth newspaper, Nguyen Ai Quoc wrote: "When alive, he was our father, teacher, comrade, and advisor. Today, he is the bright star guiding our way to the socialist revolution." Nguyen Ai Quoc was referring to whom?
A. Friedrich Engels.
B. Karl Marx.
C. V.I. Lenin.
D. Mao Zedong.
Question 39. From the New Economic Policy of Soviet Russia, what lesson can Vietnam learn for its current national renovation efforts?
A. Only focus on developing a few key economic sectors.
B. Encourage foreign private investment and business.
C. Only emphasize the development of heavy industry.
D. Build a multi-sector economy under state supervision.
Question 40. From the struggle against fascism in Germany, what lesson can humanity draw to protect world peace?
A. Focus on developing the economy and mutually beneficial cooperation among major countries.
B. Resolutely oppose militant, reactionary, and extremist forces.
C. Implement policies of friendship and peace among nations.
D. Manufacture new weapons, military equipment, and build a strong military force.
|
| --- |ANSWERS:
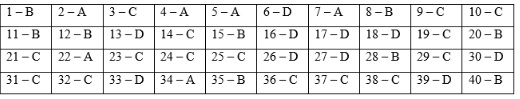
Note: Information is for reference only!
02 sets of 1st end-of-semester question papers and answers for 11th-grade History in Vietnam may be found in Download

What are the 03 sets of 1st end-of-semester question papers and answers for 11th-grade History in Vietnam? (Image from the Internet)
What competencies are developed through the 11th-grade History curriculum in Vietnam?
Under Section 6 of the General Education Program for History, issued together with Circular 32/2018/TT-BGDDT, competencies developed through the 11th-grade History curriculum in Vietnam include:
- Autonomy and self-learning capacity: formed and developed through learning activities such as gathering information from historical sources; expressing personal opinions on historical events, figures, processes; surveying, practicing history on the field, historical and cultural relics in the locality; applying historical knowledge to explain real-life issues; exploring and self-learning history;...
- Communication and cooperation capacity: formed and developed through group activities; experiential activities on the field, at museums, historical and cultural relics; interviewing historical witnesses;…
- Problem-solving and creative capacity: formed and developed through activities of identifying issues, proposing hypotheses, personal opinions about historical events and figures; finding logic in problem-solving methods, evaluating solutions for historical problem-solving; applying historical experiences in real life;…
What are the specific competencies in History required for 11th-grade students in Vietnam?
Under Section 4 of the General Education Program for History, issued together with Circular 32/2018/TT-BGDDT, the specific competencies in History required for 11th-grade students in Vietnam include:
(1) Understanding history:
- Recognize different types of historical documents; understand the content, exploit and utilize historical documents in the learning process.
- Reconstruct and present, verbally or in writing, the course of historical events, figures, and processes from simple to complex; identify historical events in specific space and time.
(2) Historical awareness and thinking:
- Explain the origins and movements of historical events from simple to complex; point out the historical development process in chronological and synchronous order; compare similarities and differences between historical events, and explain causal relationships in the historical process.
- Provide personal remarks and evaluations of historical events, figures, and processes based on historical awareness and thinking; understand historical continuity and change; know how to think in diverse directions when considering, evaluating, or seeking answers about a historical event, figure, or process.
(3) Applying learned knowledge and skills:
- Draw historical lessons and apply historical knowledge to explain real-life issues; based on that, have the ability to self-study historical issues, develop creative capacity, have the ability to access and process information from different sources, and have the awareness and ability for lifelong self-study of history.



